Abstract
Thirty four neonates presented with acute duodenal obstruction due to malrotation during a 9 year period between 1973 and the end of 1981. Of these, 20 patients (58.8%) presented in the first week of life, and 24 (70.5%) had an associated midgut volvulus. This frequent association is stressed as bowel necrosis occurs very rapidly. Massive gangrene of small bowel was present in 5 patients, extensive resection was necessary in 3 patients, of whom 2 died postoperatively (5.8%). Five patients required reoperation and 10 had additional G.I. malformations (29.4%).
Full text
PDF
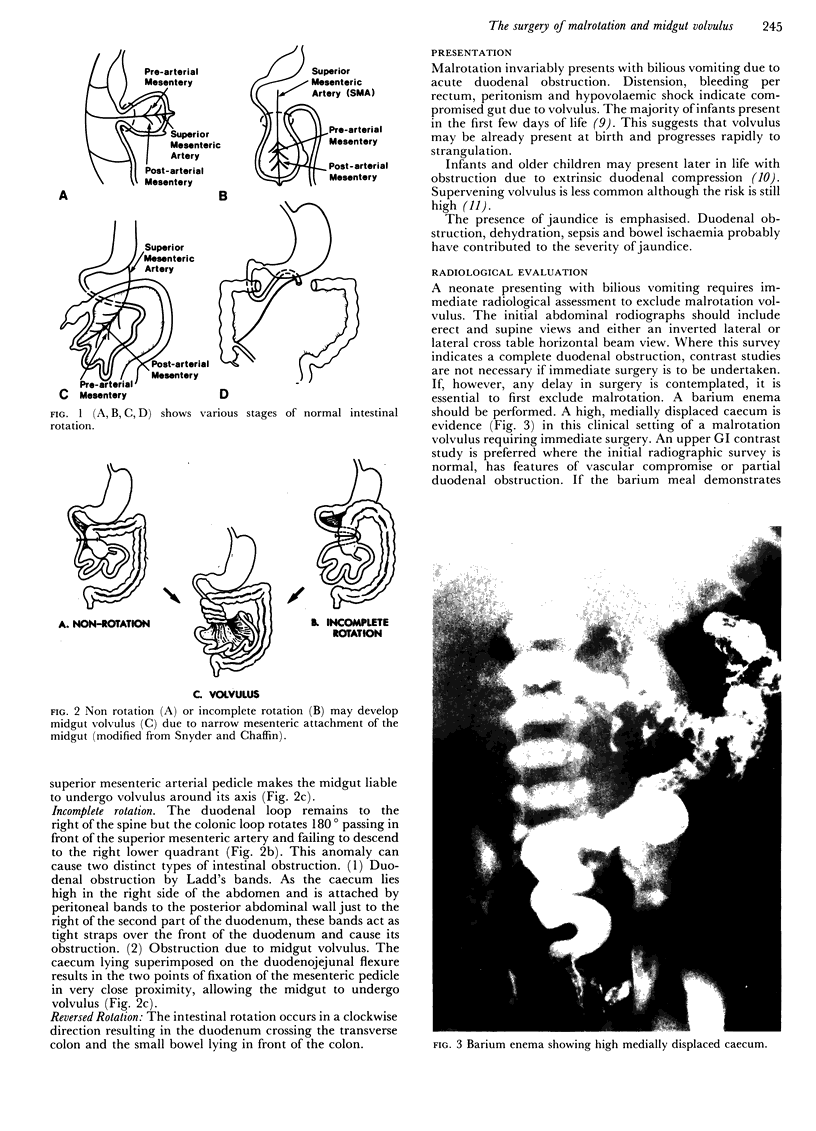
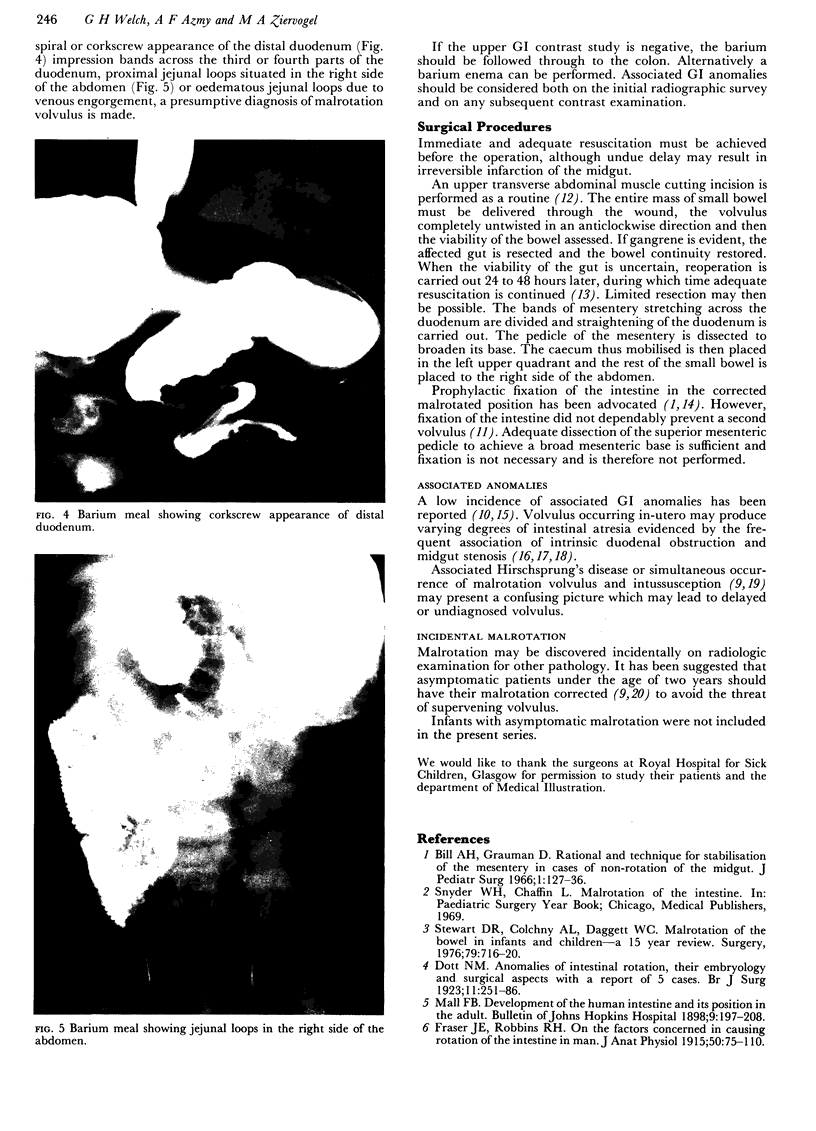

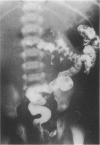
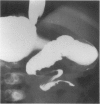
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aitken J. Congenital intrinsic duodenal obstruction in infancy. A series of 30 cases treated over a 6 year period. J Pediatr Surg. 1966 Dec;1(6):546–558. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(66)80118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennom W. S., Bill A. H. Prophylactic fixation of the intestine for midgut nonrotation. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1974 Feb;138(2):181–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filston H. C., Kirks D. R. Malrotation - the ubiquitous anomaly. J Pediatr Surg. 1981 Aug;16(4 Suppl 1):614–620. doi: 10.1016/0022-3468(81)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frazer J E, Robbins R H. On the Factors concerned in causing Rotation of the Intestine in Man. J Anat Physiol. 1915 Oct;50(Pt 1):75–110. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauderer M. W. A rationale for routine use of transverse abdominal incisions in infants and children. J Pediatr Surg. 1981 Aug;16(4 Suppl 1):583–586. doi: 10.1016/0022-3468(81)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOUSTON C. S., WITTENBORG M. H. ROENTGEN EVALUATION OF ANOMALIES OF ROTATION AND FIXATION OF THE BOWEL IN CHILDREN. Radiology. 1965 Jan;84:1–18. doi: 10.1148/84.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNUTRUD O., EEK S. Combined intrinsic duodenal obstruction and malrotation. Acta Chir Scand. 1960 Oct 15;119:506–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasna I. H., Becker J. M., Schwartz D., Schneider K. Low molecular weight dextran and reexploration in the management of ischemic midgut-volvulus. J Pediatr Surg. 1978 Oct;13(6):480–483. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(78)80309-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SNYDER W. H., Jr, CHAFFIN L. Embryology and pathology of the intestinal tract: presentation of 40 cases of malrotation. Ann Surg. 1954 Sep;140(3):368–379. doi: 10.1097/00000658-195409000-00013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauffer U. G., Herrmann P. Comparison of late results in patients with corrected intestinal malrotation with and without fixation of the mesentery. J Pediatr Surg. 1980 Feb;15(1):9–12. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(80)80393-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tryfonas G., Young D. G. Extrinsic duodenal obstruction in infants and children. Br J Surg. 1975 Feb;62(2):125–129. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800620212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]