Abstract
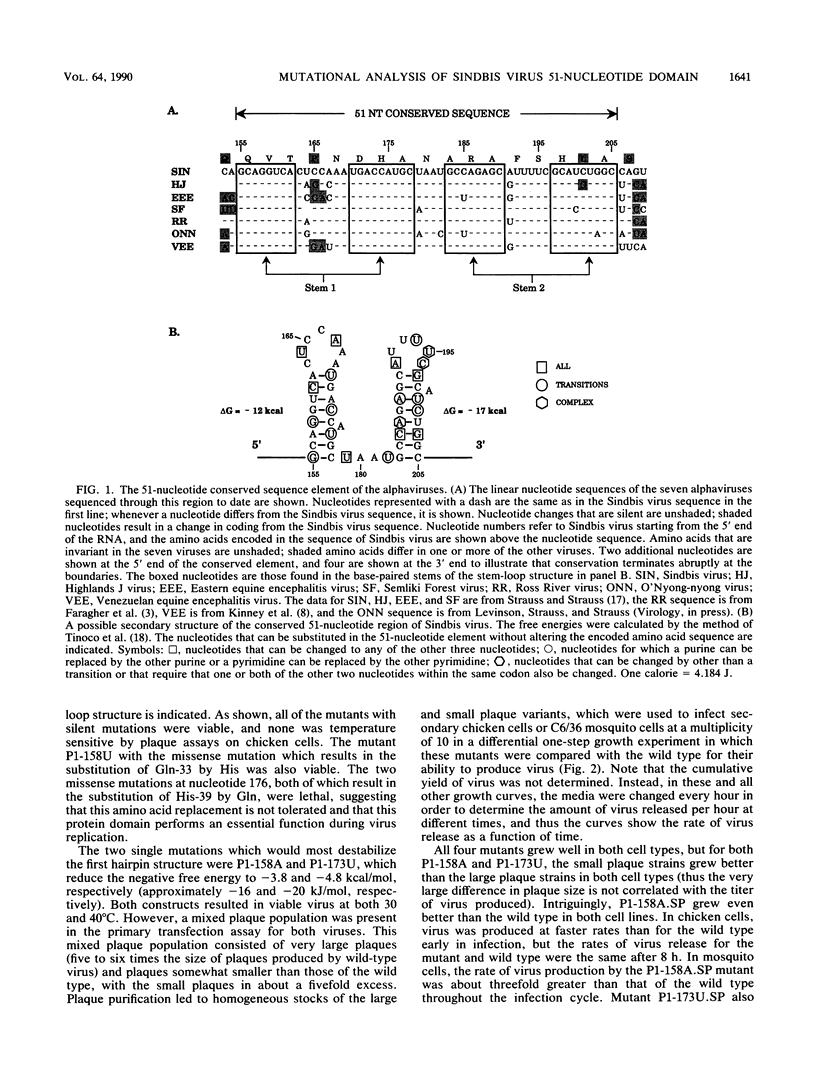
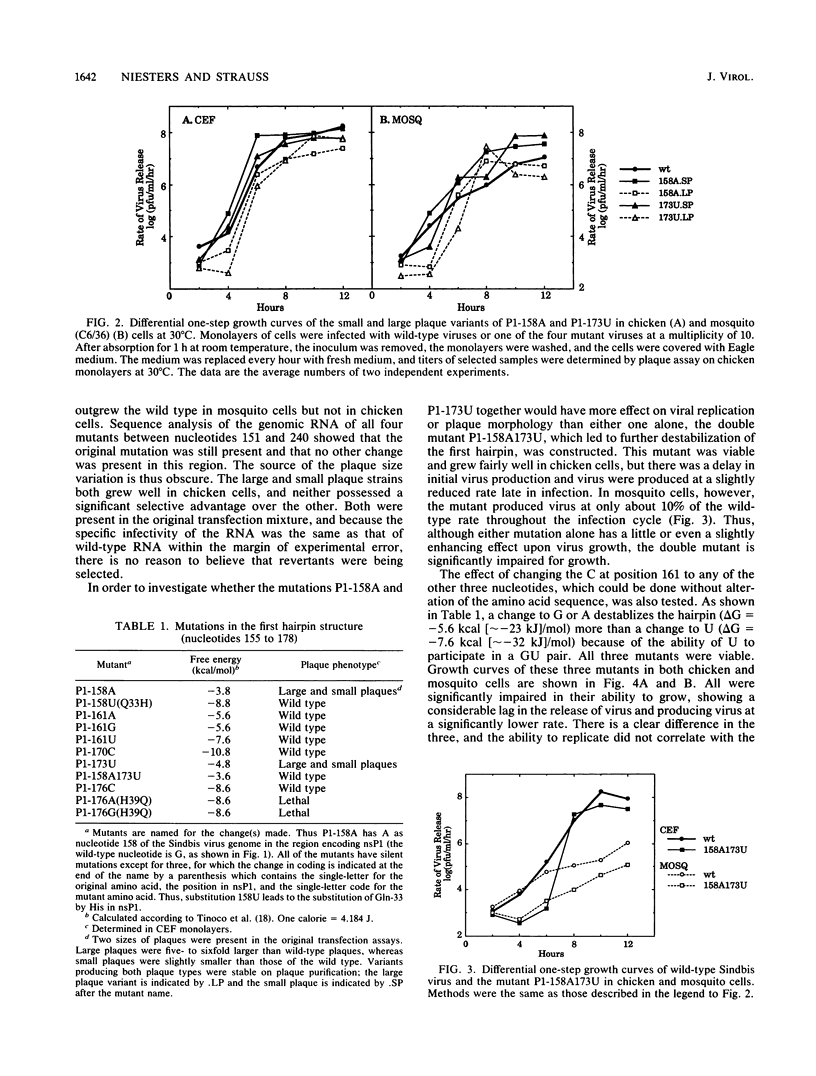
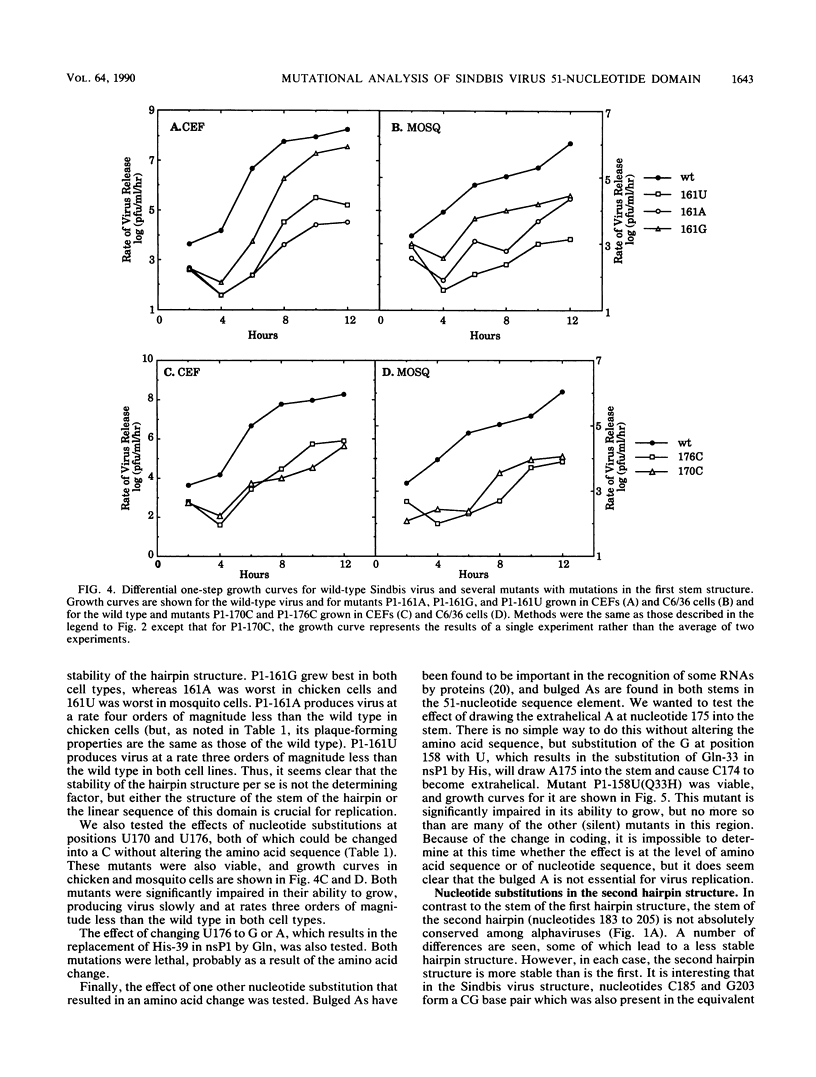
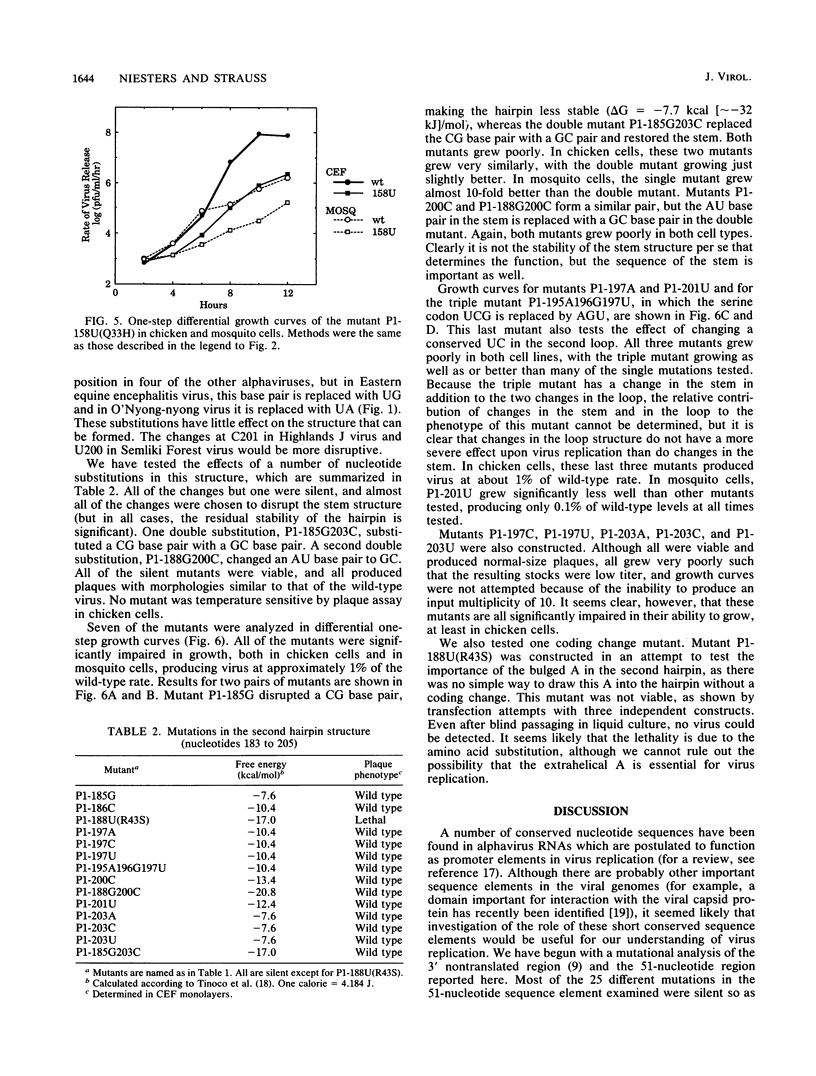
We have constructed 25 site-specific mutations in a domain of 51 nucleotides in Sindbis virus that is highly conserved among all alphaviruses sequenced to date. These 51 nucleotides are capable of forming two hairpin structures and are found from nucleotides 155 to 205 in Sindbis virus within the region encoding nsP1. Of the mutations, 21 were silent and did not lead to a change in the amino acid sequence encoded. These silent mutations changed not only the linear sequence but also the stability of the hairpins in most cases. Two double mutants that were constructed led to the replacement of one base pair by another so that the linear sequence was altered but the nature of the hairpins was not. All of the mutants with silent mutations were viable, but 19 of the 21 mutants were severely impaired for growth in both chicken and mosquito cells. Compared with the parental virus, they grew slowly and produced virus at rates of 10(-1) to 10(-4) times the parental rate. Surprisingly, however, the plaques produced by these mutants were indistinguishable from those produced by the parental virus. Two of the silent mutations, found within the first hairpin structure, produced virus at a faster rate than the parental virus. It is clear that the exact sequence of this region is important for some aspect of virus replication. We suggest that one or more proteins, either virus encoded or cellular, bind to the hairpin structures in a sequence-specific fashion in a step that promotes replication of the viral RNA. Of the mutations that resulted in a change of coding, only one of four was viable, suggesting that the amino acid sequence encoded in this domain is essential for virus replication.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. One-step growth curve of Western equine encephalomyelitis virus on chicken embryo cells grown in vitro and analysis of virus yields from single cells. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):183–199. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faragher S. G., Meek A. D., Rice C. M., Dalgarno L. Genome sequences of a mouse-avirulent and a mouse-virulent strain of Ross River virus. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):509–526. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90292-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey T. K., Gard D. L., Strauss J. H. Biophysical studies on circle formation by Sindbis virus 49 S RNA. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jul 25;132(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90493-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn Y. S., Grakoui A., Rice C. M., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. Mapping of RNA- temperature-sensitive mutants of Sindbis virus: complementation group F mutants have lesions in nsP4. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1194–1202. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1194-1202.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn Y. S., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. Mapping of RNA- temperature-sensitive mutants of Sindbis virus: assignment of complementation groups A, B, and G to nonstructural proteins. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3142–3150. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3142-3150.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy W. R., Strauss J. H. Processing the nonstructural polyproteins of Sindbis virus: study of the kinetics in vivo by using monospecific antibodies. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):998–1007. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.998-1007.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinney R. M., Johnson B. J., Welch J. B., Tsuchiya K. R., Trent D. W. The full-length nucleotide sequences of the virulent Trinidad donkey strain of Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus and its attenuated vaccine derivative, strain TC-83. Virology. 1989 May;170(1):19–30. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90347-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn R. J., Hong Z., Strauss J. H. Mutagenesis of the 3' nontranslated region of Sindbis virus RNA. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1465–1476. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1465-1476.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., Weiss B. G., Tsiang M., Huang H., Schlesinger S. Deletion mapping of Sindbis virus DI RNAs derived from cDNAs defines the sequences essential for replication and packaging. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):137–145. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90492-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lustig S., Jackson A. C., Hahn C. S., Griffin D. E., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. Molecular basis of Sindbis virus neurovirulence in mice. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2329–2336. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2329-2336.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou J. H., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. The 5'-terminal sequences of the genomic RNAs of several alphaviruses. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 25;168(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80319-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou J. H., Trent D. W., Strauss J. H. The 3'-non-coding regions of alphavirus RNAs contain repeating sequences. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 25;156(4):719–730. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90138-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice C. M., Levis R., Strauss J. H., Huang H. V. Production of infectious RNA transcripts from Sindbis virus cDNA clones: mapping of lethal mutations, rescue of a temperature-sensitive marker, and in vitro mutagenesis to generate defined mutants. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3809–3819. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3809-3819.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B., Nitschko H., Ghattas I., Wright R., Schlesinger S. Evidence for specificity in the encapsidation of Sindbis virus RNAs. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5310–5318. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5310-5318.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. N., Uhlenbeck O. C. Role of a bulged A residue in a specific RNA-protein interaction. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 15;26(25):8221–8227. doi: 10.1021/bi00399a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis: a simple method using two oligonucleotide primers and a single-stranded DNA template. DNA. 1984 Dec;3(6):479–488. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


