Abstract
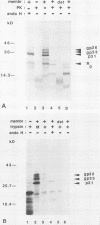
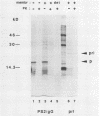
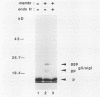
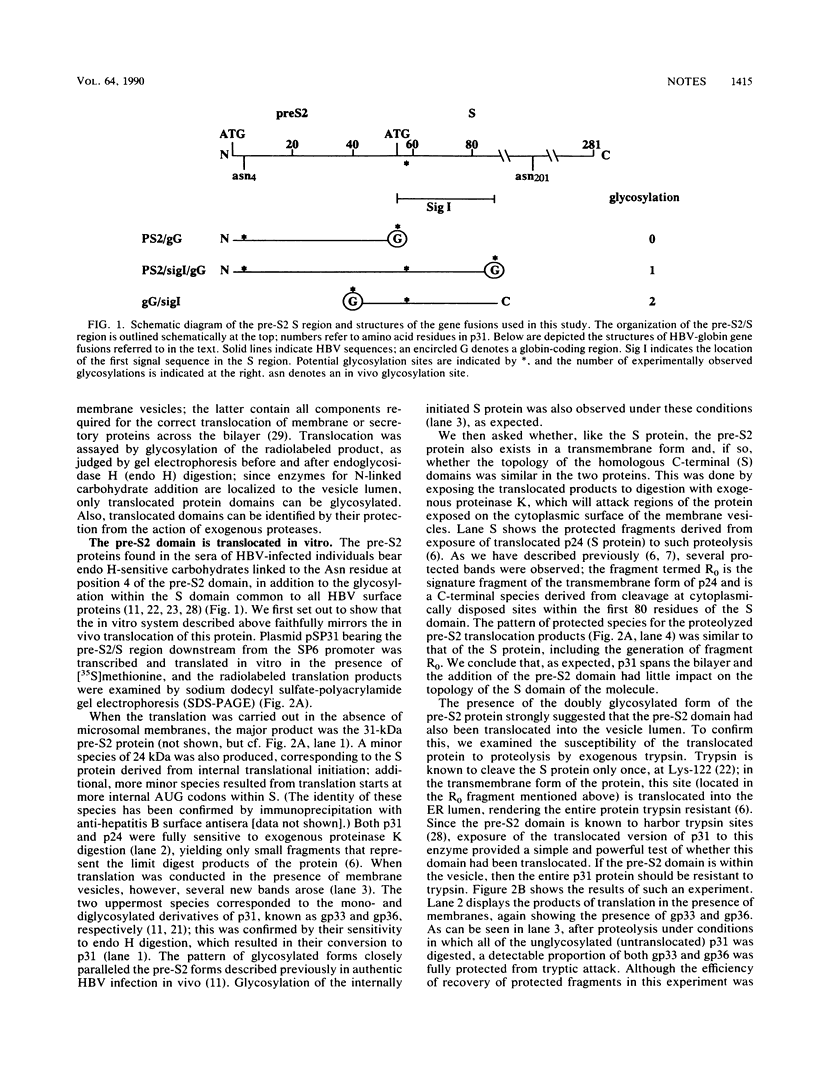
The coding region for the hepatitis B virus surface antigens contains three in-phase ATG codons which direct the synthesis of three related polypeptides. The 24-kilodalton major surface (or S) glycoprotein is initiated at the most distal ATG and is a transmembrane protein whose translocation across the bilayer is mediated by at least two uncleaved signal sequences. The product of the next upstream ATG is the 31-kilodalton pre-S2 protein, which contains 55 additional amino acids attached to the N terminus of the S protein. This pre-S2-specific domain is translocated into the endoplasmic reticulum. Using a coupled in vitro translation-translocation system, we showed that (i) the pre-S2 domain itself lacks functional signal sequence activity, (ii) its translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum membrane is mediated by downstream signals within the S domain, and (iii) the N-terminal signal sequence of the S protein can translocate upstream protein domains in the absence of other signals. The hepatitis B virus pre-S2 protein is an example of a natural protein which displays upstream domain translocation, a phenomenon whose existence was originally inferred from the behavior of synthetic fusion proteins in vitro.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cattaneo R., Will H., Schaller H. Hepatitis B virus transcription in the infected liver. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2191–2196. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02113.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirico W. J., Waters M. G., Blobel G. 70K heat shock related proteins stimulate protein translocation into microsomes. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):805–810. doi: 10.1038/332805a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier D. N., Bankaitis V. A., Weiss J. B., Bassford P. J., Jr The antifolding activity of SecB promotes the export of the E. coli maltose-binding protein. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):273–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90389-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crooke E., Wickner W. Trigger factor: a soluble protein that folds pro-OmpA into a membrane-assembly-competent form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5216–5220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshaies R. J., Koch B. D., Werner-Washburne M., Craig E. A., Schekman R. A subfamily of stress proteins facilitates translocation of secretory and mitochondrial precursor polypeptides. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):800–805. doi: 10.1038/332800a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eble B. E., Lingappa V. R., Ganem D. Hepatitis B surface antigen: an unusual secreted protein initially synthesized as a transmembrane polypeptide. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1454–1463. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eble B. E., MacRae D. R., Lingappa V. R., Ganem D. Multiple topogenic sequences determine the transmembrane orientation of the hepatitis B surface antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3591–3601. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganem D., Varmus H. E. The molecular biology of the hepatitis B viruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:651–693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavilanes F., Gonzalez-Ros J. M., Peterson D. L. Structure of hepatitis B surface antigen. Characterization of the lipid components and their association with the viral proteins. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7770–7777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen W., Garcia P. D., Walter P. In vitro protein translocation across the yeast endoplasmic reticulum: ATP-dependent posttranslational translocation of the prepro-alpha-factor. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):397–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90325-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heermann K. H., Goldmann U., Schwartz W., Seyffarth T., Baumgarten H., Gerlich W. H. Large surface proteins of hepatitis B virus containing the pre-s sequence. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):396–402. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.396-402.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurt E. C., Schatz G. A cytosolic protein contains a cryptic mitochondrial targeting signal. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):499–503. doi: 10.1038/325499a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser C. A., Preuss D., Grisafi P., Botstein D. Many random sequences functionally replace the secretion signal sequence of yeast invertase. Science. 1987 Jan 16;235(4786):312–317. doi: 10.1126/science.3541205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machida A., Kishimoto S., Ohnuma H., Miyamoto H., Baba K., Oda K., Nakamura T., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. A hepatitis B surface antigen polypeptide (P31) with the receptor for polymerized human as well as chimpanzee albumins. Gastroenterology. 1983 Aug;85(2):268–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milich D. R., Thornton G. B., Neurath A. R., Kent S. B., Michel M. L., Tiollais P., Chisari F. V. Enhanced immunogenicity of the pre-S region of hepatitis B surface antigen. Science. 1985 Jun 7;228(4704):1195–1199. doi: 10.1126/science.2408336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mize N. K., Andrews D. W., Lingappa V. R. A stop transfer sequence recognizes receptors for nascent chain translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):711–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90514-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueckler M., Lodish H. F. The human glucose transporter can insert posttranslationally into microsomes. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):629–637. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90272-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perara E., Lingappa V. R. A former amino terminal signal sequence engineered to an internal location directs translocation of both flanking protein domains. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2292–2301. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perara E., Rothman R. E., Lingappa V. R. Uncoupling translocation from translation: implications for transport of proteins across membranes. Science. 1986 Apr 18;232(4748):348–352. doi: 10.1126/science.3961485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persing D. H., Varmus H. E., Ganem D. A frameshift mutation in the pre-S region of the human hepatitis B virus genome allows production of surface antigen particles but eliminates binding to polymerized albumin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3440–3444. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson D. L. Isolation and characterization of the major protein and glycoprotein of hepatitis B surface antigen. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6975–6983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson D. L., Nath N., Gavilanes F. Structure of hepatitis B surface antigen. Correlation of subtype with amino acid sequence and location of the carbohydrate moiety. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10414–10420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothblatt J. A., Meyer D. I. Secretion in yeast: translocation and glycosylation of prepro-alpha-factor in vitro can occur via an ATP-dependent post-translational mechanism. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):1031–1036. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04318.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon K., Lingappa V. R., Ganem D. Secreted hepatitis B surface antigen polypeptides are derived from a transmembrane precursor. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2163–2168. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standring D. N., Rutter W. J., Varmus H. E., Ganem D. Transcription of the hepatitis B surface antigen gene in cultured murine cells initiates within the presurface region. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):563–571. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.563-571.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stibbe W., Gerlich W. H. Structural relationships between minor and major proteins of hepatitis B surface antigen. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):626–628. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.626-628.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Preparation of microsomal membranes for cotranslational protein translocation. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:84–93. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Gilmore R., Blobel G. Protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90520-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]