Abstract
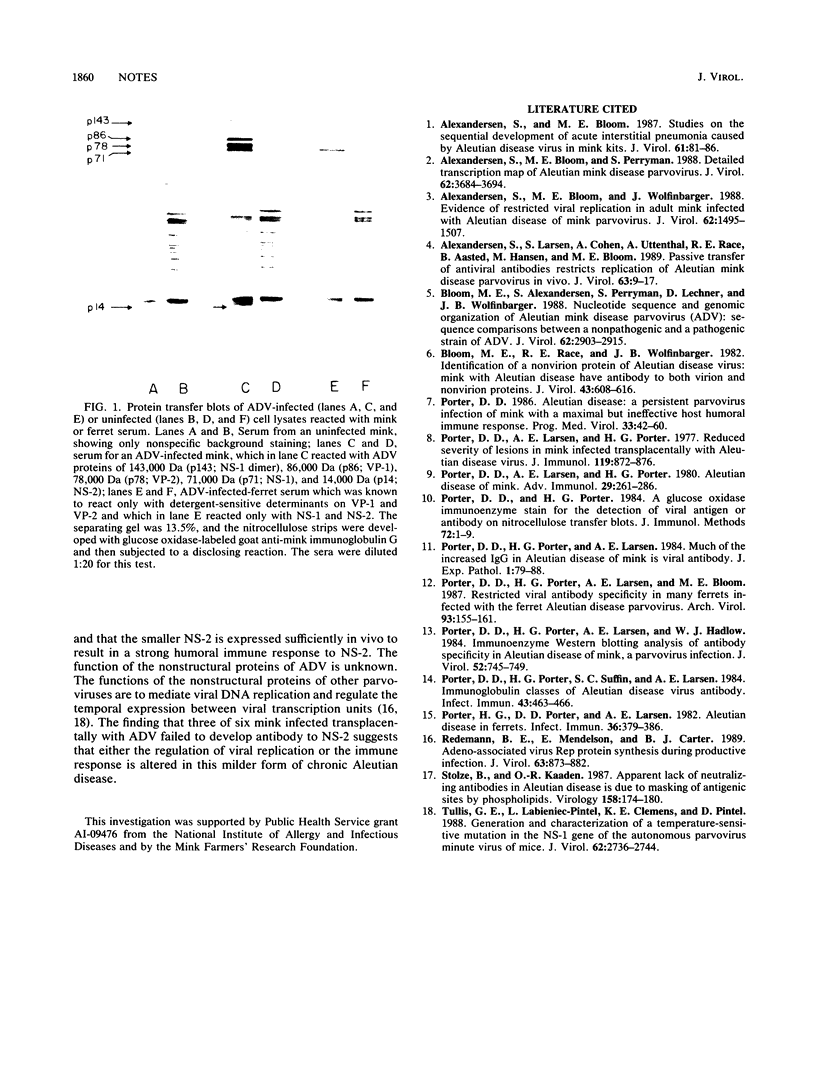
A second nonstructural protein of the Aleutian disease parvovirus was predicted from nucleotide sequence analysis and a detailed transcription map. Western immunoblotting analysis showed that infected mink and ferrets show an antibody response to this predicted protein.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexandersen S., Bloom M. E., Perryman S. Detailed transcription map of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3684–3694. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3684-3694.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersen S., Bloom M. E. Studies on the sequential development of acute interstitial pneumonia caused by Aleutian disease virus in mink kits. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):81–86. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.81-86.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersen S., Bloom M. E., Wolfinbarger J. Evidence of restricted viral replication in adult mink infected with Aleutian disease of mink parvovirus. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1495–1507. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1495-1507.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersen S., Larsen S., Cohn A., Uttenthal A., Race R. E., Aasted B., Hansen M., Bloom M. E. Passive transfer of antiviral antibodies restricts replication of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus in vivo. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):9–17. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.9-17.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M. E., Alexandersen S., Perryman S., Lechner D., Wolfinbarger J. B. Nucleotide sequence and genomic organization of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus (ADV): sequence comparisons between a nonpathogenic and a pathogenic strain of ADV. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2903–2915. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2903-2915.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M. E., Race R. E., Wolfinbarger J. B. Identification of a nonvirion protein of Aleutian disease virus: mink with Aleutian disease have antibody to both virion and nonvirion proteins. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):608–616. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.608-616.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D. Aleutian disease: a persistent parvovirus infection of mink with a maximal but ineffective host humoral immune response. Prog Med Virol. 1986;33:42–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Larsen A. E., Porter H. G. Aleutian disease of mink. Adv Immunol. 1980;29:261–286. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60046-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Larsen A. E., Porter H. G. Reduced severity of lesions in mink infected transplacentally with Aleutian disease virus. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):872–876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Porter H. G. A glucose oxidase immunoenzyme stain for the detection of viral antigen or antibody on nitrocellulose transfer blots. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Aug 3;72(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90428-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Porter H. G., Larsen A. E., Bloom M. E. Restricted viral antibody specificity in many ferrets infected with the ferret Aleutian disease parvovirus. Brief report. Arch Virol. 1987;93(1-2):155–161. doi: 10.1007/BF01313902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Porter H. G., Larsen A. E., Hadlow W. J. Immunoenzyme Western blotting analysis of antibody specificity in Aleutian disease of mink, a parvovirus infection. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):745–749. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.745-749.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Porter H. G., Larsen A. E. Much of the increased IgG in Aleutian disease of mink is viral antibody. J Exp Pathol. 1984;1(2):79–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Porter H. G., Suffin S. C., Larsen A. E. Immunoglobulin classes of Aleutian disease virus antibody. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):463–466. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.463-466.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter H. G., Porter D. D., Larsen A. E. Aleutian disease in ferrets. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):379–386. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.379-386.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redemann B. E., Mendelson E., Carter B. J. Adeno-associated virus rep protein synthesis during productive infection. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):873–882. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.873-882.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolze B., Kaaden O. R. Apparent lack of neutralizing antibodies in Aleutian disease is due to masking of antigenic sites by phospholipids. Virology. 1987 May;158(1):174–180. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90251-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullis G. E., Labieniec-Pintel L., Clemens K. E., Pintel D. Generation and characterization of a temperature-sensitive mutation in the NS-1 gene of the autonomous parvovirus minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2736–2744. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2736-2744.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]