Abstract
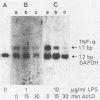
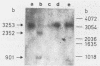
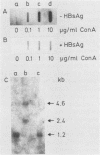
The mRNAs of transiently expressed cytokine genes contain AUUUA-rich sequences in the 3' untranslated regions. In order to examine whether the AU-specific endoribonuclease V (EC 3.1.27.8) described previously by us transinactivates those mRNA species, we introduced a 51-nucleotide ATTTA sequence from tumor necrosis factor into the 3' untranslated region of beta-globin gene. Transcripts of that construct, synthesized in vitro, were prone to endoribonuclease V digestion at those AU-rich sequences. Stimulation of human macrophages with lipopolysaccharide resulted in a shift of the association state of the enzyme from the nuclear matrix-associated to the free form. This shift was strongly prevented by the hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) and more weakly by hepatitis B nucleocapsid antigen and hepatitis B antigen of the X region. HBsAg and, to a lesser extent, hepatitis B nucleocapsid antigen and hepatitis B antigen of the X region inhibited the release of alpha interferon, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor, while it had no effect on interleukin-1 production from stimulated macrophages. Using the human hepatoma cell line PLC/PRF/5, we provide further experimental evidence that endoribonuclease V acts in trans as a posttranscriptional inactivator for nuclear matrix-associated cytokine transcripts. These results suggest that those cytokine transcripts which contain reiterated (overlapping) AUUUA sequences are degraded by nuclear matrix-associated endoribonuclease V. This degradation was comparably high in cells incubated with HBsAg or cells which produced this antigen.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander J. J., Bey E. M., Geddes E. W., Lecatsas G. Establishment of a continuously growing cell line from primary carcinoma of the liver. S Afr Med J. 1976 Dec 18;50(54):2124–2128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander M. C., Lomanto M., Nasrin N., Ramaika C. Insulin stimulates glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene expression through cis-acting DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5092–5096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auron P. E., Webb A. C., Rosenwasser L. J., Mucci S. F., Rich A., Wolff S. M., Dinarello C. A. Nucleotide sequence of human monocyte interleukin 1 precursor cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7907–7911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bate C. A., Taverne J., Playfair J. H. Malarial parasites induce TNF production by macrophages. Immunology. 1988 Jun;64(2):227–231. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Potter V. R. Nuclei from rat liver: isolation method that combines purity with high yield. Science. 1966 Dec 30;154(3757):1662–1665. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3757.1662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caput D., Beutler B., Hartog K., Thayer R., Brown-Shimer S., Cerami A. Identification of a common nucleotide sequence in the 3'-untranslated region of mRNA molecules specifying inflammatory mediators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1670–1674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citron B., Falck-Pedersen E., Salditt-Georgieff M., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcription termination occurs within a 1000 base pair region downstream from the poly(A) site of the mouse beta-globin (major) gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8723–8731. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efrat S., Kaempfer R. Control of biologically active interleukin 2 messenger RNA formation in induced human lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2601–2605. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feitelson M. A., Marion P. L., Robinson W. S. Core particles of hepatitis B virus and ground squirrel hepatitis virus. I. Relationship between hepatitis B core antigen- and ground squirrel hepatitis core antigen-associated polypeptides by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and tryptic peptide mapping. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):687–696. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.687-696.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallati H., Pracht I., Schmidt J., Häring P., Garotta G. A simple, rapid and large capacity ELISA for biologically active native and recombinant human IFN gamma. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 1987 Jul-Sep;1(3):109–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber M. A., Thung S. N. Molecular and cellular pathology of hepatitis B. Lab Invest. 1985 Jun;52(6):572–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Goeddel D. V. Structure of the human immune interferon gene. Nature. 1982 Aug 26;298(5877):859–863. doi: 10.1038/298859a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Chua A. O., Stern A. S., Hellmann C. P., Vitek M. P., DeChiara T. M., Benjamin W. R., Collier K. J., Dukovich M., Familletti P. C. Recombinant human interleukin 1 alpha: purification and biological characterization. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2492–2497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henco K., Brosius J., Fujisawa A., Fujisawa J. I., Haynes J. R., Hochstadt J., Kovacic T., Pasek M., Schamböck A., Schmid J. Structural relationship of human interferon alpha genes and pseudogenes. J Mol Biol. 1985 Sep 20;185(2):227–260. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90401-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess G., Weber C., Rossol S., Voth R., Drees N., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H. Behandlung der Hepatitis-B-Surface-Antigen(HBsAg)-positiven chronischen Hepatitis mit rekombinantem alpha-A-Interferon. Ergebnisse einer Phase-II-Studie. Z Gastroenterol. 1988 Jul;26(7):380–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakumu S., Tahara H., Fuji A., Yoshioka K. Interleukin 1 alpha production by peripheral blood monocytes from patients with chronic liver disease and effect of sera on interleukin 1 alpha production. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1988 Jul;26(3):113–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H., Gibson W., Shaper J. H. Characterization of the major polypeptides of the rat liver nuclear envelope. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2710–2719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacNab G. M., Alexander J. J., Lecatsas G., Bey E. M., Urbanowicz J. M. Hepatitis B surface antigen produced by a human hepatoma cell line. Br J Cancer. 1976 Nov;34(5):509–515. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1976.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D. The granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factors. Science. 1985 Jul 5;229(4708):16–22. doi: 10.1126/science.2990035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K. B., Faloona F. A. Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro via a polymerase-catalyzed chain reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:335–350. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. E. Endoribonuclease IV. A poly(A)-specific ribonuclease from chick oviduct. 1. Purification of the enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Nov 1;70(1):241–248. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10975.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naito K., Inaba K., Hirayama Y., Inaba-Miyama M., Sudo T., Muramatsu S. Macrophage factors which enhance the mixed leukocyte reaction initiated by dendritic cells. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 15;142(6):1834–1839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedwin G. E., Naylor S. L., Sakaguchi A. Y., Smith D., Jarrett-Nedwin J., Pennica D., Goeddel D. V., Gray P. W. Human lymphotoxin and tumor necrosis factor genes: structure, homology and chromosomal localization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 11;13(17):6361–6373. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.17.6361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawelec G., Schaudt K., Rehbein A., Busch F. W. Differential secretion of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factors but not interferon-gamma from CD4+ compared to CD8+ human T cell clones. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Jan;19(1):197–200. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson D. L. Isolation and characterization of the major protein and glycoprotein of hepatitis B surface antigen. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6975–6983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson D. L., Nath N., Gavilanes F. Structure of hepatitis B surface antigen. Correlation of subtype with amino acid sequence and location of the carbohydrate moiety. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10414–10420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossol S., Voth R., Laubenstein H. P., Müller W. E., Schröder H. C., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H., Hess G. Interferon production in patients infected with HIV-1. J Infect Dis. 1989 May;159(5):815–821. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.5.815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Bugawan T. L., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Analysis of enzymatically amplified beta-globin and HLA-DQ alpha DNA with allele-specific oligonucleotide probes. Nature. 1986 Nov 13;324(6093):163–166. doi: 10.1038/324163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saksela E., Virtanen I., Hovi T., Secher D. S., Cantell K. Monocyte is the main producer of human leukocyte alpha interferons following Sendai virus induction. Prog Med Virol. 1984;30:78–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder H. C., Dose K., Zahn R. K., Müller W. E. Isolation and characterization of the novel polyadenylate- and polyuridylate-degrading acid endoribonuclease V from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5108–5112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder H. C., Trölltsch D., Friese U., Bachmann M., Müller W. E. Mature mRNA is selectively released from the nuclear matrix by an ATP/dATP-dependent mechanism sensitive to topoisomerase inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8917–8925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder H. C., Wenger R., Kuchino Y., Müller W. E. Modulation of nuclear matrix-associated 2',5'-oligoadenylate metabolism and ribonuclease L activity in H9 cells by human immunodeficiency virus. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5669–5673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder H. C., Zahn R. K., Dose K., Müller W. E. Purification and characterization of a poly(A)-specific exoribonuclease from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4535–4538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuler G. D., Cole M. D. GM-CSF and oncogene mRNA stabilities are independently regulated in trans in a mouse monocytic tumor. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1115–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90256-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sierakowska H., Shugar D. Mammalian nucleolytic enzymes. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1977;20:59–130. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60470-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannenbaum C. S., Major J., Poptic E., DiCorleto P. E., Hamilton T. A. Lipopolysaccharide-inducible macrophage early genes are induced in Balb/c 3T3 cells by platelet-derived growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):4052–4057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela P., Gray P., Quiroga M., Zaldivar J., Goodman H. M., Rutter W. J. Nucleotide sequence of the gene coding for the major protein of hepatitis B virus surface antigen. Nature. 1979 Aug 30;280(5725):815–819. doi: 10.1038/280815a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T., Treisman R. Removal of poly(A) and consequent degradation of c-fos mRNA facilitated by 3' AU-rich sequences. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):396–399. doi: 10.1038/336396a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita Y., Koike K., Takaoki M., Matsuda S. Suppression of HBsAg production in PLC/PRF/5 human hepatoma cell line by interferons. Microbiol Immunol. 1988;32(11):1119–1126. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1988.tb01476.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]