Abstract
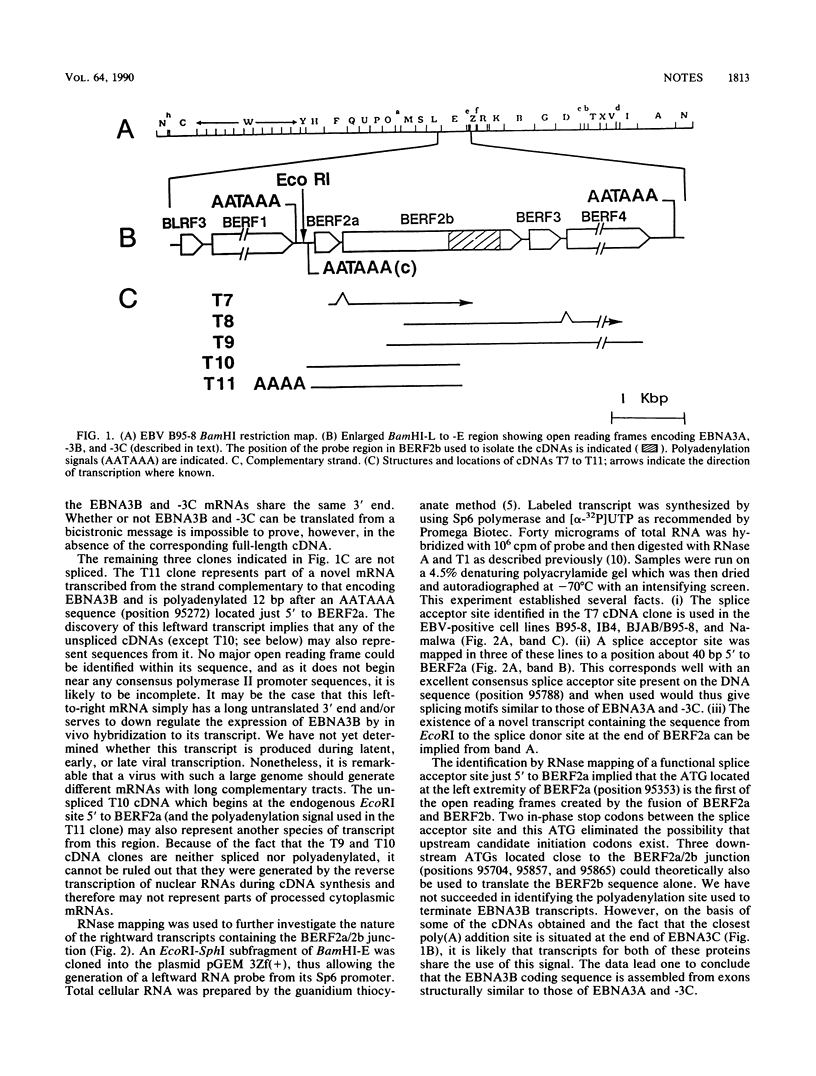
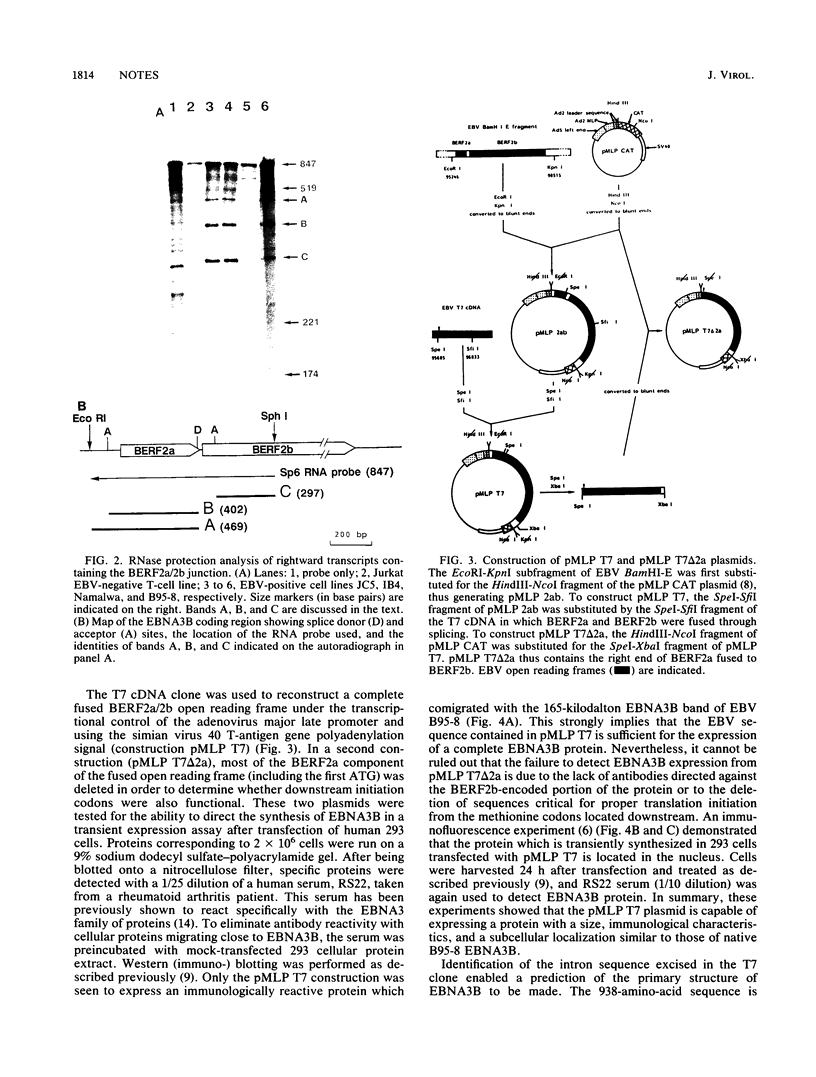
Recombinant plasmids containing sequences from the BamHI-E rightward reading frames 2a and 2b (BERF2a and 2b) of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) genome were isolated from a library of cDNA clones which had been previously made from the EBV B95-8 lymphoblastoid cell line (M. Bodescot, O. Brison, and M. Perricaudet, Nucleic Acids Res. 14:7103-7114, 1986). The characterization of these clones in combination with RNase mapping experiments led to the identification of one leftward and several rightward transcripts traversing the EBV-determined nuclear antigen EBNA3B coding region. One cDNA (T7) contains a continuous open reading frame generated by the splicing together of BERF2a and BERF2b. The T7 clone was used to reconstruct a complete fused BERF2a/2b open reading frame in an adenovirus-based expression vector. Western immunoblotting and immunofluorescence experiments using human 293 cells showed that the recombinant plasmid is capable of expressing a protein with a size, immunological characteristics, and a subcellular localization indistinguishable from those of native B95-8 EBNA3B.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allday M. J., Crawford D. H., Griffin B. E. Prediction and demonstration of a novel Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 25;16(10):4353–4367. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.10.4353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodescot M., Brison O., Perricaudet M. An Epstein-Barr virus transcription unit is at least 84 kilobases long. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2611–2620. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodescot M., Perricaudet M. Epstein-Barr virus mRNAs produced by alternative splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):7103–7114. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.17.7103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing J. C., Nicolas J. C., Levine A. J. Identification of Epstein-Barr virus sequences that encode a nuclear antigen expressed in latently infected lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4373–4377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Wang F., Bushman E. W., Kieff E. Definitive identification of a member of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 3 family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5693–5697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joab I., Rowe D. T., Bodescot M., Nicolas J. C., Farrell P. J., Perricaudet M. Mapping of the gene coding for Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen EBNA3 and its transient overexpression in a human cell line by using an adenovirus expression vector. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3340–3344. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3340-3344.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petti L., Kieff E. A sixth Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein (EBNA3B) is expressed in latently infected growth-transformed lymphocytes. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2173–2178. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2173-2178.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petti L., Sample J., Wang F., Kieff E. A fifth Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein (EBNA3C) is expressed in latently infected growth-transformed lymphocytes. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1330–1338. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1330-1338.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricksten A., Kallin B., Alexander H., Dillner J., Fåhraeus R., Klein G., Lerner R., Rymo L. BamHI E region of the Epstein-Barr virus genome encodes three transformation-associated nuclear proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):995–999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe M., Young L. S., Cadwallader K., Petti L., Kieff E., Rickinson A. B. Distinction between Epstein-Barr virus type A (EBNA 2A) and type B (EBNA 2B) isolates extends to the EBNA 3 family of nuclear proteins. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1031–1039. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1031-1039.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada K., Yamamoto M., Tabata T., Smith M., Tanaka A., Nonoyama M. Expression of EBNA-3 family in fresh B lymphocytes infected with Epstein-Barr virus. Virology. 1989 Jan;168(1):22–30. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90399-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu N., Yamaki M., Sakuma S., Ono Y., Takada K. Three Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-determined nuclear antigens induced by the BamHI E region of EBV DNA. Int J Cancer. 1988 May 15;41(5):744–751. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910410518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]