Abstract
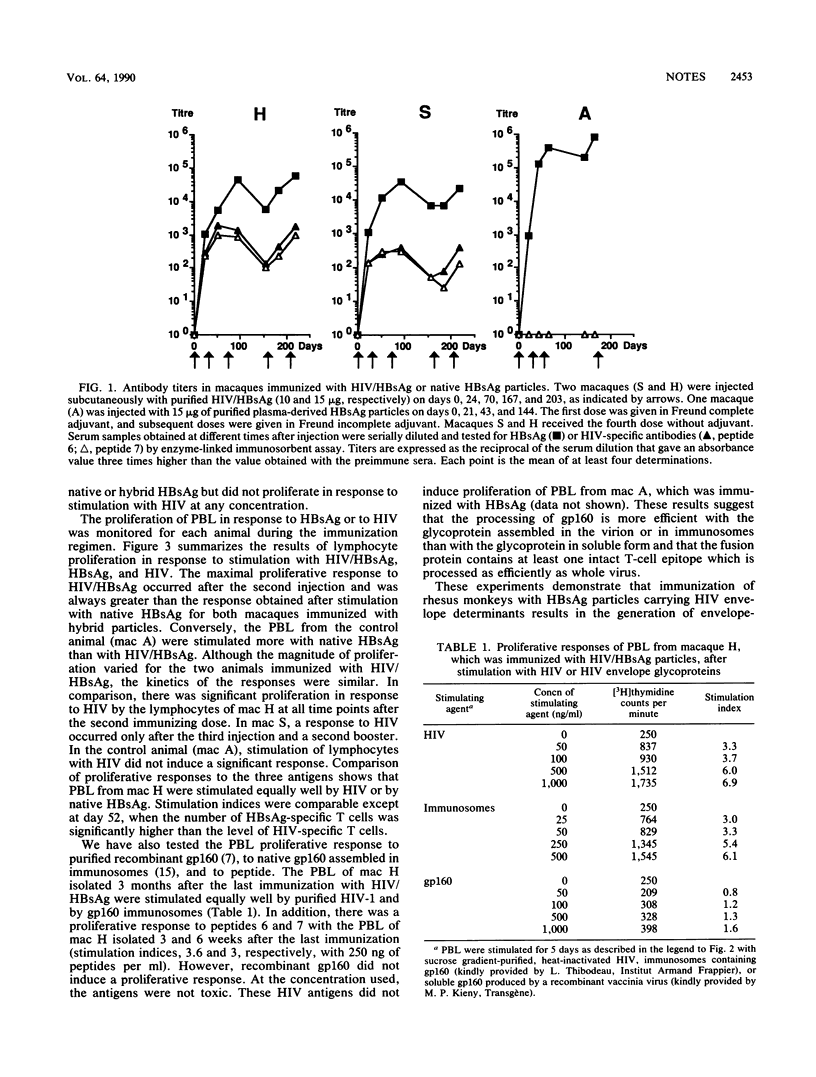
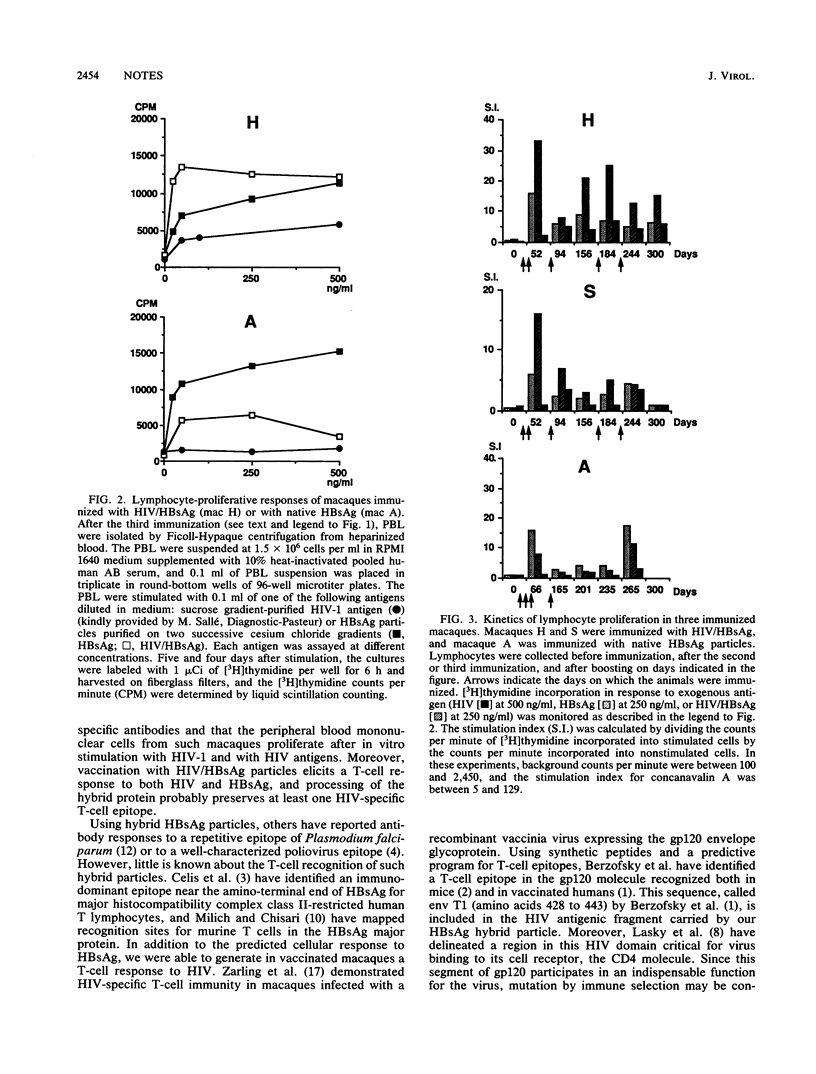
Recombinant human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)/hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) subviral particles of dual antigenicity and immunogenicity were obtained by fusing 84 amino acids of the HIV type 1 external envelope glycoprotein within the pre-S2 part of the hepatitis B middle protein (M.-L. Michel, M. Mancini, E. Sobczak, V. Favier, D. Guétard, E.-M. Bahraoui, and P. Tiollais, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85:7957-7961, 1988). We now describe the humoral and cellular immune response of rhesus monkeys immunized with these hybrid particles. Macaque antisera raised by subcutaneous injections of the HIV/HBsAg particles were shown to be specific for HIV in peptide-binding assays. Moreover, we were able to generate in these vaccinated animals a T-cell-proliferative response to both parts of the hybrid particle, i.e., HIV and HBsAg. These results establish the presence of a T-cell epitope in this HIV segment, which has been shown previously (L.A. Lasky, G. Nakamura, D. H. Smith, C. Fennie, C. Shimasaki, E. Patzer, P. Berman, T. Gregory, and D. J. Capon, Cell 50:975-985, 1987) to be an important domain involved in the binding of the virus to its cellular receptor, the CD4 molecule. This work demonstrates the feasibility of using the HBsAg subviral particle as a carrier protein for the presentation of foreign immunogenic epitopes to the immune system.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berzofsky J. A., Bensussan A., Cease K. B., Bourge J. F., Cheynier R., Lurhuma Z., Salaün J. J., Gallo R. C., Shearer G. M., Zagury D. Antigenic peptides recognized by T lymphocytes from AIDS viral envelope-immune humans. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):706–708. doi: 10.1038/334706a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cease K. B., Margalit H., Cornette J. L., Putney S. D., Robey W. G., Ouyang C., Streicher H. Z., Fischinger P. J., Gallo R. C., DeLisi C. Helper T-cell antigenic site identification in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome virus gp120 envelope protein and induction of immunity in mice to the native protein using a 16-residue synthetic peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4249–4253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celis E., Ou D., Otvos L., Jr Recognition of hepatitis B surface antigen by human T lymphocytes. Proliferative and cytotoxic responses to a major antigenic determinant defined by synthetic peptides. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 15;140(6):1808–1815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delpeyroux F., Chenciner N., Lim A., Malpièce Y., Blondel B., Crainic R., van der Werf S., Streeck R. E. A poliovirus neutralization epitope expressed on hybrid hepatitis B surface antigen particles. Science. 1986 Jul 25;233(4762):472–475. doi: 10.1126/science.2425433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desrosiers R. C. Simian immunodeficiency viruses. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:607–625. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.003135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichberg J. W., Zarling J. M., Alter H. J., Levy J. A., Berman P. W., Gregory T., Lasky L. A., McClure J., Cobb K. E., Moran P. A. T-cell responses to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and its recombinant antigens in HIV-infected chimpanzees. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3804–3808. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3804-3808.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasky L. A., Nakamura G., Smith D. H., Fennie C., Shimasaki C., Patzer E., Berman P., Gregory T., Capon D. J. Delineation of a region of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 glycoprotein critical for interaction with the CD4 receptor. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90524-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. L., Mancini M., Sobczak E., Favier V., Guetard D., Bahraoui E. M., Tiollais P. Induction of anti-human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) neutralizing antibodies in rabbits immunized with recombinant HIV--hepatitis B surface antigen particles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7957–7961. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier R. D., Gnann J. W., Jr, Landes R., Lockshin C., Richman D., McCutchan A., Kennedy C., Oldstone M. B., Nelson J. A. T cell recognition of HIV synthetic peptides in a natural infection. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 15;142(4):1166–1176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz O., Henin Y., Marechal V., Montagnier L. A rapid and simple colorimetric test for the study of anti-HIV agents. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1988 Dec;4(6):441–448. doi: 10.1089/aid.1988.4.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahren B., Morfeldt-Månsson L., Biberfeld G., Moberg L., Sönnerborg A., Ljungman P., Werner A., Kurth R., Gallo R., Bolognesi D. Characteristics of the specific cell-mediated immune response in human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):2017–2023. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.2017-2023.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarling J. M., Morton W., Moran P. A., McClure J., Kosowski S. G., Hu S. L. T-cell responses to human AIDS virus in macaques immunized with recombinant vaccinia viruses. 1986 Sep 25-Oct 1Nature. 323(6086):344–346. doi: 10.1038/323344a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


