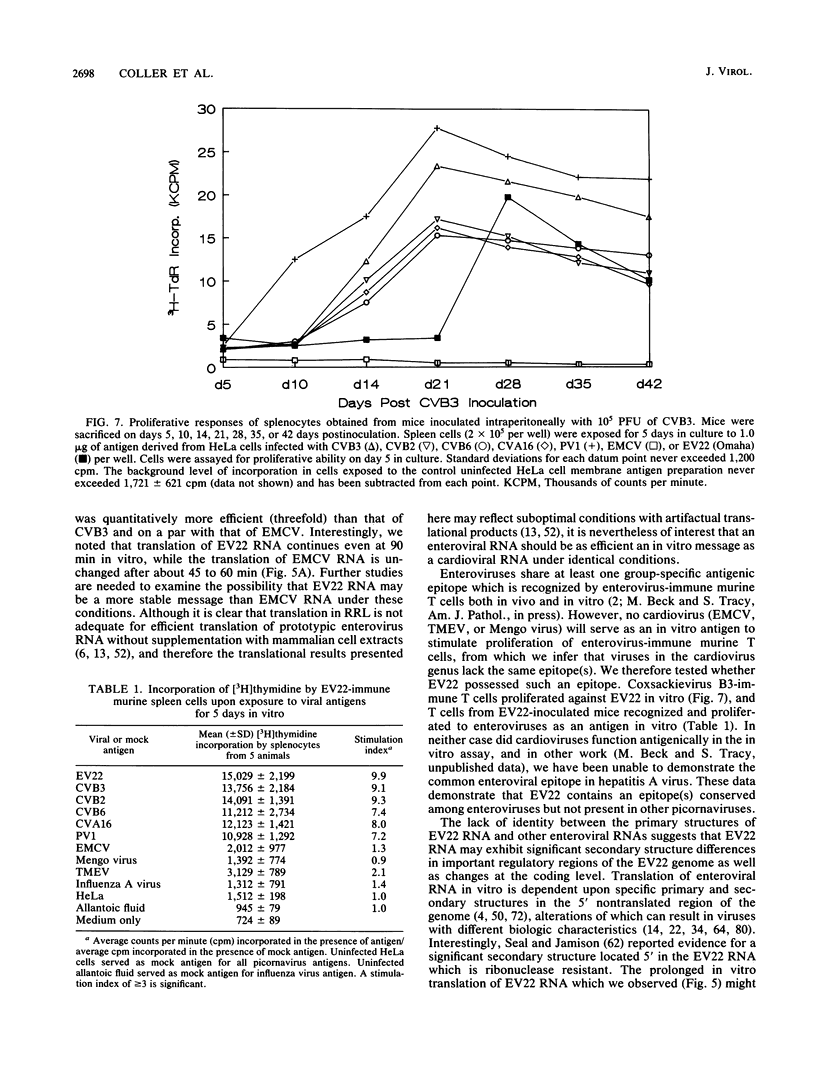
Abstract
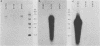
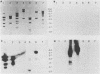
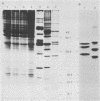
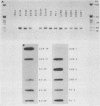
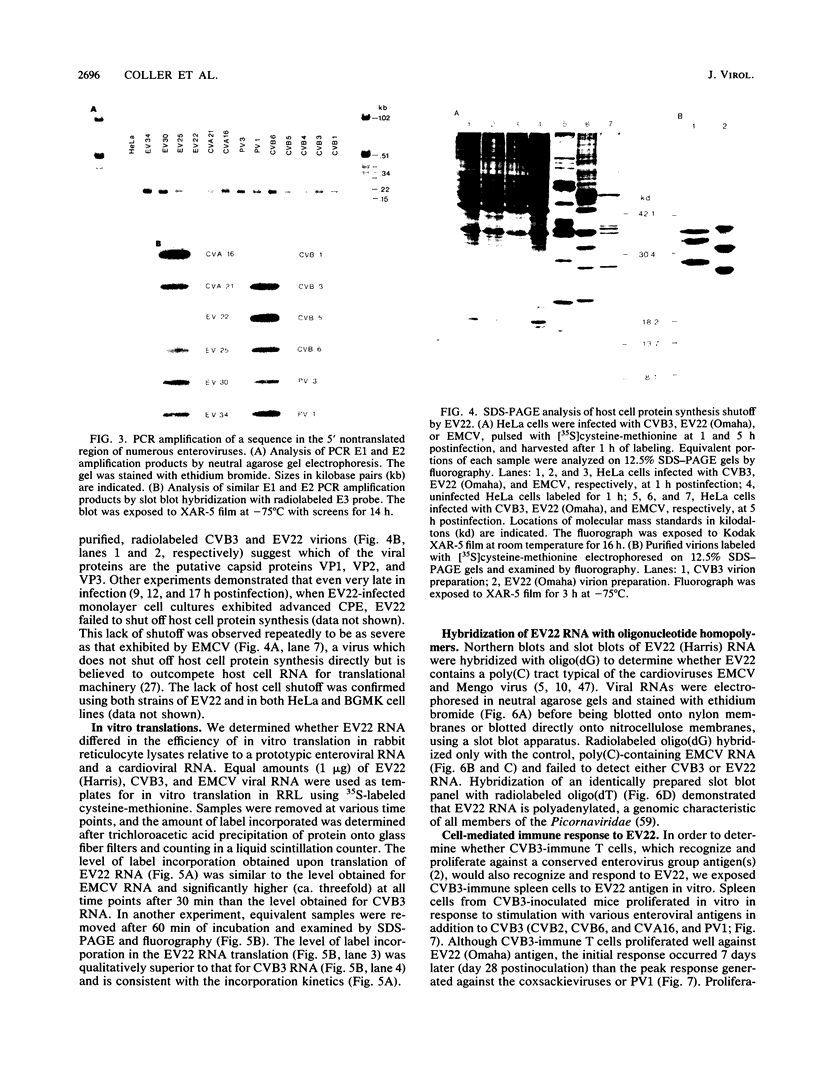
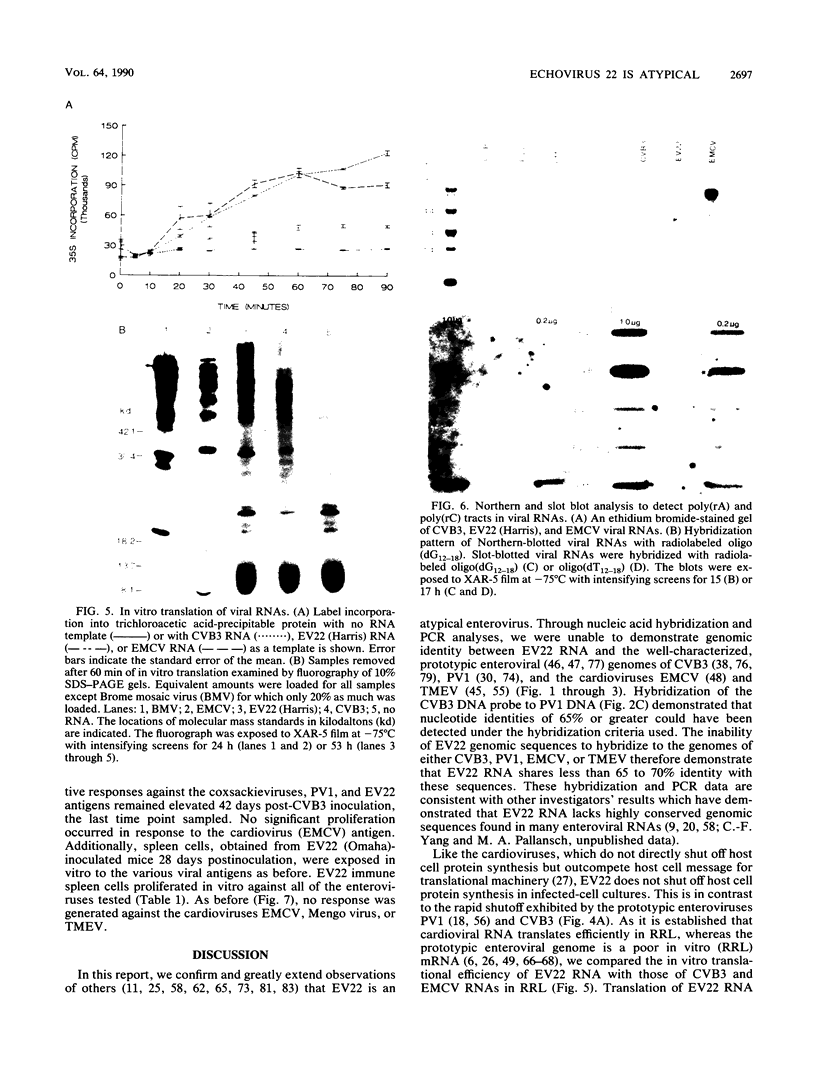
Although echovirus 22 (EV22) is classified as an enterovirus in the family Picornaviridae, it is atypical of the enterovirus paradigm, typified by the polioviruses and the coxsackie B viruses. cDNA reverse transcribed from coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3) RNA does not hybridize to genomic RNA of EV22, and conversely, cDNA made to EV22 does not hybridize to CVB3 genomic RNA or to molecular clones of CVB3 or poliovirus type 1. EV22 cDNA does not hybridize to viral RNA of encephalomyocarditis virus or to a molecular clone of Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus, members of the cardiovirus genus. The genomic RNA of EV22 cannot be detected by the polymerase chain reaction using generic enteroviral primers. EV22 does not shut off host cell protein synthesis, and the RNA of EV22 is efficiently translated in vitro in rabbit reticulocyte lysates. Murine enterovirus-immune T cells recognize and proliferate against EV22 as an antigen in vitro, demonstrating that EV22 shares an epitope(s) common to enteroviruses but not found among other picornaviruses.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acharya R., Fry E., Stuart D., Fox G., Rowlands D., Brown F. The three-dimensional structure of foot-and-mouth disease virus at 2.9 A resolution. Nature. 1989 Feb 23;337(6209):709–716. doi: 10.1038/337709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck M. A., Tracy S. M. Murine cell-mediated immune response recognizes an enterovirus group-specific antigen(s). J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4148–4156. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4148-4156.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienkowska-Szewczyk K., Ehrenfeld E. An internal 5'-noncoding region required for translation of poliovirus RNA in vitro. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):3068–3072. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.3068-3072.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black D. N., Stephenson P., Rowlands D. J., Brown F. Sequence and location of the poly C tract in aphtho- and cardiovirus RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jun 11;6(7):2381–2390. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.7.2381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown B. A., Ehrenfeld E. Translation of poliovirus RNA in vitro: changes in cleavage pattern and initiation sites by ribosomal salt wash. Virology. 1979 Sep;97(2):396–405. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90350-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROWTHER D., MELNICK J. L. Studies of the inhibitory action of guanidine on poliovirus multiplication in cell cultures. Virology. 1961 Sep;15:65–74. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90078-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. H., Auvinen P., Hyypiä T., Stanway G. The nucleotide sequence of coxsackievirus A9; implications for receptor binding and enterovirus classification. J Gen Virol. 1989 Dec;70(Pt 12):3269–3280. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-12-3269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman N. M., Tracy S., Gauntt C. J., Fortmueller U. Molecular detection and identification of enteroviruses using enzymatic amplification and nucleic acid hybridization. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 May;28(5):843–850. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.5.843-850.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chumakov K. M., Agol V. I. Poly(C) sequence is located near the 5'-end of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jul 26;71(2):551–557. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90822-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiLella A. G., Woo S. L. Hybridization of genomic DNA to oligonucleotide probes in the presence of tetramethylammonium chloride. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:447–451. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner A. J., Semler B. L., Jackson R. J., Hanecak R., Duprey E., Wimmer E. In vitro translation of poliovirus RNA: utilization of internal initiation sites in reticulocyte lysate. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):507–514. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.507-514.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duke G. M., Osorio J. E., Palmenberg A. C. Attenuation of Mengo virus through genetic engineering of the 5' noncoding poly(C) tract. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):474–476. doi: 10.1038/343474a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earle J. A., Skuce R. A., Fleming C. S., Hoey E. M., Martin S. J. The complete nucleotide sequence of a bovine enterovirus. J Gen Virol. 1988 Feb;69(Pt 2):253–263. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-2-253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J. ENTEROVIRUS ENTRANCE INTO SPECIFIC HOST CELLS, AND SUBSEQUENT ALTERATIONS OF CELL PROTEIN AND NUCLEIC ACID SYNTHESIS. Bacteriol Rev. 1964 Mar;28:2–13. doi: 10.1128/br.28.1.2-13.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogle J. M., Chow M., Filman D. J. Three-dimensional structure of poliovirus at 2.9 A resolution. Science. 1985 Sep 27;229(4720):1358–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.2994218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes P. J., North C., Minor P. D., Stanway G. The complete nucleotide sequence of coxsackievirus A21. J Gen Virol. 1989 Nov;70(Pt 11):2943–2952. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-11-2943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyypiä T., Auvinen P., Maaronen M. Polymerase chain reaction for human picornaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1989 Dec;70(Pt 12):3261–3268. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-12-3261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyypiä T., Stålhandske P., Vainionpä R., Pettersson U. Detection of enteroviruses by spot hybridization. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Mar;19(3):436–438. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.3.436-438.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iizuka N., Kohara M., Hagino-Yamagishi K., Abe S., Komatsu T., Tago K., Arita M., Nomoto A. Construction of less neurovirulent polioviruses by introducing deletions into the 5' noncoding sequence of the genome. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5354–5363. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5354-5363.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iizuka N., Kuge S., Nomoto A. Complete nucleotide sequence of the genome of coxsackievirus B1. Virology. 1987 Jan;156(1):64–73. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90436-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. J., Hunt T. Preparation and use of nuclease-treated rabbit reticulocyte lysates for the translation of eukaryotic messenger RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:50–74. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamison R. M. An electron microscopic study of the intracellular development of echovirus 22. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1974;44(3):184–194. doi: 10.1007/BF01240606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang S. K., Kräusslich H. G., Nicklin M. J., Duke G. M., Palmenberg A. C., Wimmer E. A segment of the 5' nontranslated region of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA directs internal entry of ribosomes during in vitro translation. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2636–2643. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2636-2643.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jen G., Thach R. E. Inhibition of host translation in encephalomyocarditis virus-infected L cells: a novel mechanism. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):250–261. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.250-261.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins O., Booth J. D., Minor P. D., Almond J. W. The complete nucleotide sequence of coxsackievirus B4 and its comparison to other members of the Picornaviridae. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jul;68(Pt 7):1835–1848. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-7-1835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. S., Smith T. J., Chapman M. S., Rossmann M. C., Pevear D. C., Dutko F. J., Felock P. J., Diana G. D., McKinlay M. A. Crystal structure of human rhinovirus serotype 1A (HRV1A). J Mol Biol. 1989 Nov 5;210(1):91–111. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90293-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura N., Semler B. L., Rothberg P. G., Larsen G. R., Adler C. J., Dorner A. J., Emini E. A., Hanecak R., Lee J. J., van der Werf S. Primary structure, gene organization and polypeptide expression of poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):547–553. doi: 10.1038/291547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kräusslich H. G., Nicklin M. J., Toyoda H., Etchison D., Wimmer E. Poliovirus proteinase 2A induces cleavage of eucaryotic initiation factor 4F polypeptide p220. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2711–2718. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2711-2718.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kräusslich H. G., Wimmer E. Viral proteinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:701–754. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.003413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuge S., Nomoto A. Construction of viable deletion and insertion mutants of the Sabin strain of type 1 poliovirus: function of the 5' noncoding sequence in viral replication. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1478–1487. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1478-1487.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Monica N., Meriam C., Racaniello V. R. Mapping of sequences required for mouse neurovirulence of poliovirus type 2 Lansing. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):515–525. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.515-525.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird-Meeter K., van Domburg R., Bos E., Hugenholtz P. G. Survival at 5 to 10 years after aorto-coronary bypass operations in 1041 consecutive patients. Eur Heart J. 1987 May;8(5):449–456. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a062304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. M., Stålhandske P. O., Pettersson U. Genome of coxsackievirus B3. Virology. 1987 Jan;156(1):50–63. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90435-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. E., Grubman M. J., Ehrenfeld E. Relationship of p220 cleavage during picornavirus infection to 2A proteinase sequencing. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4216–4223. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4216-4223.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo M., Vriend G., Kamer G., Minor I., Arnold E., Rossmann M. G., Boege U., Scraba D. G., Duke G. M., Palmenberg A. C. The atomic structure of Mengo virus at 3.0 A resolution. Science. 1987 Jan 9;235(4785):182–191. doi: 10.1126/science.3026048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohara Y., Stein S., Fu J. L., Stillman L., Klaman L., Roos R. P. Molecular cloning and sequence determination of DA strain of Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis viruses. Virology. 1988 May;164(1):245–255. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90642-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmenberg A. C., Kirby E. M., Janda M. R., Drake N. L., Duke G. M., Potratz K. F., Collett M. S. The nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of the encephalomyocarditis viral polyprotein coding region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2969–2985. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Translation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA in vitro yields an active proteolytic processing enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr 17;85(2):457–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12260.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Kaplan G., Racaniello V. R., Sonenberg N. Cap-independent translation of poliovirus mRNA is conferred by sequence elements within the 5' noncoding region. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1103–1112. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pevear D. C., Borkowski J., Calenoff M., Oh C. K., Ostrowski B., Lipton H. L. Insights into Theiler's virus neurovirulence based on a genomic comparison of the neurovirulent GDVII and less virulent BeAn strains. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90652-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips B. A., Emmert A. Modulation of the expression of poliovirus proteins in reticulocyte lysates. Virology. 1986 Jan 30;148(2):255–267. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90323-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R., Baltimore D. Molecular cloning of poliovirus cDNA and determination of the complete nucleotide sequence of the viral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4887–4891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos R. P., Stein S., Ohara Y., Fu J. L., Semler B. L. Infectious cDNA clones of the DA strain of Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5492–5496. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5492-5496.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Trachsel H., Leong K., Baltimore D. Inhibition of translation by poliovirus: inactivation of a specific initiation factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2732–2736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seal L. A., Jamison R. M. Evidence for secondary structure within the virion RNA of echovirus 22. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):641–644. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.641-644.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semler B. L., Dorner A. J., Wimmer E. Production of infectious poliovirus from cloned cDNA is dramatically increased by SV40 transcription and replication signals. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 25;12(12):5123–5141. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.12.5123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semler B. L., Johnson V. H., Tracy S. A chimeric plasmid from cDNA clones of poliovirus and coxsackievirus produces a recombinant virus that is temperature-sensitive. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1777–1781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih D. S., Shih C. T., Kew O., Pallansch M., Rueckert R., Kaesberg P. Cell-free synthesis and processing of the proteins of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5807–5811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih D. S., Shih C. T., Zimmern D., Rueckert R. R., Kaesberg P. Translation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA in reticulocyte lysates: kinetic analysis of the formation of virion proteins and a protein required for processing. J Virol. 1979 May;30(2):472–480. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.2.472-480.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N. Regulation of translation by poliovirus. Adv Virus Res. 1987;33:175–204. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60318-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanway G., Hughes P. J., Mountford R. C., Reeve P., Minor P. D., Schild G. C., Almond J. W. Comparison of the complete nucleotide sequences of the genomes of the neurovirulent poliovirus P3/Leon/37 and its attenuated Sabin vaccine derivative P3/Leon 12a1b. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1539–1543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strijker R., Fritz D. T., Levinson A. D. Adenovirus VAI-RNA regulates gene expression by controlling stability of ribosome-bound RNAs. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2669–2675. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08407.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svitkin Y. V., Maslova S. V., Agol V. I. The genomes of attenuated and virulent poliovirus strains differ in their in vitro translation efficiencies. Virology. 1985 Dec;147(2):243–252. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90127-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAMM I., EGGERS H. J. Differences in the selective virus inhibitory action of 2-(alpha-hydroxybenzyl)-benzimidazole and guanidine HCl. Virology. 1962 Nov;18:439–447. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90034-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda H., Kohara M., Kataoka Y., Suganuma T., Omata T., Imura N., Nomoto A. Complete nucleotide sequences of all three poliovirus serotype genomes. Implication for genetic relationship, gene function and antigenic determinants. J Mol Biol. 1984 Apr 25;174(4):561–585. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90084-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracy S. A comparison of genomic homologies among the coxsackievirus B group: use of fragments of the cloned coxsackievirus B3 genome as probes. J Gen Virol. 1984 Dec;65(Pt 12):2167–2172. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-12-2167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracy S., Chapman N. M., Liu H. L. Molecular cloning and partial characterization of the coxsackievirus B3 genome. Brief report. Arch Virol. 1985;85(1-2):157–163. doi: 10.1007/BF01317016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracy S. Improved rapid methodology for the isolation of nucleic acids from agarose gels. Prep Biochem. 1981;11(3):251–268. doi: 10.1080/00327488108061767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracy S., Liu H. L., Chapman N. M. Coxsackievirus B3: primary structure of the 5' non-coding and capsid protein-coding regions of the genome. Virus Res. 1985 Oct;3(3):263–270. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(85)90050-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trono D., Andino R., Baltimore D. An RNA sequence of hundreds of nucleotides at the 5' end of poliovirus RNA is involved in allowing viral protein synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2291–2299. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2291-2299.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIGAND R., SABIN A. B. Properties of ECHO types 22, 23 and 24 viruses. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1961;11:224–247. doi: 10.1007/BF01241688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner G., Rosenwirth B., Bauer E., Seifert J. M., Werner F. J., Besemer J. Molecular cloning and sequence determination of the genomic regions encoding protease and genome-linked protein of three picornaviruses. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1084–1093. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1084-1093.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Zeipel G. Most echoviruses reach higher titers in RD than in GMK-AH 1 cells, regardless of their passage history. Arch Virol. 1980;63(2):143–146. doi: 10.1007/BF01320771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]