Abstract
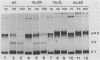
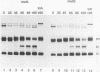
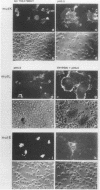
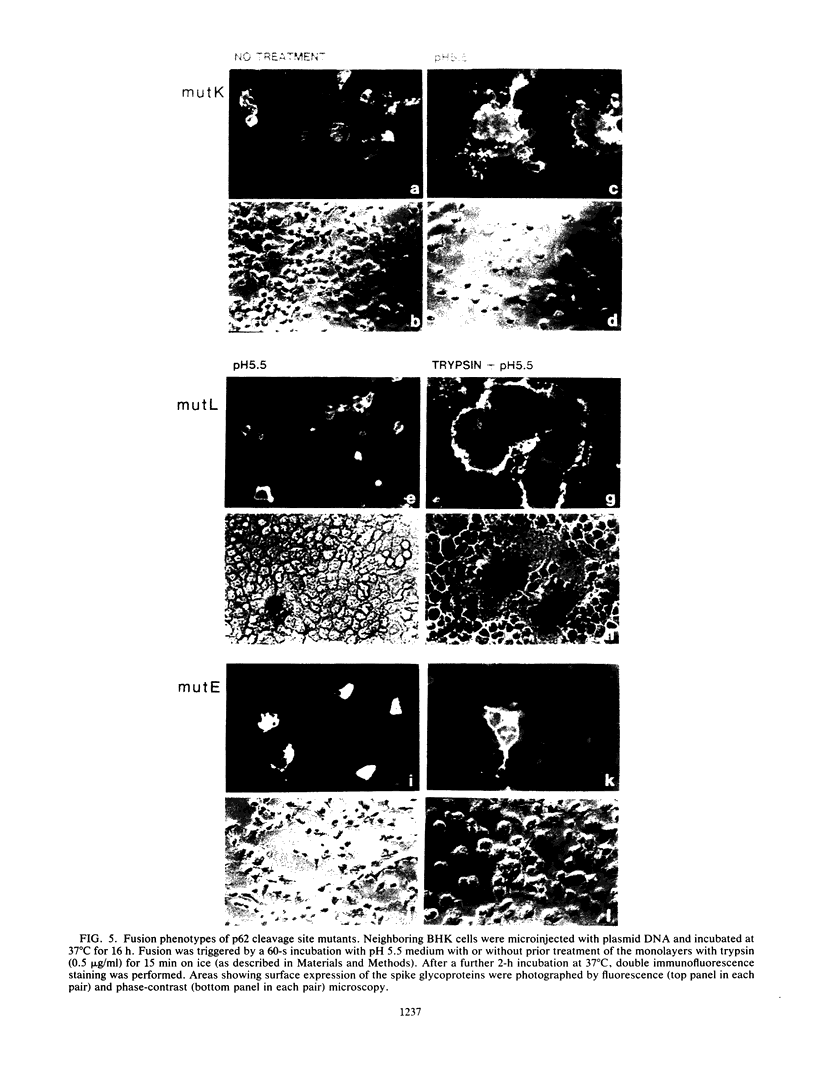
The precursor protein p62 of the prototype alphavirus Semliki Forest virus (SFV) undergoes during transport to the cell surface a proteolytic cleavage to form the mature envelope glycoprotein E2. To investigate the biological significance of this cleavage event, single amino acid substitutions were introduced at the cleavages site through mutagenesis of cDNA corresponding to the structural region of the SFV genome. The phenotypes of the cleavage site mutants were studied in BHK cells by using recombinant vaccinia virus vectors. Nonconservative substitutions completely abolished p62 cleavage. Uncleaved p62 was transported with normal kinetics to the cell surface, where it became accessible to low concentrations of exogenous trypsin. The proteolytic cleavage of envelope glycoprotein precursors has been shown to activate the membrane fusion potential of viral spikes in several virus families. Here we demonstrate that the fusion function of the SFV spike is activated by the cleavage of p62. Cleavage-deficient p62 expressed at the cell surface did not function in low-pH-triggered (pH 5.5) cell-cell membrane fusion; however, cleavage of the mutated p62 with exogenous trypsin restored the fusion function. We discuss a model for SFV assembly and fusion where p62 cleavage plays a crucial role in the stability of the multimeric association of the viral envelope glycoproteins.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams R. H., Brown D. T. Inhibition of Sindbis virus maturation after treatment of infected cells with trypsin. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):692–702. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.692-702.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. G., Orci L. A view of acidic intracellular compartments. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):539–543. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boere W. A., Harmsen T., Vinjé J., Benaissa-Trouw B. J., Kraaijeveld C. A., Snippe H. Identification of distinct antigenic determinants on Semliki Forest virus by using monoclonal antibodies with different antiviral activities. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):575–582. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.575-582.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boggs W. M., Hahn C. S., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H., Griffin D. E. Low pH-dependent Sindbis virus-induced fusion of BHK cells: differences between strains correlate with amino acid changes in the E1 glycoprotein. Virology. 1989 Apr;169(2):485–488. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90178-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonatti S., Migliaccio G., Simons K. Palmitylation of viral membrane glycoproteins takes place after exit from the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12590–12595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulay F., Doms R. W., Wilson I., Helenius A. The influenza hemagglutinin precursor as an acid-sensitive probe of the biosynthetic pathway. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2643–2650. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02555.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bracha M., Schlesinger M. J. Defects in RNA+ temperature-sensitive mutants of Sindbis virus and evidence for a complex of PE2-E1 viral glycoproteins. Virology. 1976 Oct 15;74(2):441–449. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90350-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgarno L., Rice C. M., Strauss J. H. Ross River virus 26 s RNA: complete nucleotide sequence and deduced sequence of the encoded structural proteins. Virology. 1983 Aug;129(1):170–187. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90404-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drillien R., Spehner D. Physical mapping of vaccinia virus temperature-sensitive mutations. Virology. 1983 Dec;131(2):385–393. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90506-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J., Mann E., Brown D. T. Conformational changes in Sindbis virus envelope proteins accompanying exposure to low pH. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1090–1097. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.1090-1097.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erwin C., Brown D. T. Intracellular distribution of Sindbis virus membrane proteins in BHK-21 cells infected with wild-type virus and maturation-defective mutants. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):775–786. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.775-786.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher J. M., Scheller R. H. Prohormone processing and the secretory pathway. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16515–16518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freed E. O., Risser R. The role of envelope glycoprotein processing in murine leukemia virus infection. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2852–2856. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2852-2856.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller S. D. The T=4 envelope of Sindbis virus is organized by interactions with a complementary T=3 capsid. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):923–934. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90701-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garoff H., Kondor-Koch C., Riedel H. Structure and assembly of alphaviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1982;99:1–50. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68528-6_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garten W., Bosch F. X., Linder D., Rott R., Klenk H. D. Proteolytic activation of the influenza virus hemagglutinin: The structure of the cleavage site and the enzymes involved in cleavage. Virology. 1981 Dec;115(2):361–374. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90117-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J., Griffiths G., Louvard D., Quinn P., Warren G. Passage of viral membrane proteins through the Golgi complex. J Mol Biol. 1981 Nov 15;152(4):663–698. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90122-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hänggi M., Bannwarth W., Stunnenberg H. G. Conserved TAAAT motif in vaccinia virus late promoters: overlapping TATA box and site of transcription initiation. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):1071–1076. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04324.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalkkinen N., Jörnvall H., Söderlund H., Käriäinen L. Analysis of Semliki-Forest-virus structural proteins to illustrate polyprotein processing of alpha viruses. Eur J Biochem. 1980;108(1):31–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04692.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaoka Y., Webster R. G. Sequence requirements for cleavage activation of influenza virus hemagglutinin expressed in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):324–328. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kielian M., Helenius A. pH-induced alterations in the fusogenic spike protein of Semliki Forest virus. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2284–2291. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieny M. P., Lathe R., Drillien R., Spehner D., Skory S., Schmitt D., Wiktor T., Koprowski H., Lecocq J. P. Expression of rabies virus glycoprotein from a recombinant vaccinia virus. Nature. 1984 Nov 8;312(5990):163–166. doi: 10.1038/312163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondor-Koch C., Burke B., Garoff H. Expression of Semliki Forest virus proteins from cloned complementary DNA. I. The fusion activity of the spike glycoprotein. J Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;97(3):644–651. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.3.644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondor-Koch C., Riedel H., Söderberg K., Garoff H. Expression of the structural proteins of Semliki Forest virus from cloned cDNA microinjected into the nucleus of baby hamster kidney cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4525–4529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer W., Drutsa V., Jansen H. W., Kramer B., Pflugfelder M., Fritz H. J. The gapped duplex DNA approach to oligonucleotide-directed mutation construction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9441–9456. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann E., Edwards J., Brown D. T. Polycaryocyte formation mediated by Sindbis virus glycoproteins. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1083–1089. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.1083-1089.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M., Helenius A. Virus entry into animal cells. Adv Virus Res. 1989;36:107–151. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60583-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M. The entry of enveloped viruses into cells by endocytosis. Biochem J. 1984 Feb 15;218(1):1–10. doi: 10.1042/bj2180001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCune J. M., Rabin L. B., Feinberg M. B., Lieberman M., Kosek J. C., Reyes G. R., Weissman I. L. Endoproteolytic cleavage of gp160 is required for the activation of human immunodeficiency virus. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):55–67. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90487-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melancon P., Garoff H. Processing of the Semliki Forest virus structural polyprotein: role of the capsid protease. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1301–1309. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1301-1309.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melancon P., Garoff H. Reinitiation of translocation in the Semliki Forest virus structural polyprotein: identification of the signal for the E1 glycoprotein. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1551–1560. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04396.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison T. G. Structure, function, and intracellular processing of paramyxovirus membrane proteins. Virus Res. 1988 May;10(2-3):113–135. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(88)90010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohuchi M., Orlich M., Ohuchi R., Simpson B. E., Garten W., Klenk H. D., Rott R. Mutations at the cleavage site of the hemagglutinin after the pathogenicity of influenza virus A/chick/Penn/83 (H5N2). Virology. 1989 Feb;168(2):274–280. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90267-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omar A., Koblet H. Semliki Forest virus particles containing only the E1 envelope glycoprotein are infectious and can induce cell-cell fusion. Virology. 1988 Sep;166(1):17–23. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90141-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omar A., Koblet H. The use of sulfite to study the mechanism of membrane fusion induced by E1 of Semliki Forest virus. Virology. 1989 Jan;168(1):177–179. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90418-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson R. G., Shaughnessy M. A., Lamb R. A. Analysis of the relationship between cleavability of a paramyxovirus fusion protein and length of the connecting peptide. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1293–1301. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1293-1301.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez L. G., Hunter E. Mutations within the proteolytic cleavage site of the Rous sarcoma virus glycoprotein that block processing to gp85 and gp37. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1609–1614. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1609-1614.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice C. M., Franke C. A., Strauss J. H., Hruby D. E. Expression of Sindbis virus structural proteins via recombinant vaccinia virus: synthesis, processing, and incorporation into mature Sindbis virions. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):227–239. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.227-239.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice C. M., Strauss J. H. Association of sindbis virion glycoproteins and their precursors. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jan 15;154(2):325–348. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90067-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. L., Dalrymple J. M., Johnston R. E. Sindbis virus mutations which coordinately affect glycoprotein processing, penetration, and virulence in mice. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1619–1629. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1619-1629.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheefers H., Scheefers-Borchel U., Edwards J., Brown D. T. Distribution of virus structural proteins and protein-protein interactions in plasma membrane of baby hamster kidney cells infected with Sindbis or vesicular stomatitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7277–7281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons K., Garoff H. The budding mechanisms of enveloped animal viruses. J Gen Virol. 1980 Sep;50(1):1–21. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-50-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Docherty K., Carroll R. Golgi/granule processing of peptide hormone and neuropeptide precursors: a minireview. J Cell Biochem. 1984;24(2):121–130. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240240204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturman L. S., Holmes K. V. Proteolytic cleavage of peplomeric glycoprotein E2 of MHV yields two 90K subunits and activates cell fusion. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1984;173:25–35. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9373-7_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturman L. S., Ricard C. S., Holmes K. V. Proteolytic cleavage of the E2 glycoprotein of murine coronavirus: activation of cell-fusing activity of virions by trypsin and separation of two different 90K cleavage fragments. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):904–911. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.904-911.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timm B., Kondor-Koch C., Lehrach H., Riedel H., Edström J. E., Garoff H. Expression of viral membrane proteins from cloned cDNA by microinjection into eukaryotic cell nuclei. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:496–511. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96043-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaux D. J., Helenius A., Mellman I. Spike--nucleocapsid interaction in Semliki Forest virus reconstructed using network antibodies. Nature. 1988 Nov 3;336(6194):36–42. doi: 10.1038/336036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel R. H., Provencher S. W., von Bonsdorff C. H., Adrian M., Dubochet J. Envelope structure of Semliki Forest virus reconstructed from cryo-electron micrographs. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):533–535. doi: 10.1038/320533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahlberg J. M., Boere W. A., Garoff H. The heterodimeric association between the membrane proteins of Semliki Forest virus changes its sensitivity to low pH during virus maturation. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):4991–4997. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.4991-4997.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Helenius A. pH-dependent fusion between the Semliki Forest virus membrane and liposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3273–3277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Kartenbeck J., Helenius A. Fusion of Semliki forest virus with the plasma membrane can be induced by low pH. J Cell Biol. 1980 Oct;87(1):264–272. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.1.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Kielian M., Helenius A. Membrane fusion proteins of enveloped animal viruses. Q Rev Biophys. 1983 May;16(2):151–195. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Matlin K., Helenius A. Cell fusion by Semliki Forest, influenza, and vesicular stomatitis viruses. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jun;89(3):674–679. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.3.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley D. C., Skehel J. J. The structure and function of the hemagglutinin membrane glycoprotein of influenza virus. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:365–394. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Curtis I., Simons K. Dissection of Semliki Forest virus glycoprotein delivery from the trans-Golgi network to the cell surface in permeabilized BHK cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8052–8056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]