Abstract
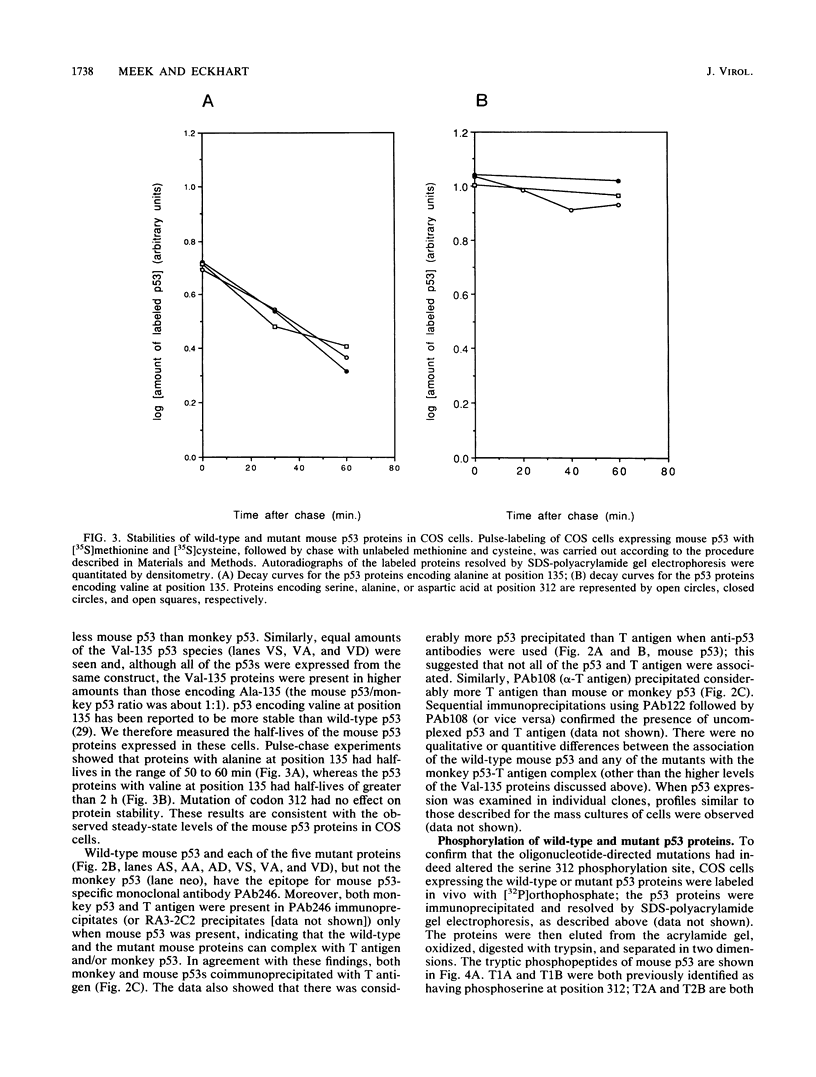
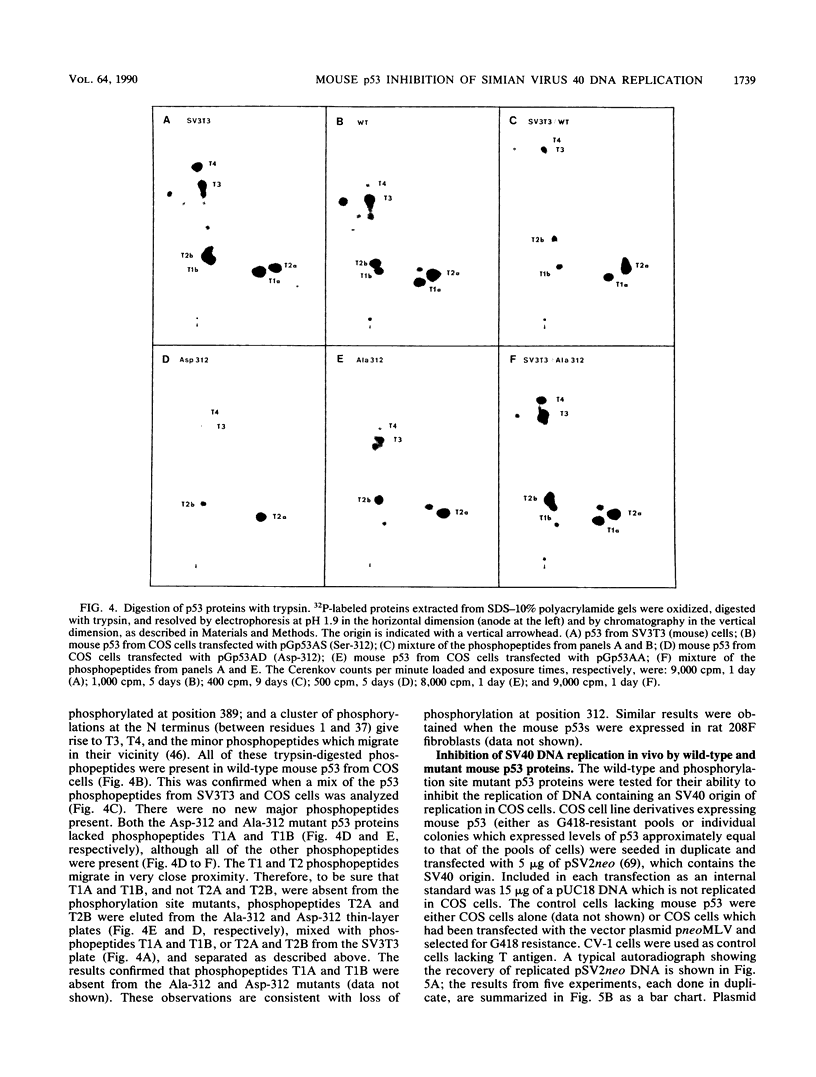
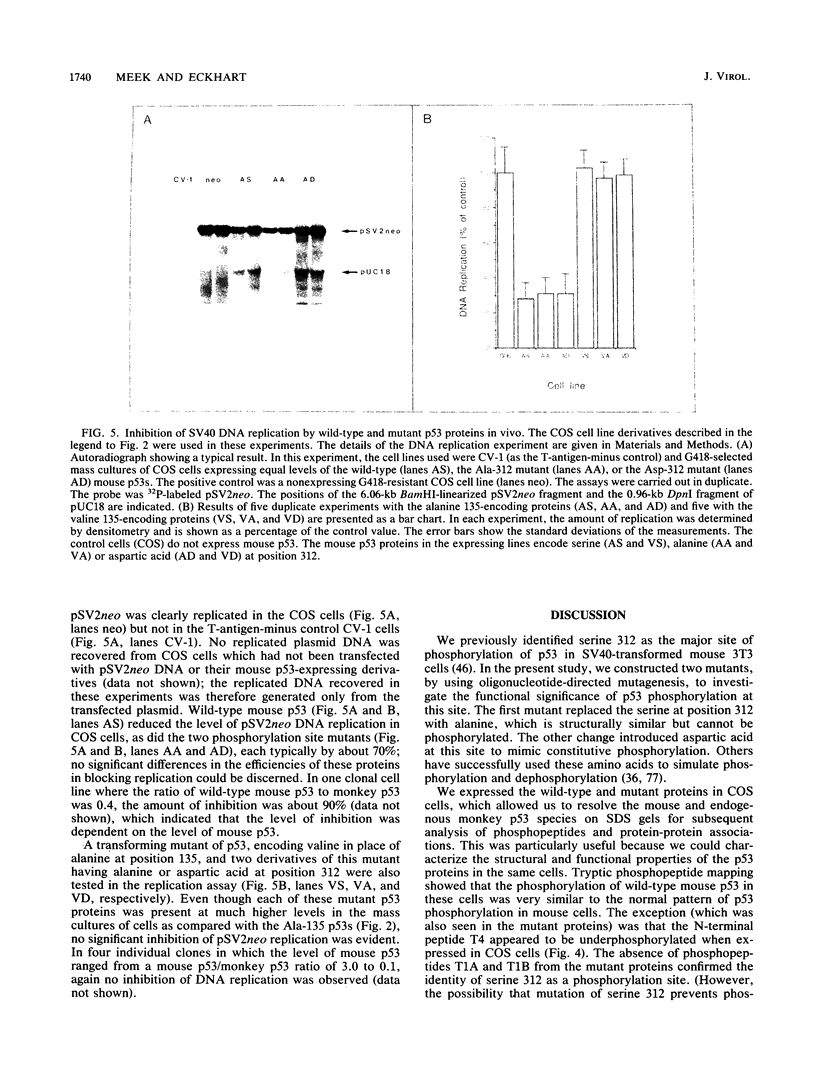
Two mutations were introduced into the wild-type mouse p53 gene by oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis. These mutations substituted alanine or aspartic acid for serine at position 312, which is constitutively phosphorylated. Phosphopeptide mapping of the mutant proteins, expressed in COS cells, confirmed the loss of phosphorylation at position 312. There were no changes in the ability of the mutant p53s to express the conformation-dependent epitope for monoclonal antibody PAb246 or to participate in complexes with the simian virus 40 (SV40) large T antigen. Replication of a plasmid containing the SV40 origin of replication was inhibited in COS cells by wild-type p53 and both of the phosphorylation site mutants with equal efficiency. A transforming mutant of p53, encoding valine at position 135, did not inhibit SV40 DNA replication in COS cells.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amrein K. E., Sefton B. M. Mutation of a site of tyrosine phosphorylation in the lymphocyte-specific tyrosine protein kinase, p56lck, reveals its oncogenic potential in fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4247–4251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S. J., Fearon E. R., Nigro J. M., Hamilton S. R., Preisinger A. C., Jessup J. M., vanTuinen P., Ledbetter D. H., Barker D. F., Nakamura Y. Chromosome 17 deletions and p53 gene mutations in colorectal carcinomas. Science. 1989 Apr 14;244(4901):217–221. doi: 10.1126/science.2649981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnstable C. J., Bodmer W. F., Brown G., Galfre G., Milstein C., Williams A. F., Ziegler A. Production of monoclonal antibodies to group A erythrocytes, HLA and other human cell surface antigens-new tools for genetic analysis. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beemon K., Hunter T. Characterization of Rous sarcoma virus src gene products synthesized in vitro. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):551–566. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.551-566.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braithwaite A. W., Sturzbecher H. W., Addison C., Palmer C., Rudge K., Jenkins J. R. Mouse p53 inhibits SV40 origin-dependent DNA replication. Nature. 1987 Oct 1;329(6138):458–460. doi: 10.1038/329458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright C. A., Eckhart W., Simon S., Kaplan P. L. Cell transformation by pp60c-src mutated in the carboxy-terminal regulatory domain. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):83–91. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90758-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow V., Ben-David Y., Bernstein A., Benchimol S., Mowat M. Multistage Friend erythroleukemia: independent origin of tumor clones with normal or rearranged p53 cellular oncogenes. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2777–2781. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2777-2781.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman R. L., Weissman I. L. A monoclonal antibody that recognizes B cells and B cell precursors in mice. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):269–279. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J., Meisner H. Regulation of transferrin receptor cycling by protein kinase C is independent of receptor phosphorylation at serine 24 in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):16041–16047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deppert W., Haug M. Evidence for free and metabolically stable p53 protein in nuclear subfractions of simian virus 40-transformed cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2233–2240. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deppert W., Haug M., Steinmayer T. Modulation of p53 protein expression during cellular transformation with simian virus 40. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4453–4463. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliyahu D., Michalovitz D., Oren M. Overproduction of p53 antigen makes established cells highly tumorigenic. Nature. 1985 Jul 11;316(6024):158–160. doi: 10.1038/316158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliyahu D., Raz A., Gruss P., Givol D., Oren M. Participation of p53 cellular tumour antigen in transformation of normal embryonic cells. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):646–649. doi: 10.1038/312646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L., Clauser E., Morgan D. O., Edery M., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of insulin receptor tyrosine residues 1162 and 1163 compromises insulin-stimulated kinase activity and uptake of 2-deoxyglucose. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90786-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay C. A., Hinds P. W., Levine A. J. The p53 proto-oncogene can act as a suppressor of transformation. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1083–1093. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90045-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay C. A., Hinds P. W., Tan T. H., Eliyahu D., Oren M., Levine A. J. Activating mutations for transformation by p53 produce a gene product that forms an hsc70-p53 complex with an altered half-life. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):531–539. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon J. V., Lane D. P. p53 and DNA polymerase alpha compete for binding to SV40 T antigen. Nature. 1987 Oct 1;329(6138):456–458. doi: 10.1038/329456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. When the products of oncogenes and anti-oncogenes meet. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90975-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurney E. G., Harrison R. O., Fenno J. Monoclonal antibodies against simian virus 40 T antigens: evidence for distinct sublcasses of large T antigen and for similarities among nonviral T antigens. J Virol. 1980 Jun;34(3):752–763. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.3.752-763.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurney E. G., Tamowski S., Deppert W. Antigenic binding sites of monoclonal antibodies specific for simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1168–1172. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1168-1172.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halevy O., Hall A., Oren M. Stabilization of the p53 transformation-related protein in mouse fibrosarcoma cell lines: effects of protein sequence and intracellular environment. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3385–3392. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks G. G., Mowat M. Integration of Friend murine leukemia virus into both alleles of the p53 oncogene in an erythroleukemic cell line. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4752–4755. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4752-4755.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds P. W., Finlay C. A., Frey A. B., Levine A. J. Immunological evidence for the association of p53 with a heat shock protein, hsc70, in p53-plus-ras-transformed cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2863–2869. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds P., Finlay C., Levine A. J. Mutation is required to activate the p53 gene for cooperation with the ras oncogene and transformation. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):739–746. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.739-746.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Transforming gene product of Rous sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1311–1315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins J. R., Rudge K., Chumakov P., Currie G. A. The cellular oncogene p53 can be activated by mutagenesis. 1985 Oct 31-Nov 6Nature. 317(6040):816–818. doi: 10.1038/317816a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins J. R., Rudge K., Currie G. A. Cellular immortalization by a cDNA clone encoding the transformation-associated phosphoprotein p53. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):651–654. doi: 10.1038/312651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan P. L., Simon S., Cartwright C. A., Eckhart W. cDNA cloning with a retrovirus expression vector: generation of a pp60c-src cDNA clone. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1731–1734. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1731-1734.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Davies M. V., Pathak V. K., Hershey J. W. The phosphorylation state of eucaryotic initiation factor 2 alters translational efficiency of specific mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):946–958. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelekar A., Cole M. D. Tumorigenicity of fibroblast lines expressing the adenovirus E1a, cellular p53, or normal c-myc genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):7–14. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiecik T. E., Shalloway D. Activation and suppression of pp60c-src transforming ability by mutation of its primary sites of tyrosine phosphorylation. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90756-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kress M., May E., Cassingena R., May P. Simian virus 40-transformed cells express new species of proteins precipitable by anti-simian virus 40 tumor serum. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):472–483. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.472-483.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Derivation of specific antibody-producing tissue culture and tumor lines by cell fusion. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Jul;6(7):511–519. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P., Crawford L. V. T antigen is bound to a host protein in SV40-transformed cells. Nature. 1979 Mar 15;278(5701):261–263. doi: 10.1038/278261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P. p53 in Paris, an oncogene comes of age. Oncogene. 1987;1(3):241–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Levine A. J. Characterization of a 54K dalton cellular SV40 tumor antigen present in SV40-transformed cells and uninfected embryonal carcinoma cells. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90293-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livneh E., Dull T. J., Berent E., Prywes R., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Release of a phorbol ester-induced mitogenic block by mutation at Thr-654 of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2302–2308. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda H., Miller C., Koeffler H. P., Battifora H., Cline M. J. Rearrangement of the p53 gene in human osteogenic sarcomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7716–7719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meek D. W., Eckhart W. Phosphorylation of p53 in normal and simian virus 40-transformed NIH 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):461–465. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner J. Different forms of p53 detected by monoclonal antibodies in non-dividing and dividing lymphocytes. Nature. 1984 Jul 12;310(5973):143–145. doi: 10.1038/310143a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowat M., Cheng A., Kimura N., Bernstein A., Benchimol S. Rearrangements of the cellular p53 gene in erythroleukaemic cells transformed by Friend virus. Nature. 1985 Apr 18;314(6012):633–636. doi: 10.1038/314633a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munroe D. G., Rovinski B., Bernstein A., Benchimol S. Loss of a highly conserved domain on p53 as a result of gene deletion during Friend virus-induced erythroleukemia. Oncogene. 1988 Jun;2(6):621–624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamaye K. L., Eckstein F. Inhibition of restriction endonuclease Nci I cleavage by phosphorothioate groups and its application to oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 22;14(24):9679–9698. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.24.9679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parada L. F., Land H., Weinberg R. A., Wolf D., Rotter V. Cooperation between gene encoding p53 tumour antigen and ras in cellular transformation. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):649–651. doi: 10.1038/312649a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peden K. W., Pipas J. M., Pearson-White S., Nathans D. Isolation of mutants of an animal virus in bacteria. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1392–1396. doi: 10.1126/science.6251547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinhasi O., Oren M. Expression of the mouse p53 cellular tumor antigen in monkey cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):2180–2186. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.2180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piwnica-Worms H., Saunders K. B., Roberts T. M., Smith A. E., Cheng S. H. Tyrosine phosphorylation regulates the biochemical and biological properties of pp60c-src. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90757-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich N. C., Levine A. J. Growth regulation of a cellular tumour antigen, p53, in nontransformed cells. Nature. 1984 Mar 8;308(5955):199–201. doi: 10.1038/308199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter V., Witte O. N., Coffman R., Baltimore D. Abelson murine leukemia virus-induced tumors elicit antibodies against a host cell protein, P50. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):547–555. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.547-555.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovinski B., Benchimol S. Immortalization of rat embryo fibroblasts by the cellular p53 oncogene. Oncogene. 1988 May;2(5):445–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovinski B., Munroe D., Peacock J., Mowat M., Bernstein A., Benchimol S. Deletion of 5'-coding sequences of the cellular p53 gene in mouse erythroleukemia: a novel mechanism of oncogene regulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):847–853. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samad A., Anderson C. W., Carroll R. B. Mapping of phosphomonoester and apparent phosphodiester bonds of the oncogene product p53 from simian virus 40-transformed 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):897–901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnow P., Ho Y. S., Williams J., Levine A. J. Adenovirus E1b-58kd tumor antigen and SV40 large tumor antigen are physically associated with the same 54 kd cellular protein in transformed cells. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):387–394. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90356-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayers J. R., Schmidt W., Eckstein F. 5'-3' exonucleases in phosphorothioate-based oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):791–802. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J., Fanning E. Mutations in the phosphorylation sites of simian virus 40 (SV40) T antigen alter its origin DNA-binding specificity for sites I or II and affect SV40 DNA replication activity. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1598–1605. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1598-1605.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shohat O., Greenberg M., Reisman D., Oren M., Rotter V. Inhibition of cell growth mediated by plasmids encoding p53 anti-sense. Oncogene. 1987;1(3):277–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Debouck C., Rosenberg M., Culp J. S. Phosphorylation of serine residue 89 of human adenovirus E1A proteins is responsible for their characteristic electrophoretic mobility shifts, and its mutation affects biological function. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1569–1577. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1569-1577.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Summers M. D. The bidirectional transfer of DNA and RNA to nitrocellulose or diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stürzbecher H. W., Brain R., Maimets T., Addison C., Rudge K., Jenkins J. R. Mouse p53 blocks SV40 DNA replication in vitro and downregulates T antigen DNA helicase activity. Oncogene. 1988 Oct;3(4):405–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stürzbecher H. W., Chumakov P., Welch W. J., Jenkins J. R. Mutant p53 proteins bind hsp 72/73 cellular heat shock-related proteins in SV40-transformed monkey cells. Oncogene. 1987 May;1(2):201–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tack L. C., Wright J. H., Deb S. P., Tegtmeyer P. The p53 complex from monkey cells modulates the biochemical activities of simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1310–1317. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1310-1317.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan T. H., Wallis J., Levine A. J. Identification of the p53 protein domain involved in formation of the simian virus 40 large T-antigen-p53 protein complex. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):574–583. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.574-583.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. W., Ott J., Eckstein F. The rapid generation of oligonucleotide-directed mutations at high frequency using phosphorothioate-modified DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8765–8785. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. W., Schmidt W., Cosstick R., Okruszek A., Eckstein F. The use of phosphorothioate-modified DNA in restriction enzyme reactions to prepare nicked DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8749–8764. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorsness P. E., Koshland D. E., Jr Inactivation of isocitrate dehydrogenase by phosphorylation is mediated by the negative charge of the phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10422–10425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto A. S., Ponticelli A., Berk A. J., Gaynor R. B. Genetic mapping of a major site of phosphorylation in adenovirus type 2 E1A proteins. J Virol. 1986 Jul;59(1):14–22. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.1.14-22.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Roy F., Fransen L., Fiers W. Protein kinase activities in immune complexes of simian virus 40 large T-antigen and transformation-associated cellular p53 protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):232–239. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E. H., Friedman P. N., Prives C. The murine p53 protein blocks replication of SV40 DNA in vitro by inhibiting the initiation functions of SV40 large T antigen. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):379–392. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90913-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinmaster G. A., Middlemas D. S., Hunter T. A major site of tyrosine phosphorylation within the SH2 domain of Fujinami sarcoma virus P130gag-fps is not required for protein-tyrosine kinase activity or transforming potential. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2016–2025. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2016-2025.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf D., Harris N., Rotter V. Reconstitution of p53 expression in a nonproducer Ab-MuLV-transformed cell line by transfection of a functional p53 gene. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90532-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R., Alberts B. M., Benzinger R., Lawhorne L., Treiber G. Rapid bacteriophage sedimentation in the presence of polyethylene glycol and its application to large-scale virus purification. Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):734–744. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90218-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yewdell J. W., Gannon J. V., Lane D. P. Monoclonal antibody analysis of p53 expression in normal and transformed cells. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):444–452. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.444-452.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





