Abstract
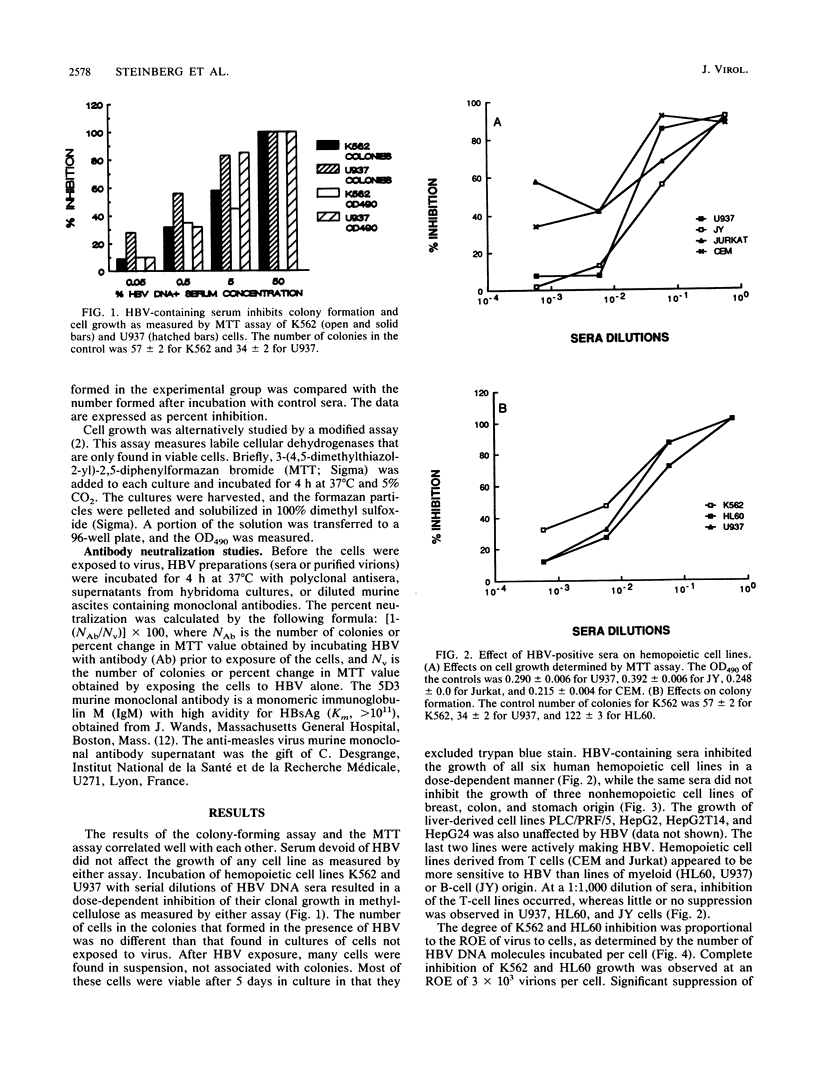
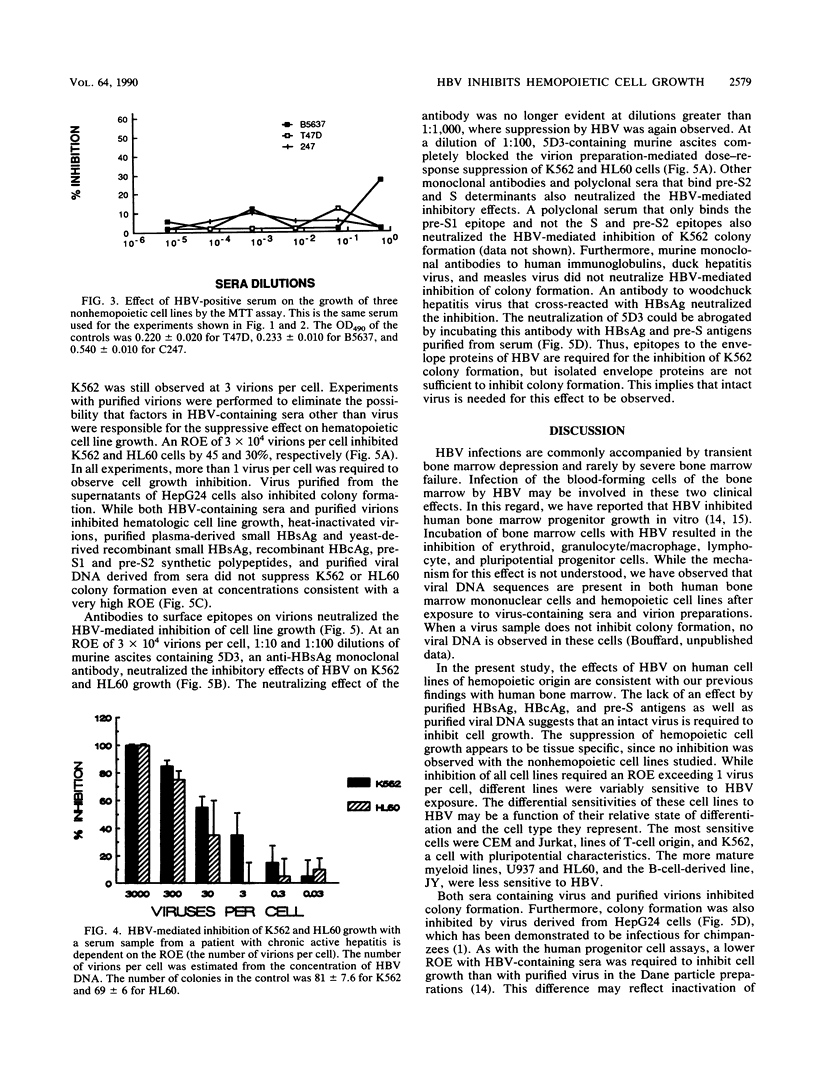
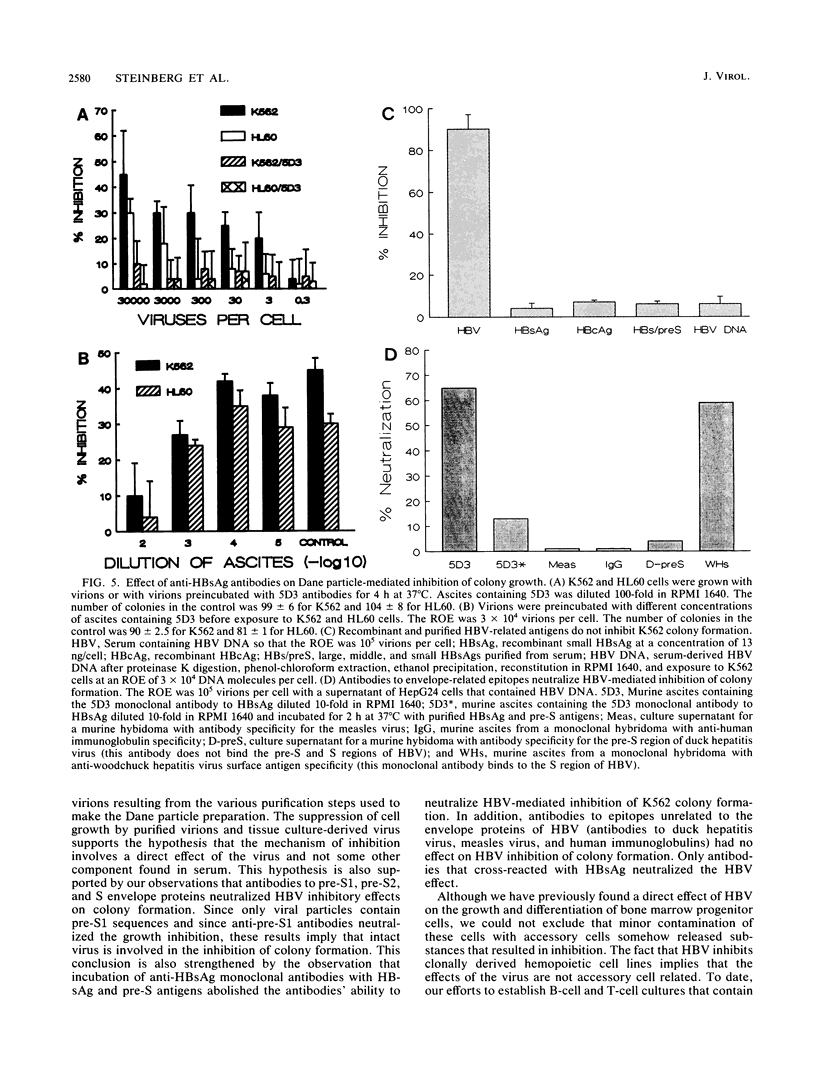
The effects of hepatitis B virus (HBV) on established human cell lines of various tissue origins were evaluated by clonal or colorimetric assays in methylcellulose culture. HBV exposure inhibited the growth of six hemopoietic cell lines, while similar incubation did not affect the growth of seven nonhemopoietic carcinoma cell lines of breast, colon, liver, and stomach origin. The inhibition of hemopoietic cell line colony formation was dependent on the presence of intact viral (Dane) particles and the ratio of exposure of virions to cells and was reversible with antibodies to pre-S1, pre-S2, and S envelope protein epitopes. Purified HBV DNA, surface antigen pre-S antigens, and core antigen did not inhibit cell line growth. These results further demonstrate the tropism of HBV for cells of hemopoietic origin, confirming our previous findings on the effects of HBV on the growth of normal bone marrow progenitor cells in vitro. Established human tissue culture cell lines may be used to study the interactions of hemopoietic cells with HBV.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acs G., Sells M. A., Purcell R. H., Price P., Engle R., Shapiro M., Popper H. Hepatitis B virus produced by transfected Hep G2 cells causes hepatitis in chimpanzees. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4641–4644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael J., DeGraff W. G., Gazdar A. F., Minna J. D., Mitchell J. B. Evaluation of a tetrazolium-based semiautomated colorimetric assay: assessment of chemosensitivity testing. Cancer Res. 1987 Feb 15;47(4):936–942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colucci G., Lyons P., Beazer Y., Waksal S. D. Production of hepatitis B virus-infected human B-cell hybridomas: transmission of the viral genome to normal lymphocytes in cocultures. Virology. 1988 May;164(1):238–244. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90641-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dejean A., Lugassy C., Zafrani S., Tiollais P., Brechot C. Detection of hepatitis B virus DNA in pancreas, kidney and skin of two human carriers of the virus. J Gen Virol. 1984 Mar;65(Pt 3):651–655. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-3-651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elfassi E., Romet-Lemonne J. L., Essex M., Frances-McLane M., Haseltine W. A. Evidence of extrachromosomal forms of hepatitis B viral DNA in a bone marrow culture obtained from a patient recently infected with hepatitis B virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3526–3528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gripon P., Diot C., Thézé N., Fourel I., Loreal O., Brechot C., Guguen-Guillouzo C. Hepatitis B virus infection of adult human hepatocytes cultured in the presence of dimethyl sulfoxide. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4136–4143. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4136-4143.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lie-Injo L. E., Balasegaram M., Lopez C. G., Herrera A. R. Hepatitis B virus DNA in liver and white blood cells of patients with hepatoma. DNA. 1983;2(4):301–308. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontisso P., Poon M. C., Tiollais P., Brechot C. Detection of hepatitis B virus DNA in mononuclear blood cells. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 May 26;288(6430):1563–1566. doi: 10.1136/bmj.288.6430.1563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romet-Lemonne J. L., McLane M. F., Elfassi E., Haseltine W. A., Azocar J., Essex M. Hepatitis B virus infection in cultured human lymphoblastoid cells. Science. 1983 Aug 12;221(4611):667–669. doi: 10.1126/science.6867736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sells M. A., Chen M. L., Acs G. Production of hepatitis B virus particles in Hep G2 cells transfected with cloned hepatitis B virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1005–1009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sureau C., Romet-Lemonne J. L., Mullins J. I., Essex M. Production of hepatitis B virus by a differentiated human hepatoma cell line after transfection with cloned circular HBV DNA. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):37–47. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90364-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wands J. R., Zurawski V. R., Jr High affinity monoclonal antibodies to hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) produced by somatic cell hybrids. Gastroenterology. 1981 Feb;80(2):225–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeldis J. B., Ben-Porath E., Enat R., Kirsch K., Wands J. Correlation of HBV DNA and monoclonal reactivity to HBsAg in serum of patients with HBV infection. J Virol Methods. 1986 Sep;14(2):153–166. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(86)90046-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeldis J. B., Farraye F. A., Steinberg H. N. In vitro hepatitis B virus suppression of erythropoiesis is dependent on the multiplicity of infection and is reversible with anti-HBs antibodies. Hepatology. 1988 Jul-Aug;8(4):755–759. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeldis J. B., Mugishima H., Steinberg H. N., Nir E., Gale R. P. In vitro hepatitis B virus infection of human bone marrow cells. J Clin Invest. 1986 Aug;78(2):411–417. doi: 10.1172/JCI112591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



