Abstract
We obtained neutralizing monoclonal antibodies against a continuous neutralization epitope on VP2 of poliovirus type 1 strain Mahoney by using a combined in vivo-in vitro immunization procedure. The antibody-binding site was mapped to amino acid residues within the peptide segment (residues 164 through 170) of VP2 by competition with synthetic peptide and sequencing of resistant mutants. Cross-neutralization of these mutants with another neutralizing monoclonal antibody revealed a linkage of the continuous epitope and a discontinuous neutralization epitope involving both loops of the double-loop structure of VP2 at the twofold axis on the surface of the virion.
Full text
PDF

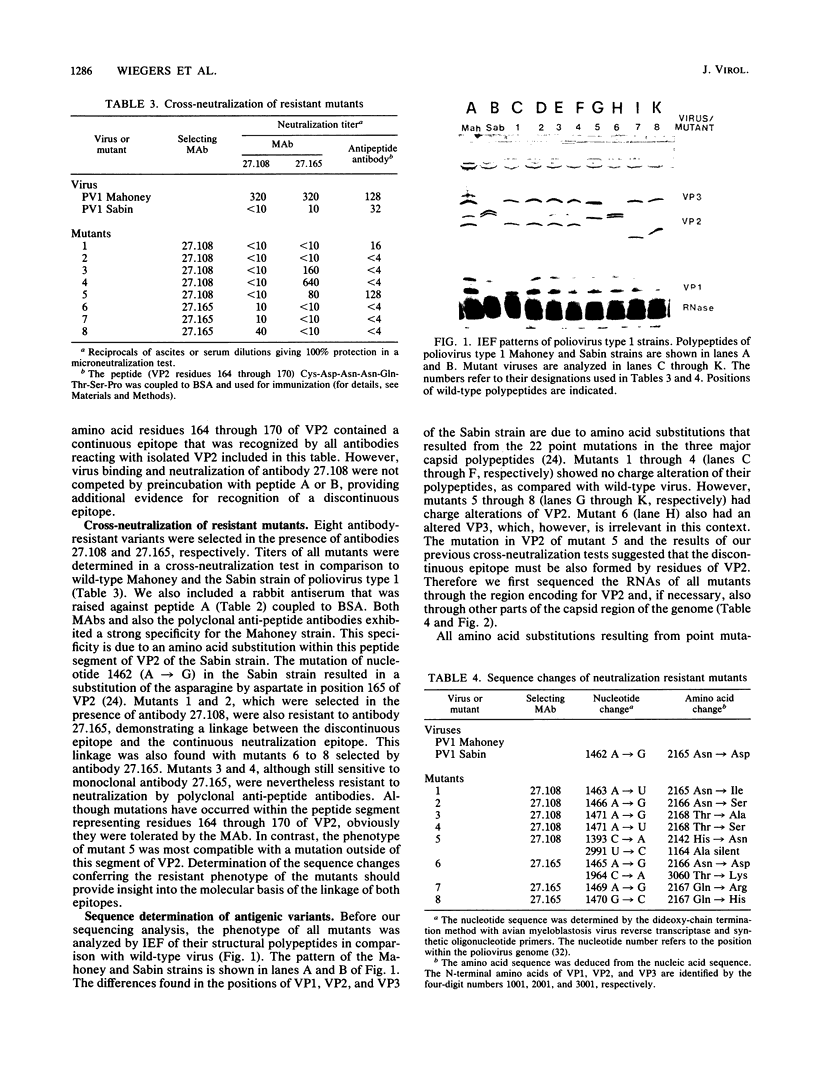


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blondel B., Akacem O., Crainic R., Couillin P., Horodniceanu F. Detection by monoclonal antibodies of an antigenic determinant critical for poliovirus neutralization present on VP1 and on heat-inactivated virions. Virology. 1983 Apr 30;126(2):707–710. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(83)80027-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blondel B., Crainic R., Fichot O., Dufraisse G., Candrea A., Diamond D., Girard M., Horaud F. Mutations conferring resistance to neutralization with monoclonal antibodies in type 1 poliovirus can be located outside or inside the antibody-binding site. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):81–90. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.81-90.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blondel B., Crainic R., Horodniceanu F. Le polypeptide structural VP1 du poliovirus type 1 induit des anticorps neutralisants. C R Seances Acad Sci III. 1982 Jan 11;294(2):91–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow M., Baltimore D. Isolated poliovirus capsid protein VP1 induces a neutralizing response in rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7518–7521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow M., Yabrov R., Bittle J., Hogle J., Baltimore D. Synthetic peptides from four separate regions of the poliovirus type 1 capsid protein VP1 induce neutralizing antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):910–914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dernick R., Heukeshoven J., Hilbrig M. Induction of neutralizing antibodies by all three structural poliovirus polypeptides. Virology. 1983 Oct 15;130(1):243–246. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90134-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond D. C., Jameson B. A., Bonin J., Kohara M., Abe S., Itoh H., Komatsu T., Arita M., Kuge S., Nomoto A. Antigenic variation and resistance to neutralization in poliovirus type 1. Science. 1985 Sep 13;229(4718):1090–1093. doi: 10.1126/science.2412292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drzeniek R., Bilello P. Absence of glycoproteins in poliovirus particles. J Gen Virol. 1974 Oct;25(1):125–132. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-25-1-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Jameson B. A., Wimmer E. Identification of a new neutralization antigenic site on poliovirus coat protein VP2. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):719–721. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.719-721.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Jameson B. A., Wimmer E. Priming for and induction of anti-poliovirus neutralizing antibodies by synthetic peptides. Nature. 1983 Aug 25;304(5928):699–703. doi: 10.1038/304699a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M., Evans D. M., Magrath D. I., Minor P. D., Almond J. W., Schild G. C. Induction by synthetic peptides of broadly reactive, type-specific neutralizing antibody to poliovirus type 3. Virology. 1985 Jun;143(2):505–515. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90389-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamann A., Wiegers K. J., Drzeniek R. Isoelectric focusing and 2D-analysis of poliovirus proteins. Virology. 1977 May 1;78(1):359–362. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90111-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heukeshoven J., Dernick R. Reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography of virus proteins and other large hydrophobic proteins in formic acid containing solvents. J Chromatogr. 1982 Dec 3;252:241–254. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)88415-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogle J. M., Chow M., Filman D. J. Three-dimensional structure of poliovirus at 2.9 A resolution. Science. 1985 Sep 27;229(4720):1358–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.2994218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Icenogle J. P., Minor P. D., Ferguson M., Hogle J. M. Modulation of humoral response to a 12-amino-acid site on the poliovirus virion. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):297–301. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.297-301.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennett R. H., Denis K. A., Tung A. S., Klinman N. R. Hybrid plasmacytoma production: fusions with adult spleen cells, monoclonal spleen fragments, neonatal spleen cells and human spleen cells. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;81:77–91. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67448-8_13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebe R. J., Harriss J. V. A technically simple "non-lethal" vital staining procedure for viral plaque and cell transformation assays. Brief report. Arch Virol. 1984;81(3-4):359–362. doi: 10.1007/BF01310007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. T., Zinnecker M., Hamaoka T., Katz D. H. New procedures for preparation and isolation of conjugates of proteins and a synthetic copolymer of D-amino acids and immunochemical characterization of such conjugates. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 20;18(4):690–693. doi: 10.1021/bi00571a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor P. D., Evans D. M., Ferguson M., Schild G. C., Westrop G., Almond J. W. Principal and subsidiary antigenic sites of VP1 involved in the neutralization of poliovirus type 3. J Gen Virol. 1985 May;66(Pt 5):1159–1165. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-5-1159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor P. D., Ferguson M., Evans D. M., Almond J. W., Icenogle J. P. Antigenic structure of polioviruses of serotypes 1, 2 and 3. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jul;67(Pt 7):1283–1291. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-7-1283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor P. D., Schild G. C., Bootman J., Evans D. M., Ferguson M., Reeve P., Spitz M., Stanway G., Cann A. J., Hauptmann R. Location and primary structure of a major antigenic site for poliovirus neutralization. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):674–679. doi: 10.1038/301674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Omata T., Toyoda H., Kuge S., Horie H., Kataoka Y., Genba Y., Nakano Y., Imura N. Complete nucleotide sequence of the attenuated poliovirus Sabin 1 strain genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5793–5797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page G. S., Mosser A. G., Hogle J. M., Filman D. J., Rueckert R. R., Chow M. Three-dimensional structure of poliovirus serotype 1 neutralizing determinants. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1781–1794. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1781-1794.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G., Arnold E., Erickson J. W., Frankenberger E. A., Griffith J. P., Hecht H. J., Johnson J. E., Kamer G., Luo M., Mosser A. G. Structure of a human common cold virus and functional relationship to other picornaviruses. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):145–153. doi: 10.1038/317145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherry B., Mosser A. G., Colonno R. J., Rueckert R. R. Use of monoclonal antibodies to identify four neutralization immunogens on a common cold picornavirus, human rhinovirus 14. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):246–257. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.246-257.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherry B., Rueckert R. Evidence for at least two dominant neutralization antigens on human rhinovirus 14. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):137–143. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.137-143.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skern T., Neubauer C., Frasel L., Gründler P., Sommergruber W., Zorn M., Kuechler E., Blaas D. A neutralizing epitope on human rhinovirus type 2 includes amino acid residues between 153 and 164 of virus capsid protein VP2. J Gen Virol. 1987 Feb;68(Pt 2):315–323. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-2-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda H., Kohara M., Kataoka Y., Suganuma T., Omata T., Imura N., Nomoto A. Complete nucleotide sequences of all three poliovirus serotype genomes. Implication for genetic relationship, gene function and antigenic determinants. J Mol Biol. 1984 Apr 25;174(4):561–585. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90084-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlig H., Rutter G., Dernick R. Evidence for several unrelated neutralization epitopes of poliovirus, type 1, strain Mahoney, provided by neutralization tests and quantitative enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). J Gen Virol. 1983 Dec;64(Pt 12):2809–2812. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-12-2809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vrijsen R., Rombaut B., Boeyé A. A simple quantitative protein A micro-immunoprecipitation method; assay of antibodies to the N and H antigens of poliovirus. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Apr 29;59(2):217–220. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90033-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiegers K. J., Dernick R. Binding site of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies obtained after in vivo priming with purified VP1 of poliovirus type 1 is located between amino acid residues 93 and 104 of VP1. Virology. 1987 Mar;157(1):248–251. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90337-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiegers K. J., Dernick R. Monospecific antisera against capsid polypeptides of poliovirus type 1 distinguish antigenic structures of poliovirus proteins. J Gen Virol. 1983 Apr;64(Pt 4):777–785. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-4-777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiegers K. J., Uhlig H., Dernick R. In vitro stimulation of presensitized mouse spleen cells with poliovirus type 1, Mahoney, and enhancement of poliovirus-specific hybridomas. J Gen Virol. 1986 Sep;67(Pt 9):2053–2057. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-9-2053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiegers K., Uhlig H., Dernick R. Evidence for a complex structure of neutralization antigenic site I of poliovirus type 1 Mahoney. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1845–1848. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1845-1848.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiegers K., Uhlig H., Dernick R. N-AgIB of poliovirus type 1: a discontinuous epitope formed by two loops of VP1 comprising residues 96-104 and 141-152. Virology. 1989 Jun;170(2):583–586. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90452-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wychowski C., van der Werf S., Siffert O., Crainic R., Bruneau P., Girard M. A poliovirus type 1 neutralization epitope is located within amino acid residues 93 to 104 of viral capsid polypeptide VP1. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):2019–2024. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01694.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Marel P., Hazendonk T. G., Henneke M. A., van Wezel A. L. Induction of neutralizing antibodies by poliovirus capsid polypeptides VP1, VP2 and VP3. Vaccine. 1983 Dec;1(1):17–22. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(83)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Werf S., Wychowski C., Bruneau P., Blondel B., Crainic R., Horodniceanu F., Girard M. Localization of a poliovirus type 1 neutralization epitope in viral capsid polypeptide VP1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):5080–5084. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.5080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]