Abstract
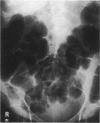
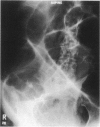
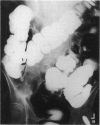
Nineteen patients presenting with pseudo-obstruction of the colon are described. Thirteen were female and the mean age was 65.7 years (48-82). Five cases appeared idiopathic but the remainder were associated with either intercurrent disease, surgery or trauma. Six patients underwent laparotomy, 3 for gross caecal distension and 1 subsequently died with bronchopneumonia. Thirteen patients were treated conservatively with flatus tube decompression or colonoscopy, but 3 died, 1 from a perforated caecum, 1 from a recurrent subarachnoid haemorrhage and 1 from bronchopneumonia. The high mortality of caecal perforation in this condition is stressed, and gross radiological caecal distension with overlying tenderness is an indication for urgent decompression.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Addison N. V. Pseudo-obstruction of the large bowel. J R Soc Med. 1983 Apr;76(4):252–255. doi: 10.1177/014107688307600403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachulis B. L., Smith P. E. Pseudoobstruction of the colon. Am J Surg. 1978 Jul;136(1):66–72. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(78)90202-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardsley D. Pseudo-obstruction of the large bowel. Br J Surg. 1974 Dec;61(12):963–969. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800611210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUDLEY H. A., SINCLAIR I. S., McLAREN I. F., McNAIR T. J., NEWSAM J. E. Intestinal pseudo-obstruction. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 1958 Mar;3(3):206–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierson E. D., Storm F. K., Shaw W., Coyne S. K. Caecal rupture due to colonic ileus. Br J Surg. 1975 May;62(5):383–386. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800620514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOHL R. D., NIXON R. K. MYXEDEMA ILEUS. Arch Intern Med. 1965 Feb;115:145–150. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1965.03860140025006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack M. Caecal rupture in psychotic patients. Br Med J. 1974 Oct 12;4(5936):82–83. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5936.82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanni G., Garbini A., Luchetti P., Nanni G., Ronconi P., Castagneto M. Ogilvie's syndrome (acute colonic pseudo-obstruction): review of the literature (October 1948 to March 1980) and report of four additional cases. Dis Colon Rectum. 1982 Mar;25(2):157–166. doi: 10.1007/BF02553265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neely J., Catchpole B. Ileus: the restoration of alimentary-tract motility by pharmacological means. Br J Surg. 1971 Jan;58(1):21–28. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800580104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton L., Young D., Scribner R. Management of pseudo-obstruction of the colon. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1974 Apr;138(4):595–598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OGILVIE H. Large-intestine colic due to sympathetic deprivation; a new clinical syndrome. Br Med J. 1948 Oct 9;2(4579):671–673. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4579.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTHWELL-JACKSON R. L. IDIOPATHIC LARGE-BOWEL OBSTRUCTION. Br J Surg. 1963 Sep;50:797–800. doi: 10.1002/bjs.18005022606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens F. O. Syndrome of Intestinal Pseudo-obstruction. Br Med J. 1962 May 5;1(5287):1248–1238.2. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5287.1248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanebo H., Mathewson C., Conolly B. Pseudo-obstruction of the colon. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1971 Jul;133(1):44–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]