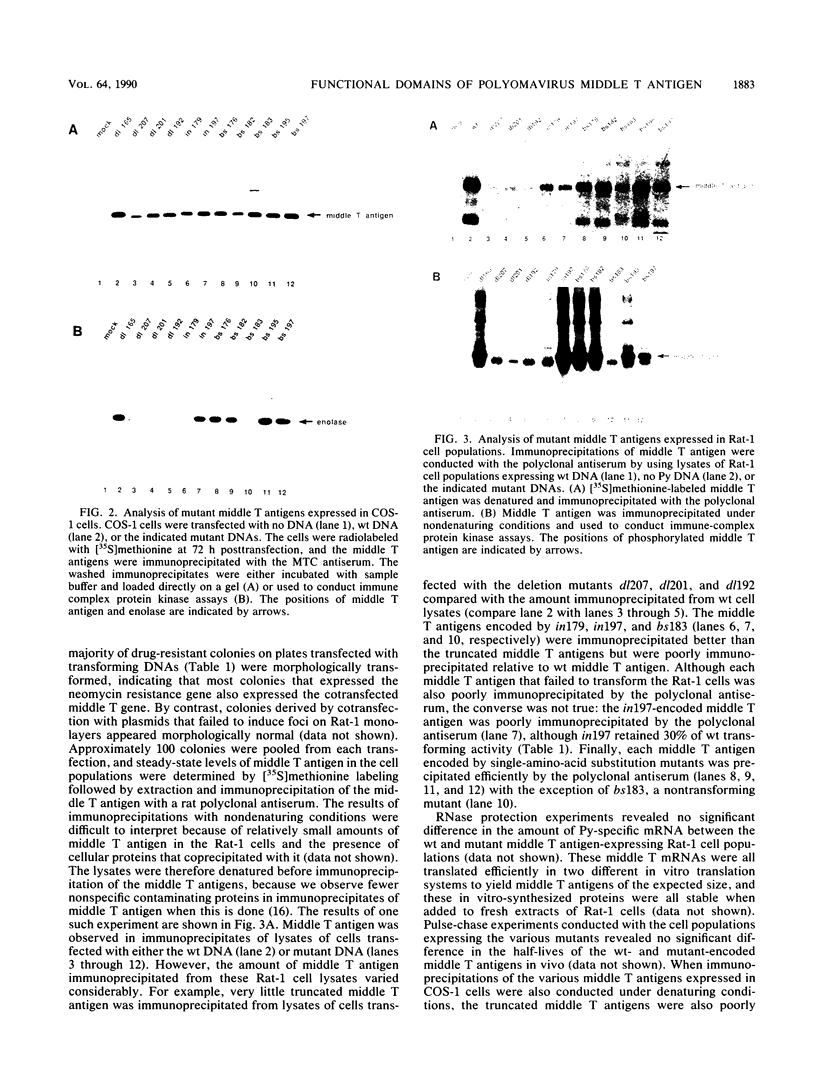
Abstract
In polyomavirus-transformed cells, pp60c-src is activated by association with polyomavirus middle T antigen. These complexes have a higher tyrosine kinase activity compared with that of unassociated pp60c-src. Genetic analyses have revealed that the carboxy-terminal 15 amino acids of pp60c-src and the amino-terminal half of middle T antigen are required for this association and consequent activation of the tyrosine kinase. To define in greater detail the borders of the domain in middle T antigen required for activation of pp60c-src, we constructed a set of unidirectional amino-terminal deletion mutants of middle T antigen. Analysis of these mutants revealed that the first six amino acids of middle T antigen are required for it to activate the kinase activity of pp60c-src and to transform Rat-1 fibroblasts. Analysis of a series of insertion and substitution mutants confirmed these observations and further revealed that mutations affecting the first four amino acids of middle T antigen reduced or abolished its capacity to activate the kinase activity of pp60c-src and to transform Rat-1 cells in culture. Our results suggest that the first four amino acids of middle T antigen constitute part of a domain required for activation of the pp60c-src tyrosyl kinase activity and for consequent cellular transformation.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asselin C., Gélinas C., Branton P. E., Bastin M. Polyoma middle T antigen requires cooperation from another gene to express the malignant phenotype in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;4(4):755–760. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.4.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bautch V. L., Toda S., Hassell J. A., Hanahan D. Endothelial cell tumors develop in transgenic mice carrying polyoma virus middle T oncogene. Cell. 1987 Nov 20;51(4):529–537. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90122-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin T. L. Host range mutants of polyoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):394–399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. B., Israel M. A. Middle tumor antigen of polyomavirus transformation-defective mutant NG59 is associated with pp60c-src. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):114–119. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.114-119.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. B., Thiele C. J., Israel M. A., Yonemoto W., Lipsich L. A., Brugge J. S. Enhancement of cellular src gene product associated tyrosyl kinase activity following polyoma virus infection and transformation. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):767–777. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90272-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael G. G., Benjamin T. L. Identification of DNA sequence changes leading to loss of transforming ability in polyoma virus. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):230–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael G. G., Schaffhausen B. S., Dorsky D. I., Oliver D. B., Benjamin T. L. Carboxy terminus of polyoma middle-sized tumor antigen is required for attachment to membranes, associated protein kinase activities, and cell transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3579–3583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright C. A., Eckhart W., Simon S., Kaplan P. L. Cell transformation by pp60c-src mutated in the carboxy-terminal regulatory domain. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):83–91. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90758-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright C. A., Kaplan P. L., Cooper J. A., Hunter T., Eckhart W. Altered sites of tyrosine phosphorylation in pp60c-src associated with polyomavirus middle tumor antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1562–1570. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. H., Markland W., Markham A. F., Smith A. E. Mutations around the NG59 lesion indicate an active association of polyoma virus middle-T antigen with pp60c-src is required for cell transformation. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):325–334. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04216.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A. Activation of the pp60c-src kinase by middle T antigen binding or by dephosphorylation. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1471–1477. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03805.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Heber A. An 81 kd protein complexed with middle T antigen and pp60c-src: a possible phosphatidylinositol kinase. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1031–1037. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90169-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Smith A. E. Polyoma virus transforming protein associates with the product of the c-src cellular gene. Nature. 1983 Jun 2;303(5916):435–439. doi: 10.1038/303435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Smith A. E. The complex of polyoma virus middle-T antigen and pp60c-src. EMBO J. 1984 Mar;3(3):585–591. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01852.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson D., Hassell J. A. Overproduction of polyomavirus middle T antigen in mammalian cells through the use of an adenovirus vector. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1226–1239. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1226-1239.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhart W., Hutchinson M. A., Hunter T. An activity phosphorylating tyrosine in polyoma T antigen immunoprecipitates. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):925–933. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90205-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
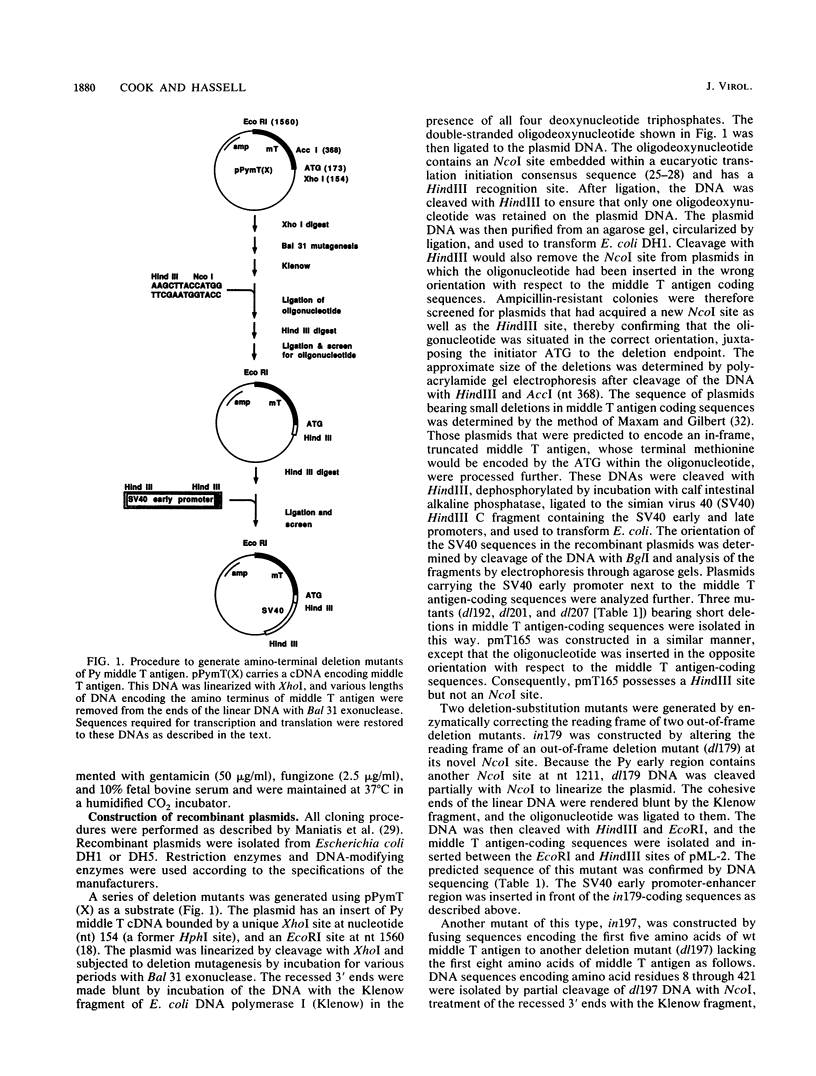
- Featherstone M. S., Naujokas M. A., Pomerantz B. J., Hassell J. A. A plasmid vehicle suitable for the molecular cloning and characterization of mammalian promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7235–7249. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Oostra B. A., Ely B. K., Smith A. E. Deletion loop mutagenesis: a novel method for the construction of point mutations using deletion mutants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Sep 11;10(17):5161–5171. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.17.5161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Whitman M., Schaffhausen B., Pallas D. C., White M., Cantley L., Roberts T. M. Common elements in growth factor stimulation and oncogenic transformation: 85 kd phosphoprotein and phosphatidylinositol kinase activity. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1021–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90168-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katinka M., Yaniv M. Deletions of N-terminal sequences of polyoma virus T-antigens reduce but do not abolish transformation of rat fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;2(10):1238–1246. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.10.1238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiecik T. E., Shalloway D. Activation and suppression of pp60c-src transforming ability by mutation of its primary sites of tyrosine phosphorylation. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90756-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornbluth S., Cross F. R., Harbison M., Hanafusa H. Transformation of chicken embryo fibroblasts and tumor induction by the middle T antigen of polyomavirus carried in an avian retroviral vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1545–1551. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations close to the AUG initiator codon affect the efficiency of translation of rat preproinsulin in vivo. Nature. 1984 Mar 15;308(5956):241–246. doi: 10.1038/308241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Selection of initiation sites by eucaryotic ribosomes: effect of inserting AUG triplets upstream from the coding sequence for preproinsulin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 11;12(9):3873–3893. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.9.3873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markland W., Cheng S. H., Oostra B. A., Smith A. E. In vitro mutagenesis of the putative membrane-binding domain of polyomavirus middle-T antigen. J Virol. 1986 Jul;59(1):82–89. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.1.82-89.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markland W., Smith A. E. Mapping of the amino-terminal half of polyomavirus middle-T antigen indicates that this region is the binding domain for pp60c-src. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):285–292. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.285-292.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mes-Masson A. M., Schaffhausen B., Hassell J. A. The major site of tyrosine phosphorylation in polyomavirus middle T antigen is not required for transformation. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):457–464. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.457-464.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mes A. M., Hassell J. A. Polyoma viral middle T-antigen is required for transformation. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):621–629. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.621-629.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller W. J., Dufort D., Hassell J. A. Multiple subelements within the polyomavirus enhancer function synergistically to activate DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):5000–5015. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.5000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson S. V., Tyndall C., Magnusson G. Deletion mapping of a short polyoma virus middle T antigen segment important for transformation. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):284–287. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.284-287.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oostra B. A., Harvey R., Ely B. K., Markham A. F., Smith A. E. Transforming activity of polyoma virus middle-T antigen probed by site-directed mutagenesis. Nature. 1983 Aug 4;304(5925):456–459. doi: 10.1038/304456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piwnica-Worms H., Saunders K. B., Roberts T. M., Smith A. E., Cheng S. H. Tyrosine phosphorylation regulates the biochemical and biological properties of pp60c-src. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90757-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffhausen B. S., Benjamin T. L. Phosphorylation of polyoma T antigens. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):935–946. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90206-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffhausen B. S., Dorai H., Arakere G., Benjamin T. L. Polyoma virus middle T antigen: relationship to cell membranes and apparent lack of ATP-binding activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;2(10):1187–1198. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.10.1187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffhausen B., Benjamin T. L. Comparison of phosphorylation of two polyoma virus middle T antigens in vivo and in vitro. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):184–196. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.184-196.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffhausen B., Benjamin T. L., Lodge J., Kaplan D., Roberts T. M. Expression of polyoma early gene products in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jan 25;13(2):501–519. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.2.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffhausen B. Transforming genes and gene products of polyoma and SV40. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1982;13(3):215–286. doi: 10.3109/10409238209114230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. E., Smith R., Griffin B., Fried M. Protein kinase activity associated with polyoma virus middle T antigen in vitro. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):915–924. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90204-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spandidos D. A., Riggio M. Polyoma virus middle T gene can trigger malignant transformation of early passage rodent cells. J Gen Virol. 1986 Apr;67(Pt 4):793–799. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-4-793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor G. R., Reedijk M., Rothwell V., Rohrschneider L., Pawson T. The unique insert of cellular and viral fms protein tyrosine kinase domains is dispensable for enzymatic and transforming activities. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2029–2037. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03611.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Templeton D., Eckhart W. Mutation causing premature termination of the polyoma virus medium T antigen blocks cell transformation. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):1014–1024. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.1014-1024.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Templeton D., Voronova A., Eckhart W. Construction and expression of a recombinant DNA gene encoding a polyomavirus middle-size tumor antigen with the carboxyl terminus of the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein G. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):282–289. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Novak U., Favaloro J., Kamen R. Transformation of rat cells by an altered polyoma virus genome expressing only the middle-T protein. Nature. 1981 Aug 13;292(5824):595–600. doi: 10.1038/292595a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. L., Courtneidge S. A., Wagner E. F. Embryonic lethalities and endothelial tumors in chimeric mice expressing polyoma virus middle T oncogene. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):121–131. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90536-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]