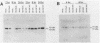Abstract
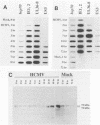
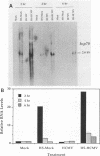
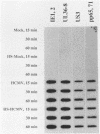
Expression of the cellular heat shock protein 70 gene (hsp70) is transiently induced by human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infection of permissive human diploid fibroblasts. Induction of the cellular heat shock response during critical times of infection had previously been reported to alter the growth of HCMV in vitro. Thus, a potential interaction between heat shock proteins and HCMV expression was indicated. HCMV dramatically increased expression of hsp70 RNA within 8 h of infection. hsp70 RNA remained elevated at 24 and 48 h postinfection and decreased to low levels of 72 h postinfection. Induction of HSP70 protein occurred more slowly; inducible HSP70 protein encoded by this RNA increased within 16 h postinfection and continued to increase throughout infection until 72 h postinfection, when the highest abundance of inducible HSP70 protein was observed. Cells that received both heat (43 degrees C for 70 min) treatment and HCMV infection expressed hsp70 RNA to levels above the sum of levels present in cells given either treatment alone. Furthermore, hsp70 RNA induction occurred earlier and remained elevated longer than in cells infected with HCMV alone or in cells treated with heat alone, respectively. Nevertheless, the pattern of HCMV immediate-early transcript expression at 2, 4, and 6 h postinfection appeared to be unchanged by this prior heat treatment. Our results suggest that heat shock treatment and HCMV infection can act additively in stimulating hsp70 RNA expression. The previously reported stimulation of HCMV growth in vitro following the heat shock response apparently does not result from alterations in the steady-state expression of HCMV immediate-early transcripts.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berk A. J. Adenovirus promoters and E1A transactivation. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:45–79. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.000401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdon R. H. Heat shock and the heat shock proteins. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 1;240(2):313–324. doi: 10.1042/bj2400313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirico W. J., Waters M. G., Blobel G. 70K heat shock related proteins stimulate protein translocation into microsomes. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):805–810. doi: 10.1038/332805a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua C. C., Carter T. H., St Jeor S. Transcription of the human cytomegalovirus genome in productively infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1981 Sep;56(Pt 1):1–11. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-56-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colberg-Poley A. M., Santomenna L. D. Selective induction of chromosomal gene expression by human cytomegalovirus. Virology. 1988 Sep;166(1):217–228. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90163-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A. The heat shock response. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1985;18(3):239–280. doi: 10.3109/10409238509085135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMarchi J. M. Post-transcriptional control of human cytomegalovirus gene expression. Virology. 1983 Jan 30;124(2):390–402. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90355-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depto A. S., Stenberg R. M. Regulated expression of the human cytomegalovirus pp65 gene: octamer sequence in the promoter is required for activation by viral gene products. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1232–1238. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1232-1238.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshaies R. J., Koch B. D., Werner-Washburne M., Craig E. A., Schekman R. A subfamily of stress proteins facilitates translocation of secretory and mitochondrial precursor polypeptides. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):800–805. doi: 10.1038/332800a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geballe A. P., Leach F. S., Mocarski E. S. Regulation of cytomegalovirus late gene expression: gamma genes are controlled by posttranscriptional events. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):864–874. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.864-874.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geballe A. P., Mocarski E. S. Translational control of cytomegalovirus gene expression is mediated by upstream AUG codons. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3334–3340. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3334-3340.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geelen J. L., Boom R., Klaver G. P., Minnaar R. P., Feltkamp M. C., van Milligen F. J., Sol C. J., van der Noordaa J. Transcriptional activation of the major immediate early transcription unit of human cytomegalovirus by heat-shock, arsenite and protein synthesis inhibitors. J Gen Virol. 1987 Nov;68(Pt 11):2925–2931. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-11-2925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goins W. F., Stinski M. F. Expression of a human cytomegalovirus late gene is posttranscriptionally regulated by a 3'-end-processing event occurring exclusively late after infection. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4202–4213. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Gies D., McCray G., Huang M. The human cytomegalovirus major immediate early promoter can be trans-activated by adenovirus early proteins. Virology. 1989 Aug;171(2):377–385. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90605-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Ponte P., Okayama H., Engel J., Blau H., Kedes L. Isolation and characterization of full-length cDNA clones for human alpha-, beta-, and gamma-actin mRNAs: skeletal but not cytoplasmic actins have an amino-terminal cysteine that is subsequently removed. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):787–795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermiston T. W., Malone C. L., Witte P. R., Stinski M. F. Identification and characterization of the human cytomegalovirus immediate-early region 2 gene that stimulates gene expression from an inducible promoter. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3214–3221. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3214-3221.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt C., Morimoto R. I. Conserved features of eukaryotic hsp70 genes revealed by comparison with the nucleotide sequence of human hsp70. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6455–6459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. N., Kucey B. L. Competitive inhibition of hsp70 gene expression causes thermosensitivity. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1551–1554. doi: 10.1126/science.3201244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahana C., Nathans D. Isolation of cloned cDNA encoding mammalian ornithine decarboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3645–3649. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao H. T., Nevins J. R. Transcriptional activation and subsequent control of the human heat shock gene during adenovirus infection. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;3(11):2058–2065. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.11.2058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay R. J., Russnak R. H., Jones D., Mathias C., Candido E. P. Expression of intron-containing C. elegans heat shock genes in mouse cells demonstrates divergence of 3' splice site recognition sequences between nematodes and vertebrates, and an inhibitory effect of heat shock on the mammalian splicing apparatus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 11;15(9):3723–3741. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.9.3723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khandjian E. W., Türler H. Simian virus 40 and polyoma virus induce synthesis of heat shock proteins in permissive cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;3(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouzarides T., Bankier A. T., Satchwell S. C., Preddy E., Barrell B. G. An immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus encodes a potential membrane glycoprotein. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):151–164. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90668-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Thangue N. B., Latchman D. S. A cellular protein related to heat-shock protein 90 accumulates during herpes simplex virus infection and is overexpressed in transformed cells. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Sep;178(1):169–179. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90388-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaThangue N. B., Latchman D. S. Nuclear accumulation of a heat-shock 70-like protein during herpes simplex virus replication. Biosci Rep. 1987 Jun;7(6):475–483. doi: 10.1007/BF01116504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liberek K., Georgopoulos C., Zylicz M. Role of the Escherichia coli DnaK and DnaJ heat shock proteins in the initiation of bacteriophage lambda DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6632–6636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S., Craig E. A. The heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:631–677. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milarski K. L., Morimoto R. I. Expression of human HSP70 during the synthetic phase of the cell cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9517–9521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizzen L. A., Welch W. J. Characterization of the thermotolerant cell. I. Effects on protein synthesis activity and the regulation of heat-shock protein 70 expression. J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;106(4):1105–1116. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.4.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M., Schaack J., Baim S. B., Morimoto R. I., Shenk T. Induced heat shock mRNAs escape the nucleocytoplasmic transport block in adenovirus-infected HeLa cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4505–4512. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Induction of the synthesis of a 70,000 dalton mammalian heat shock protein by the adenovirus E1A gene product. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):913–919. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90453-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notarianni E. L., Preston C. M. Activation of cellular stress protein genes by herpes simplex virus temperature-sensitive mutants which overproduce immediate early polypeptides. Virology. 1982 Nov;123(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90299-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Speculations on the functions of the major heat shock and glucose-regulated proteins. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):959–961. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90693-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riabowol K. T., Mizzen L. A., Welch W. J. Heat shock is lethal to fibroblasts microinjected with antibodies against hsp70. Science. 1988 Oct 21;242(4877):433–436. doi: 10.1126/science.3175665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüger B., Klages S., Walla B., Albrecht J., Fleckenstein B., Tomlinson P., Barrell B. Primary structure and transcription of the genes coding for the two virion phosphoproteins pp65 and pp71 of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):446–453. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.446-453.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer-Nielsen C., Svendsen P. J., Rose C. Separation of macromolecules in isotachophoresis systems involving single or multiple counterions. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1980 Aug;3(2):97–128. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(80)90032-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. C., Fisch T. M., Benecke B. J., Nevins J. R., Heintz N. Definition of multiple, functionally distinct TATA elements, one of which is a target in the hsp70 promoter for E1A regulation. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):723–729. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90410-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Pelham H. R. Yeast heat shock factor is an essential DNA-binding protein that exhibits temperature-dependent phosphorylation. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):855–864. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. J., Tevethia M. J. Identification of a human cytomegalovirus virus DNA segment that complements an adenovirus 5 immediate early mutant. Virology. 1986 Jun;151(2):329–338. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90053-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus D. B., Walter W. A., Gross C. A. Escherichia coli heat shock gene mutants are defective in proteolysis. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1851–1858. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tevethia M. J., Spector D. J., Leisure K. M., Stinski M. F. Participation of two human cytomegalovirus immediate early gene regions in transcriptional activation of adenovirus promoters. Virology. 1987 Dec;161(2):276–285. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90119-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theodorakis N. G., Morimoto R. I. Posttranscriptional regulation of hsp70 expression in human cells: effects of heat shock, inhibition of protein synthesis, and adenovirus infection on translation and mRNA stability. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4357–4368. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathen M. W., Stinski M. F. Temporal patterns of human cytomegalovirus transcription: mapping the viral RNAs synthesized at immediate early, early, and late times after infection. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):462–477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.462-477.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston K. An enhancer element in the short unique region of human cytomegalovirus regulates the production of a group of abundant immediate early transcripts. Virology. 1988 Feb;162(2):406–416. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90481-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. T., McClanahan T. K., Morimoto R. I. E1a transactivation of the human HSP70 promoter is mediated through the basal transcriptional complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2574–2587. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu B. J., Hurst H. C., Jones N. C., Morimoto R. I. The E1A 13S product of adenovirus 5 activates transcription of the cellular human HSP70 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2994–2999. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu B. J., Kingston R. E., Morimoto R. I. Human HSP70 promoter contains at least two distinct regulatory domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):629–633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu B. J., Morimoto R. I. Transcription of the human hsp70 gene is induced by serum stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6070–6074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu B., Hunt C., Morimoto R. Structure and expression of the human gene encoding major heat shock protein HSP70. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):330–341. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yost H. J., Lindquist S. Translation of unspliced transcripts after heat shock. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1544–1548. doi: 10.1126/science.3201243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerbini M., Musiani M., La Placa M. Stimulating effect of heat shock on the early stage of human cytomegalovirus replication cycle. Virus Res. 1986 Dec;6(3):211–216. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(86)90070-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]