Abstract
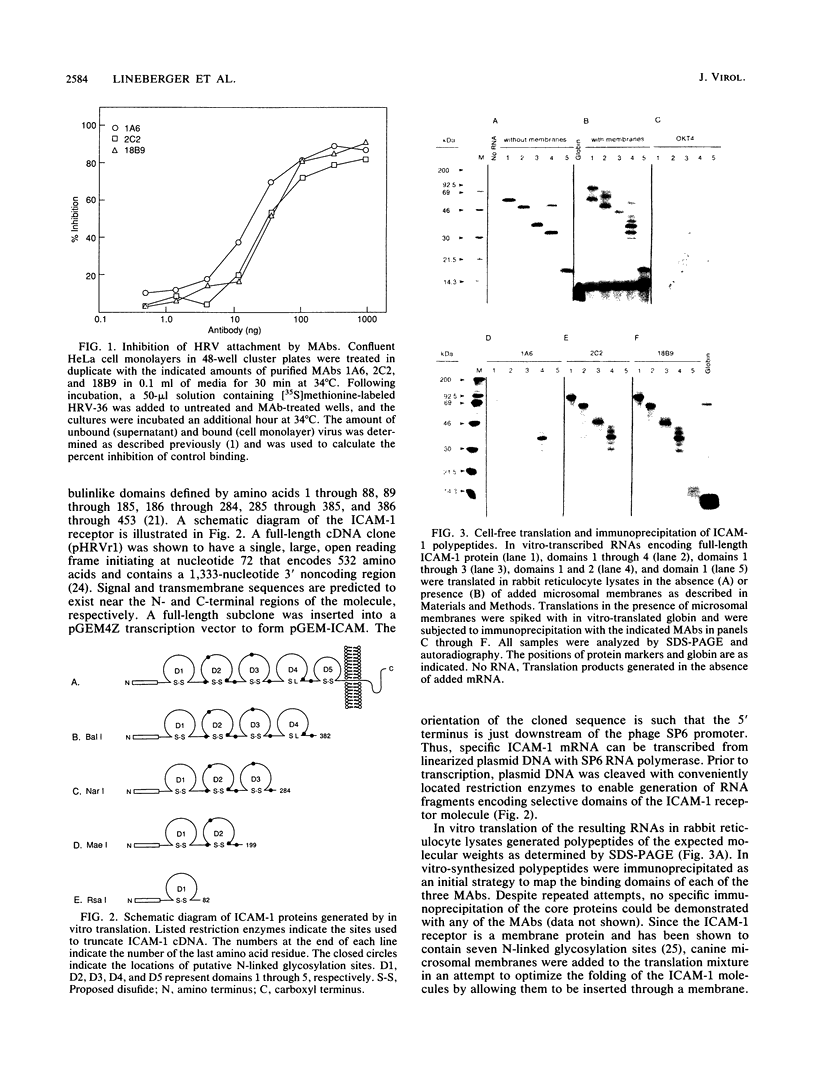
The vast majority of human rhinovirus serotypes utilize the intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) as the attachment site on susceptible cells. Twelve murine monoclonal antibodies were isolated and shown by competition binding studies to recognize three distinct, nonoverlapping epitopes on the ICAM-1 receptor. Titration of three antibodies representing each of the binding sites demonstrated that they were equally effective at blocking viral attachment. By using in vitro transcription and translation systems, a series of progressive C-terminal truncations of ICAM-1 molecules was generated. Immunoprecipitation of these fragments with each of the three antibodies indicated that all three epitopes reside within the first 82 amino acids of the receptor. Attempts to demonstrate specific binding of these in vitro-synthesized receptor fragments to virions were unsuccessful. The inability to show virion binding was most likely due to a failure of the lysates to properly glycosylate the receptor molecule, since native, unglycosylated receptor molecules isolated from cell membranes were also inactive in virus binding assays.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham G., Colonno R. J. Many rhinovirus serotypes share the same cellular receptor. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):340–345. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.340-345.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger E. A., Fuerst T. R., Moss B. A soluble recombinant polypeptide comprising the amino-terminal half of the extracellular region of the CD4 molecule contains an active binding site for human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2357–2361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonno R. J., Callahan P. L., Long W. J. Isolation of a monoclonal antibody that blocks attachment of the major group of human rhinoviruses. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):7–12. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.7-12.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonno R. J. Cell surface receptors for picornaviruses. Bioessays. 1986 Dec;5(6):270–274. doi: 10.1002/bies.950050609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonno R. J., Condra J. H., Mizutani S., Callahan P. L., Davies M. E., Murcko M. A. Evidence for the direct involvement of the rhinovirus canyon in receptor binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5449–5453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dustin M. L., Staunton D. E., Springer T. A. Supergene families meet in the immune system. Immunol Today. 1988 Jul-Aug;9(7-8):213–215. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91216-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman B. M., Blobel G. In vitro biosynthesis, core glycosylation, and membrane integration of opsin. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jul;90(1):236–242. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.1.236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greve J. M., Davis G., Meyer A. M., Forte C. P., Yost S. C., Marlor C. W., Kamarck M. E., McClelland A. The major human rhinovirus receptor is ICAM-1. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):839–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90688-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayden F. G., Gwaltney J. M., Jr, Colonno R. J. Modification of experimental rhinovirus colds by receptor blockade. Antiviral Res. 1988 Jul;9(4):233–247. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(88)90055-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameson B. A., Rao P. E., Kong L. I., Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M., Hood L. E., Kent S. B. Location and chemical synthesis of a binding site for HIV-1 on the CD4 protein. Science. 1988 Jun 3;240(4857):1335–1339. doi: 10.1126/science.2453925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landau N. R., Warton M., Littman D. R. The envelope glycoprotein of the human immunodeficiency virus binds to the immunoglobulin-like domain of CD4. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):159–162. doi: 10.1038/334159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makgoba M. W., Sanders M. E., Ginther Luce G. E., Gugel E. A., Dustin M. L., Springer T. A., Shaw S. Functional evidence that intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) is a ligand for LFA-1-dependent adhesion in T cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Apr;18(4):637–640. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn C. L., Wimmer E., Racaniello V. R. Cellular receptor for poliovirus: molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of a new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):855–865. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90690-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson A., Seed B. Genetic analysis of monoclonal antibody and HIV binding sites on the human lymphocyte antigen CD4. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):65–72. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90180-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G., Palmenberg A. C. Conservation of the putative receptor attachment site in picornaviruses. Virology. 1988 Jun;164(2):373–382. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90550-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheele G., Jacoby R. Conformational changes associated with proteolytic processing of presecretory proteins allow glutathione-catalyzed formation of native disulfide bonds. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12277–12282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D., Makgoba M. W., Seed B. ICAM, an adhesion ligand of LFA-1, is homologous to the neural cell adhesion molecule NCAM. Nature. 1988 Feb 18;331(6157):624–627. doi: 10.1038/331624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staunton D. E., Marlin S. D., Stratowa C., Dustin M. L., Springer T. A. Primary structure of ICAM-1 demonstrates interaction between members of the immunoglobulin and integrin supergene families. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):925–933. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90434-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staunton D. E., Merluzzi V. J., Rothlein R., Barton R., Marlin S. D., Springer T. A. A cell adhesion molecule, ICAM-1, is the major surface receptor for rhinoviruses. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):849–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90689-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomassini J. E., Colonno R. J. Isolation of a receptor protein involved in attachment of human rhinoviruses. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):290–295. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.290-295.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomassini J. E., Graham D., DeWitt C. M., Lineberger D. W., Rodkey J. A., Colonno R. J. cDNA cloning reveals that the major group rhinovirus receptor on HeLa cells is intercellular adhesion molecule 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4907–4911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomassini J. E., Maxson T. R., Colonno R. J. Biochemical characterization of a glycoprotein required for rhinovirus attachment. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1656–1662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]