Abstract
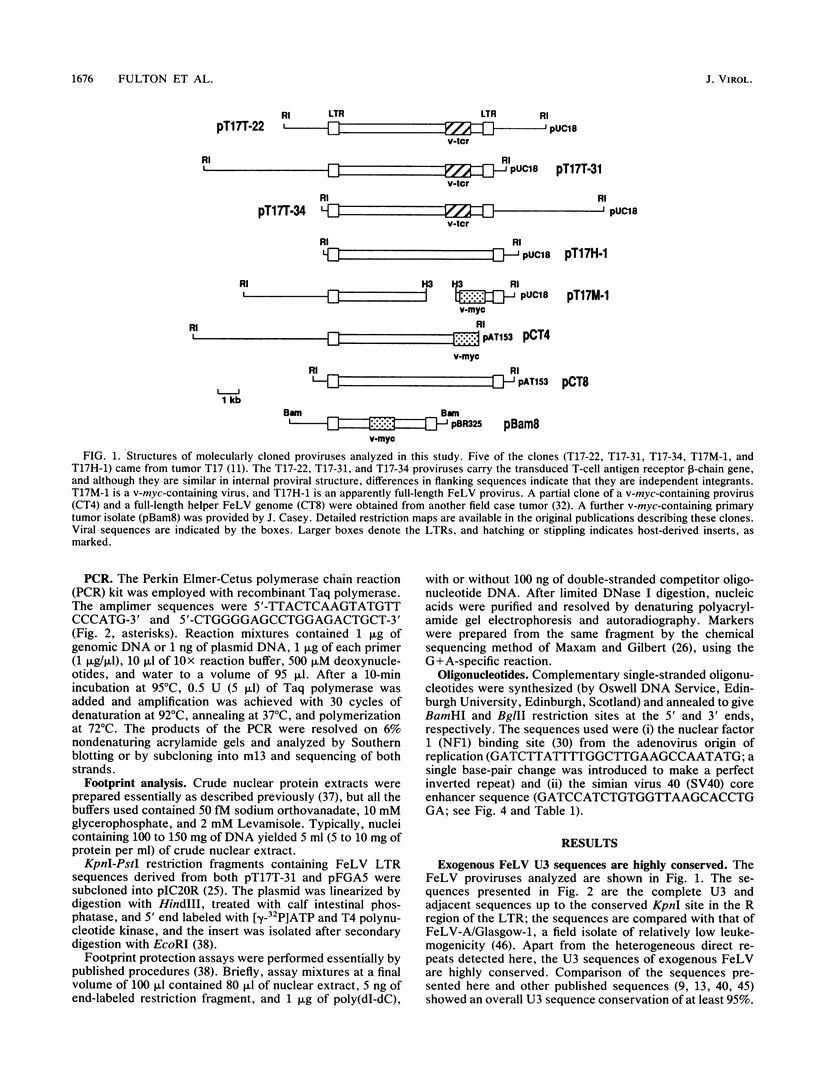
The long terminal repeat U3 sequences were determined for multiple feline leukemia virus proviruses isolated from naturally occurring T-cell tumors. Heterogeneity was evident, even among proviruses cloned from individual tumors. Proviruses with one, two, or three repeats of the long terminal repeat enhancer sequences coexisted in one tumor, while two proviruses with distinct direct repeats were found in another. The enhancer repeats are characteristic of retrovirus variants with accelerated leukemogenic potential and occur between -155 and -244 base pairs relative to the RNA cap site. The termini of the repeats occur at or near sequence features which have been recognized at other retrovirus recombinational junctions. In vitro footprint analysis of the feline leukemia virus enhancer revealed three major nuclear protein binding sites, located at consensus sequences for the simian virus 40 core enhancer, the nuclear factor 1 binding site, and an indirect repeat which is homologous to the PEA2 binding site in the polyomavirus enhancer. Only the simian virus 40 core enhancer sequence is present in all of the enhancer repeats. Cell type differences in binding activities to the three motifs may underlie the selective process which leads to outgrowth of viruses with specific sequence duplications.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besmer P., Murphy J. E., George P. C., Qiu F. H., Bergold P. J., Lederman L., Snyder H. W., Jr, Brodeur D., Zuckerman E. E., Hardy W. D. A new acute transforming feline retrovirus and relationship of its oncogene v-kit with the protein kinase gene family. Nature. 1986 Apr 3;320(6061):415–421. doi: 10.1038/320415a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boral A. L., Okenquist S. A., Lenz J. Identification of the SL3-3 virus enhancer core as a T-lymphoma cell-specific element. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):76–84. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.76-84.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Baroudy B. M., Holmes K. L., Fredrickson T. N., Lander M. R., Morse H. C., 3rd, Hartley J. W. Biologic and molecular genetic characteristics of a unique MCF virus that is highly leukemogenic in ecotropic virus-negative mice. Virology. 1989 Jan;168(1):90–100. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90407-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. P., Kaufhold R., Chan A., Mak T. W. Comparison of the transcriptional properties of the Friend and Moloney retrovirus long terminal repeats: importance of tandem duplications and of the core enhancer sequence. Virology. 1985 Jul 30;144(2):481–494. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90288-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuypers H. T., Selten G. C., Zijlstra M., de Goede R. E., Melief C. J., Berns A. J. Tumor progression in murine leukemia virus-induced T-cell lymphomas: monitoring clonal selections with viral and cellular probes. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):230–241. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.230-241.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doggett D. L., Drake A. L., Hirsch V., Rowe M. E., Stallard V., Mullins J. I. Structure, origin, and transforming activity of feline leukemia virus-myc recombinant provirus FTT. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2108–2117. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2108-2117.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelmann W., Kröger B., Goller M., Horak I. A recombination hotspot in the LTR of a mouse retrotransposon identified in an in vitro system. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):937–946. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90332-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Mullins J. I. Nucleotide sequence of the envelope gene of Gardner-Arnstein feline leukemia virus B reveals unique sequence homologies with a murine mink cell focus-forming virus. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):871–880. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.871-880.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrest D., Onions D., Lees G., Neil J. C. Altered structure and expression of c-myc in feline T-cell tumours. Virology. 1987 May;158(1):194–205. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90253-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulton R., Forrest D., McFarlane R., Onions D., Neil J. C. Retroviral transduction of T-cell antigen receptor beta-chain and myc genes. Nature. 1987 Mar 12;326(6109):190–194. doi: 10.1038/326190a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronostajski R. M. Analysis of nuclear factor I binding to DNA using degenerate oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):9117–9132. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.9117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilhot S., Hampe A., D'Auriol L., Galibert F. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the LTRs and env genes of SM-FeSV and GA-FeSV. Virology. 1987 Nov;161(1):252–258. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90194-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampe A., Gobet M., Even J., Sherr C. J., Galibert F. Nucleotide sequences of feline sarcoma virus long terminal repeats and 5' leaders show extensive homology to those of other mammalian retroviruses. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):466–472. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.466-472.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. C., Rigby P. W., Ziff E. B. Trans-acting protein factors and the regulation of eukaryotic transcription: lessons from studies on DNA tumor viruses. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):267–281. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kryszke M. H., Piette J., Yaniv M. Induction of a factor that binds to the polyoma virus A enhancer on differentiation of embryonal carcinoma cells. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):254–256. doi: 10.1038/328254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo W. L., Vilander L. R., Huang M., Peterson D. O. A transcriptionally defective long terminal repeat within an endogenous copy of mouse mammary tumor virus proviral DNA. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2394–2402. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2394-2402.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., Adashi E. Y., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Isolation of a recombinant copy of the gene encoding C/EBP. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):786–800. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenz J., Celander D., Crowther R. L., Patarca R., Perkins D. W., Haseltine W. A. Determination of the leukaemogenicity of a murine retrovirus by sequences within the long terminal repeat. 1984 Mar 29-Apr 4Nature. 308(5958):467–470. doi: 10.1038/308467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy L. S., Gardner M. B., Casey J. W. Isolation of a feline leukaemia provirus containing the oncogene myc from a feline lymphosarcoma. 1984 Apr 26-May 2Nature. 308(5962):853–856. doi: 10.1038/308853a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Golemis E., Hartley J. W., Hopkins N. Disease specificity of nondefective Friend and Moloney murine leukemia viruses is controlled by a small number of nucleotides. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):693–700. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.693-700.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LoSardo J. E., Cupelli L. A., Short M. K., Berman J. W., Lenz J. Differences in activities of murine retroviral long terminal repeats in cytotoxic T lymphocytes and T-lymphoma cells. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1087–1094. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1087-1094.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy D. R., Rands E., Chattopadhyay S. K., Garon C. F., Hager G. L. Molecular cloning of infectious integrated murine leukemia virus DNA from infected mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):614–618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh J. L., Erfle M., Wykes E. J. The pIC plasmid and phage vectors with versatile cloning sites for recombinant selection by insertional inactivation. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):481–485. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercurio F., Karin M. Transcription factors AP-3 and AP-2 interact with the SV40 enhancer in a mutually exclusive manner. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1455–1460. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miksicek R., Heber A., Schmid W., Danesch U., Posseckert G., Beato M., Schütz G. Glucocorticoid responsiveness of the transcriptional enhancer of Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):283–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90745-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura T., Shibuya M., Tsujimoto H., Fukasawa M., Hayami M. Molecular cloning of a feline leukemia provirus integrated adjacent to the c-myc gene in a feline T-cell leukemia cell line and the unique structure of its long terminal repeat. Virology. 1989 Apr;169(2):458–461. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90172-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Guggenheimer R. A., Hurwitz J. Specific binding of a cellular DNA replication protein to the origin of replication of adenovirus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6177–6181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neil J. C., Forrest D., Doggett D. L., Mullins J. I. The role of feline leukaemia virus in naturally occurring leukaemias. Cancer Surv. 1987;6(1):117–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neil J. C., Hughes D., McFarlane R., Wilkie N. M., Onions D. E., Lees G., Jarrett O. Transduction and rearrangement of the myc gene by feline leukaemia virus in naturally occurring T-cell leukaemias. 1984 Apr 26-May 2Nature. 308(5962):814–820. doi: 10.1038/308814a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ondek B., Gloss L., Herr W. The SV40 enhancer contains two distinct levels of organization. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):40–45. doi: 10.1038/333040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onions D., Lees G., Forrest D., Neil J. Recombinant feline viruses containing the myc gene rapidly produce clonal tumours expressing T-cell antigen receptor gene transcripts. Int J Cancer. 1987 Jul 15;40(1):40–45. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910400108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G., Lee A. E., Dickson C. Concerted activation of two potential proto-oncogenes in carcinomas induced by mouse mammary tumour virus. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):628–631. doi: 10.1038/320628a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plumb M., Frampton J., Wainwright H., Walker M., Macleod K., Goodwin G., Harrison P. GATAAG; a cis-control region binding an erythroid-specific nuclear factor with a role in globin and non-globin gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):73–92. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedel N., Hoover E. A., Gasper P. W., Nicolson M. O., Mullins J. I. Molecular analysis and pathogenesis of the feline aplastic anemia retrovirus, feline leukemia virus C-Sarma. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):242–250. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.242-250.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojko J. L., Hoover E. A., Mathes L. E., Olsen R. G., Schaller J. P. Pathogenesis of experimental feline leukemia virus infection. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1979 Sep;63(3):759–768. doi: 10.1093/jnci/63.3.759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck N. A., Baltimore D. Six distinct nuclear factors interact with the 75-base-pair repeat of the Moloney murine leukemia virus enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1101–1110. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro C., Li J. P., Bestwick R. K., Kabat D. An enhancer sequence instability that diversifies the cell repertoire for expression of a murine leukemia virus. Virology. 1988 Jun;164(2):350–361. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90548-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M. A., Forrest D., McFarlane R., Onions D., Wilkie N., Neil J. C. Conservation of the c-myc coding sequence in transduced feline v-myc genes. Virology. 1986 Oct 15;154(1):121–134. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90435-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M. A., Warnock M., Wheeler A., Wilkie N., Mullins J. I., Onions D. E., Neil J. C. Nucleotide sequences of a feline leukemia virus subgroup A envelope gene and long terminal repeat and evidence for the recombinational origin of subgroup B viruses. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):825–834. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.825-834.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornell A., Hallberg B., Grundström T. Differential protein binding in lymphocytes to a sequence in the enhancer of the mouse retrovirus SL3-3. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1625–1637. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsichlis P. N., Strauss P. G., Lohse M. A. Concerted DNA rearrangements in Moloney murine leukemia virus-induced thymomas: a potential synergistic relationship in oncogenesis. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):258–267. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.258-267.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingender E. Compilation of transcription regulating proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(5):1879–1902. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.1879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong T. C., Goodenow R. S., Sher B. T., Davidson N. The promoter of the long terminal repeat of feline leukemia virus is effective for expression of a mouse H-2 histocompatibility gene in mouse and human cells. Gene. 1985;34(1):27–38. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90291-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]