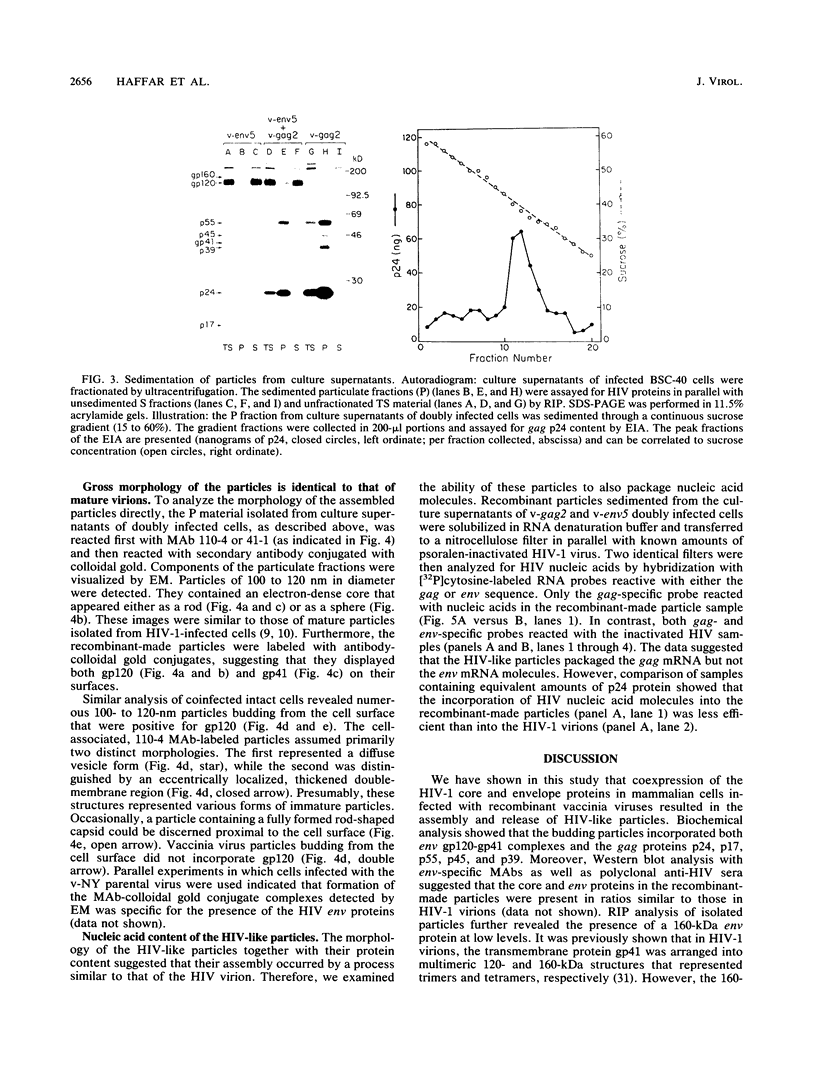
Abstract
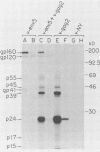
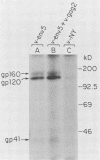
We report the assembly of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-like particles in African green monkey kidney cells coinfected with two recombinant vaccinia viruses, one carrying the HIV-1 gag and protease genes and the other the env gene. Biochemical analysis of particles sedimented from culture supernatants of doubly infected cells revealed that they were composed of gag proteins, primarily p24, as well as the env proteins gp120 and gp41. Thin-section immunoelectron microscopy showed that these particles were 100 to 120 nm in diameter, were characterized by the presence of cylindrical core structures, and displayed the mature gp120-gp41 complexes on their surfaces. Furthermore, thin-section immunoelectron microscopy analysis of infected cells showed that particle assembly and budding occurred at the plasma membrane. Nucleic acid hybridization suggested that the particles packaged only the gag mRNA but not the env mRNA. Therefore, the system we present is well suited for studies of HIV virion maturation. In addition, the HIV-like particles provide a novel and attractive approach for vaccine development.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan J. S., Coligan J. E., Barin F., McLane M. F., Sodroski J. G., Rosen C. A., Haseltine W. A., Lee T. H., Essex M. Major glycoprotein antigens that induce antibodies in AIDS patients are encoded by HTLV-III. Science. 1985 May 31;228(4703):1091–1094. doi: 10.1126/science.2986290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bathurst I. C., Chester N., Gibson H. L., Dennis A. F., Steimer K. S., Barr P. J. N myristylation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gag polyprotein precursor in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3176–3179. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3176-3179.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman P. W., Nunes W. M., Haffar O. K. Expression of membrane-associated and secreted variants of gp160 of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in vitro and in continuous cell lines. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3135–3142. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3135-3142.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabral G. A., Marciano-Cabral F., Funk G. A., Sanchez Y., Hollinger F. B., Melnick J. L., Dreesman G. R. Cellular and humoral immunity in guinea pigs to two major polypeptides derived from hepatitis B surface antigen. J Gen Virol. 1978 Feb;38(2):339–350. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-38-2-339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanh T. C., Dreesman G. R., Kanda P., Linette G. P., Sparrow J. T., Ho D. D., Kennedy R. C. Induction of anti-HIV neutralizing antibodies by synthetic peptides. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):3065–3071. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04607.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher A. G., Ratner L., Mitsuya H., Marselle L. M., Harper M. E., Broder S., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Infectious mutants of HTLV-III with changes in the 3' region and markedly reduced cytopathic effects. Science. 1986 Aug 8;233(4764):655–659. doi: 10.1126/science.3014663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhardt A., Bosch J. V., Ziemiecki A., Friis R. R. Rous sarcoma virus p19 and gp35 can be chemically crosslinked to high molecular weight complexes. An insight into virus assembly. J Mol Biol. 1984 Apr 5;174(2):297–317. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90340-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelderblom H. R., Hausmann E. H., Ozel M., Pauli G., Koch M. A. Fine structure of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and immunolocalization of structural proteins. Virology. 1987 Jan;156(1):171–176. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90449-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gendelman H. E., Orenstein J. M., Baca L. M., Weiser B., Burger H., Kalter D. C., Meltzer M. S. The macrophage in the persistence and pathogenesis of HIV infection. AIDS. 1989 Aug;3(8):475–495. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198908000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gheysen D., Jacobs E., de Foresta F., Thiriart C., Francotte M., Thines D., De Wilde M. Assembly and release of HIV-1 precursor Pr55gag virus-like particles from recombinant baculovirus-infected insect cells. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):103–112. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90873-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosting L. H., McClure J., Dickinson E. S., Watanabe S. M., Shriver K., Goldstein L. C. Monoclonal antibodies to gp110 and gp41 of human immunodeficiency virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 May;25(5):845–848. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.5.845-848.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gowda S. D., Stein B. S., Engleman E. G. Identification of protein intermediates in the processing of the p55 HIV-1 gag precursor in cells infected with recombinant vaccinia virus. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8459–8462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göttlinger H. G., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. Role of capsid precursor processing and myristoylation in morphogenesis and infectivity of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5781–5785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffar O. K., Dowbenko D. J., Berman P. W. Topogenic analysis of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein, gp160, in microsomal membranes. J Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;107(5):1677–1687. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.5.1677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffar O. K., Nakamura G. R., Berman P. W. The carboxy terminus of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp160 limits its proteolytic processing and transport in transfected cell lines. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):3100–3103. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.3100-3103.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffar O. K., Vallerga A. K., Marenda S. A., Witchel H. J., Firestone G. L. Glucocorticoid-regulated compartmentalization of cell surface-associated glycoproteins in rat hepatoma cells: evidence for an independent response that requires receptor function and de novo RNA synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1508–1517. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Sarngadharan M. G., Hirsch M. S., Schooley R. T., Rota T. R., Kennedy R. C., Chanh T. C., Sato V. L. Human immunodeficiency virus neutralizing antibodies recognize several conserved domains on the envelope glycoproteins. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):2024–2028. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.2024-2028.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho R. J., Burke R. L., Merigan T. C. Antigen-presenting liposomes are effective in treatment of recurrent herpes simplex virus genitalis in guinea pigs. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):2951–2958. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.2951-2958.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. L., Fultz P. N., McClure H. M., Eichberg J. W., Thomas E. K., Zarling J., Singhal M. C., Kosowski S. G., Swenson R. B., Anderson D. C. Effect of immunization with a vaccinia-HIV env recombinant on HIV infection of chimpanzees. Nature. 1987 Aug 20;328(6132):721–723. doi: 10.1038/328721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. L., Kosowski S. G., Dalrymple J. M. Expression of AIDS virus envelope gene in recombinant vaccinia viruses. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):537–540. doi: 10.1038/320537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatzmann D., Barré-Sinoussi F., Nugeyre M. T., Danquet C., Vilmer E., Griscelli C., Brun-Veziret F., Rouzioux C., Gluckman J. C., Chermann J. C. Selective tropism of lymphadenopathy associated virus (LAV) for helper-inducer T lymphocytes. Science. 1984 Jul 6;225(4657):59–63. doi: 10.1126/science.6328660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski M., Potz J., Basiripour L., Dorfman T., Goh W. C., Terwilliger E., Dayton A., Rosen C., Haseltine W., Sodroski J. Functional regions of the envelope glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Science. 1987 Sep 11;237(4820):1351–1355. doi: 10.1126/science.3629244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. J., Hu W., Fisher A. G., Looney D. J., Kao V. F., Mitsuya H., Ratner L., Wong-Staal F. Role of the carboxy-terminal portion of the HIV-1 transmembrane protein in viral transmission and cytopathogenicity. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1989 Aug;5(4):441–449. doi: 10.1089/aid.1989.5.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lever A., Gottlinger H., Haseltine W., Sodroski J. Identification of a sequence required for efficient packaging of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA into virions. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):4085–4087. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.4085-4087.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsley P. S., Ledbetter J. A., Kinney-Thomas E., Hu S. L. Effects of anti-gp120 monoclonal antibodies on CD4 receptor binding by the env protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3695–3702. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3695-3702.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal J. S., Kennedy M. S., Sligh J. M., Cort S. P., Mawle A., Nicholson J. K. Binding of HTLV-III/LAV to T4+ T cells by a complex of the 110K viral protein and the T4 molecule. Science. 1986 Jan 24;231(4736):382–385. doi: 10.1126/science.3001934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nixon D. F., Townsend A. R., Elvin J. G., Rizza C. R., Gallwey J., McMichael A. J. HIV-1 gag-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes defined with recombinant vaccinia virus and synthetic peptides. Nature. 1988 Dec 1;336(6198):484–487. doi: 10.1038/336484a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez L. G., Davis G. L., Hunter E. Mutants of the Rous sarcoma virus envelope glycoprotein that lack the transmembrane anchor and cytoplasmic domains: analysis of intracellular transport and assembly into virions. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):2981–2988. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.2981-2988.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinter A., Honnen W. J., Tilley S. A., Bona C., Zaghouani H., Gorny M. K., Zolla-Pazner S. Oligomeric structure of gp41, the transmembrane protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2674–2679. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2674-2679.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satake M., Luftig R. B. Comparative immunofluorescence of murine leukemia virus-derived membrane-associated antigens. Virology. 1983 Jan 30;124(2):259–273. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90343-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A. M., Rein A. Unmyristylated Moloney murine leukemia virus Pr65gag is excluded from virus assembly and maturation events. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2370–2373. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2370-2373.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons K., Garoff H. The budding mechanisms of enveloped animal viruses. J Gen Virol. 1980 Sep;50(1):1–21. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-50-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M. A., Langlois A. J., McDanal C. B., McDougal J. S., Bolognesi D. P., Matthews T. J. Neutralizing antibodies to an immunodominant envelope sequence do not prevent gp120 binding to CD4. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4195–4200. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4195-4200.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. J., Cho M. I., Hammarskjöld M. L., Rekosh D. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Pr55gag and Pr160gag-pol expressed from a simian virus 40 late replacement vector are efficiently processed and assembled into viruslike particles. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2743–2750. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2743-2750.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. K., Weber J. N., McClure J., Clapham P. R., Singhal M. C., Shriver M. K., Weiss R. A. Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies to the AIDS virus. AIDS. 1988 Feb;2(1):25–29. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198802000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venable R. M., Pastor R. W., Brooks B. R., Carson F. W. Theoretically determined three-dimensional structures for amphipathic segments of the HIV-1 gp41 envelope protein. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1989 Feb;5(1):7–22. doi: 10.1089/aid.1989.5.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarling J. M., Eichberg J. W., Moran P. A., McClure J., Sridhar P., Hu S. L. Proliferative and cytotoxic T cells to AIDS virus glycoproteins in chimpanzees immunized with a recombinant vaccinia virus expressing AIDS virus envelope glycoproteins. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 15;139(4):988–990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]