Abstract
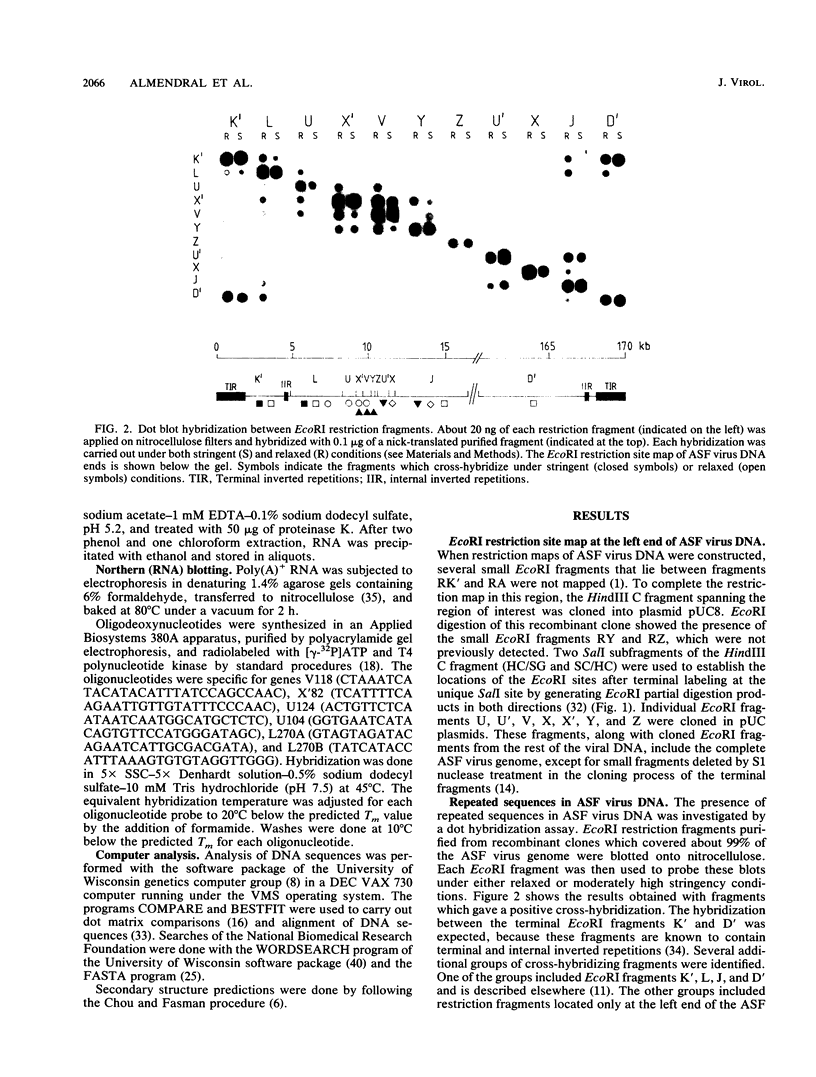
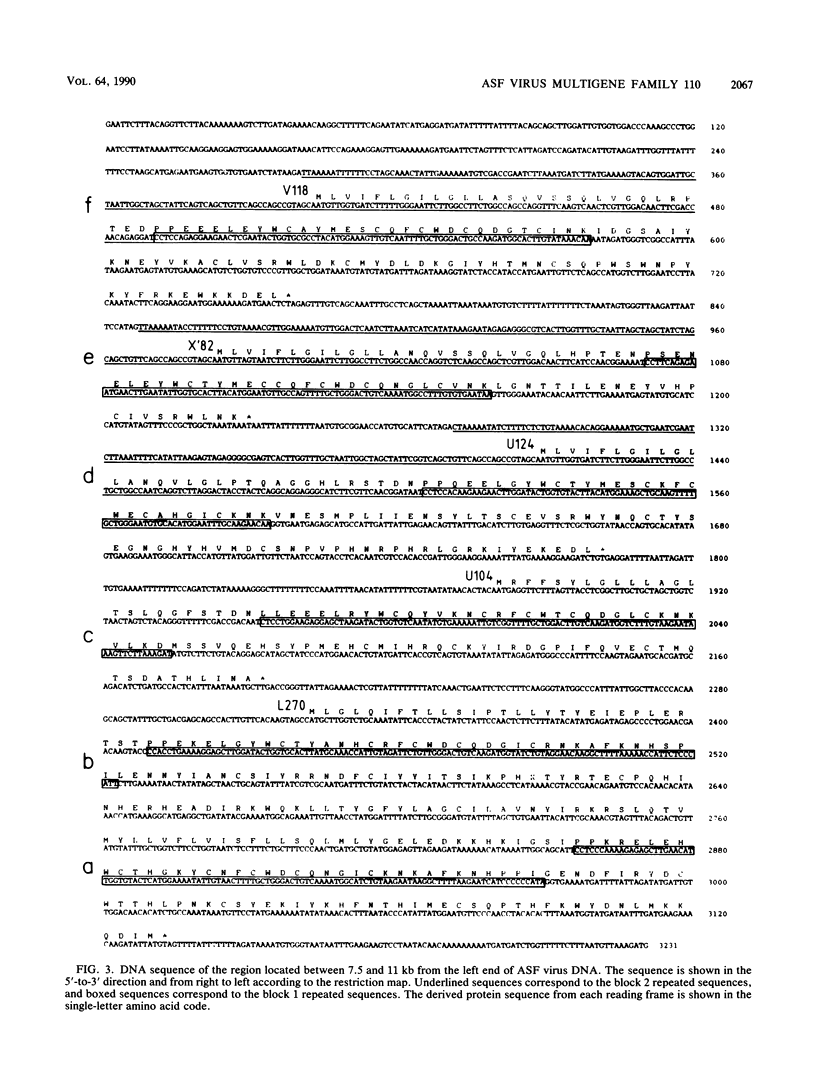
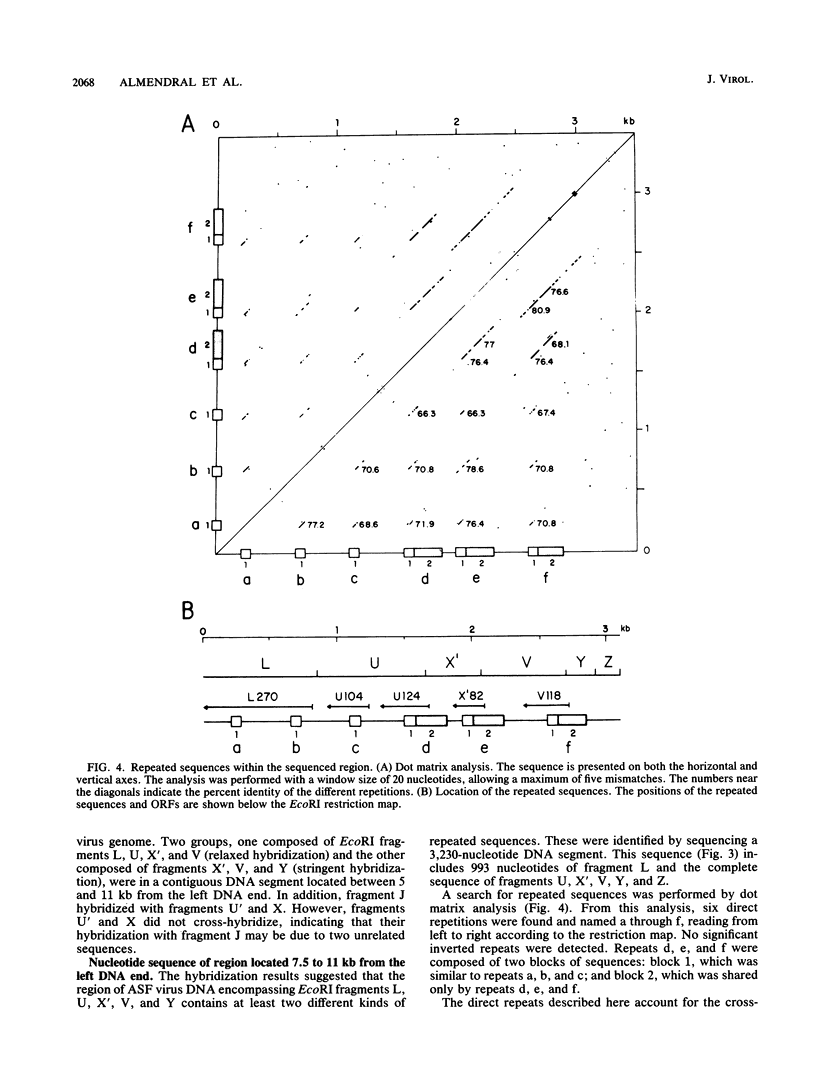
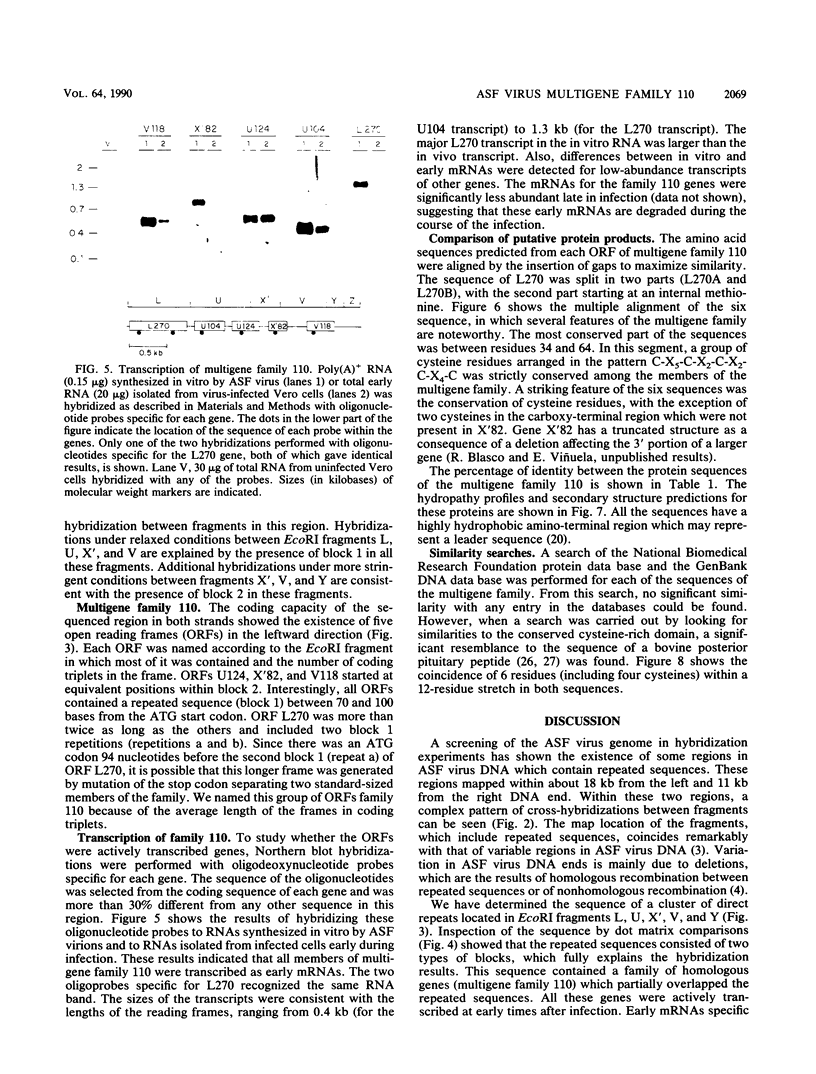
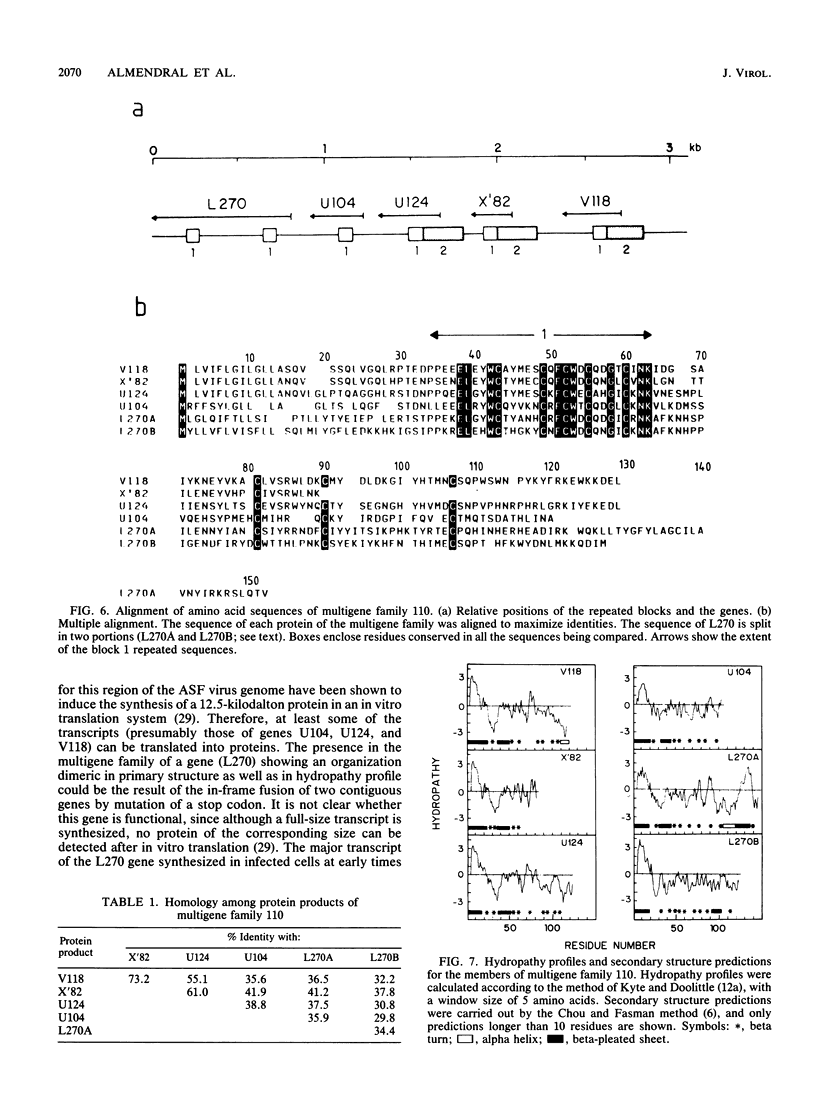
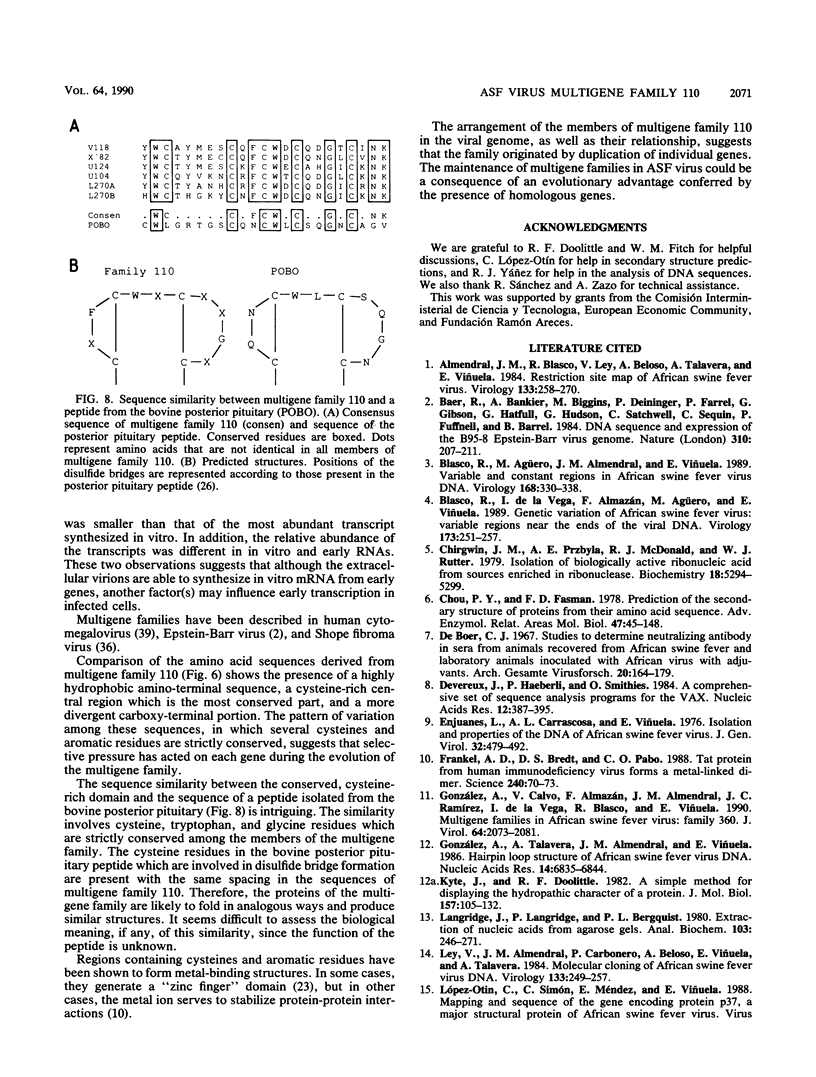
The genome of African swine fever virus was screened for the existence of repetitive sequences by hybridization between different cloned restriction fragments covering the viral DNA. Several sets of repeated sequences were detected in fragments located close to the DNA ends. One of these groups of repetitions involved fragments located at both ends of the genome. The remaining groups involved fragments that were located exclusively at the left end. The sequence of a 3.2-kilobase segment spanning from 7.5 to 11 kilobases from the left DNA end, which showed a complex pattern of cross-hybridizations, was determined. Two short and three long blocks of direct repeated sequences were found in this DNA region, which accounted for the hybridization results. The repeated sequences formed a family of five homologous genes with an average length of 116 codons (multigene family 110), one of which had a dimeric structure. Transcripts of the five members of the family were detected both in RNA synthesized in vitro by purified African swine fever virions and in RNA isolated at early times after infection. Comparison of the predicted protein sequences revealed a striking conservation of a cysteine-rich domain in the central part of the proteins. In addition, a highly hydrophobic NH2-terminal sequence present in all the proteins suggests that these proteins are processed through the endoplasmic reticulum.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almendral J. M., Blasco R., Ley V., Beloso A., Talavera A., Viñuela E. Restriction site map of African swine fever virus DNA. Virology. 1984 Mar;133(2):258–270. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90393-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasco R., Agüero M., Almendral J. M., Viñuela E. Variable and constant regions in African swine fever virus DNA. Virology. 1989 Feb;168(2):330–338. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90273-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasco R., de la Vega I., Almazán F., Agüero M., Viñuela E. Genetic variation of African swine fever virus: variable regions near the ends of the viral DNA. Virology. 1989 Nov;173(1):251–257. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90241-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Boer C. J. Studies to determine neutralizing antibody in sera from animals recovered from African swine fever and laboratory animals inoculated with African virus with adjuvants. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1967;20(2):164–179. doi: 10.1007/BF01241270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enjuanes L., Carrascosa A. L., Viñuela E. Isolation and properties of the DNA of African swine fever (ASF) virus. J Gen Virol. 1976 Sep;32(3):479–492. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-32-3-479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A. D., Bredt D. S., Pabo C. O. Tat protein from human immunodeficiency virus forms a metal-linked dimer. Science. 1988 Apr 1;240(4848):70–73. doi: 10.1126/science.2832944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González A., Calvo V., Almazán F., Almendral J. M., Ramírez J. C., de la Vega I., Blasco R., Viñuela E. Multigene families in African swine fever virus: family 360. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2073–2081. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2073-2081.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González A., Talavera A., Almendral J. M., Viñuela E. Hairpin loop structure of African swine fever virus DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):6835–6844. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.17.6835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langridge J., Langridge P., Bergquist P. L. Extraction of nucleic acids from agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Apr;103(2):264–271. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90266-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ley V., Almendral J. M., Carbonero P., Beloso A., Viñuela E., Talavera A. Molecular cloning of African swine fever virus DNA. Virology. 1984 Mar;133(2):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90392-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALMQUIST W. A. Serologic and immunologic studies with African swine fever virus. Am J Vet Res. 1963 May;24:450–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maizel J. V., Jr, Lenk R. P. Enhanced graphic matrix analysis of nucleic acid and protein sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7665–7669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J. On the predictive recognition of signal peptide sequences. Virus Res. 1985 Oct;3(3):271–286. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(85)90051-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G. L., Connell T. D., Barritt D. S., Koomey M., Cannon J. G. Phase variation of gonococcal protein II: regulation of gene expression by slipped-strand mispairing of a repetitive DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):539–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90577-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preddie E. C., Saffran M. Isolation of a large polypeptide from bovine posterior pituitary powder. J Biol Chem. 1965 Nov;240(11):4189–4193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preddie E. C. Structure of a large polypeptide of bovine posterior pituitary tissue. J Biol Chem. 1965 Nov;240(11):4194–4203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salas M. L., Rey-Campos J., Almendral J. M., Talavera A., Viñuela E. Transcription and translation maps of African swine fever virus. Virology. 1986 Jul 15;152(1):228–240. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90387-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santarén J. F., Viñuela E. African swine fever virus-induced polypeptides in Vero cells. Virus Res. 1986 Sep;5(4):391–405. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(86)90031-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. A simple method for DNA restriction site mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. F., Waterman M. S. Identification of common molecular subsequences. J Mol Biol. 1981 Mar 25;147(1):195–197. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90087-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogo J. M., Almendral J. M., Talavera A., Viñuela E. Terminal and internal inverted repetitions in African swine fever virus DNA. Virology. 1984 Mar;133(2):271–275. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90394-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upton C., McFadden G. Tumorigenic poxviruses: analysis of viral DNA sequences implicated in the tumorigenicity of Shope fibroma virus and malignant rabbit virus. Virology. 1986 Jul 30;152(2):308–321. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90134-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viñuela E. African swine fever virus. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;116:151–170. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70280-8_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston K., Barrell B. G. Sequence of the short unique region, short repeats, and part of the long repeats of human cytomegalovirus. J Mol Biol. 1986 Nov 20;192(2):177–208. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90359-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilbur W. J., Lipman D. J. Rapid similarity searches of nucleic acid and protein data banks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):726–730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]