Abstract
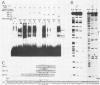
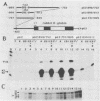
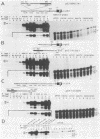
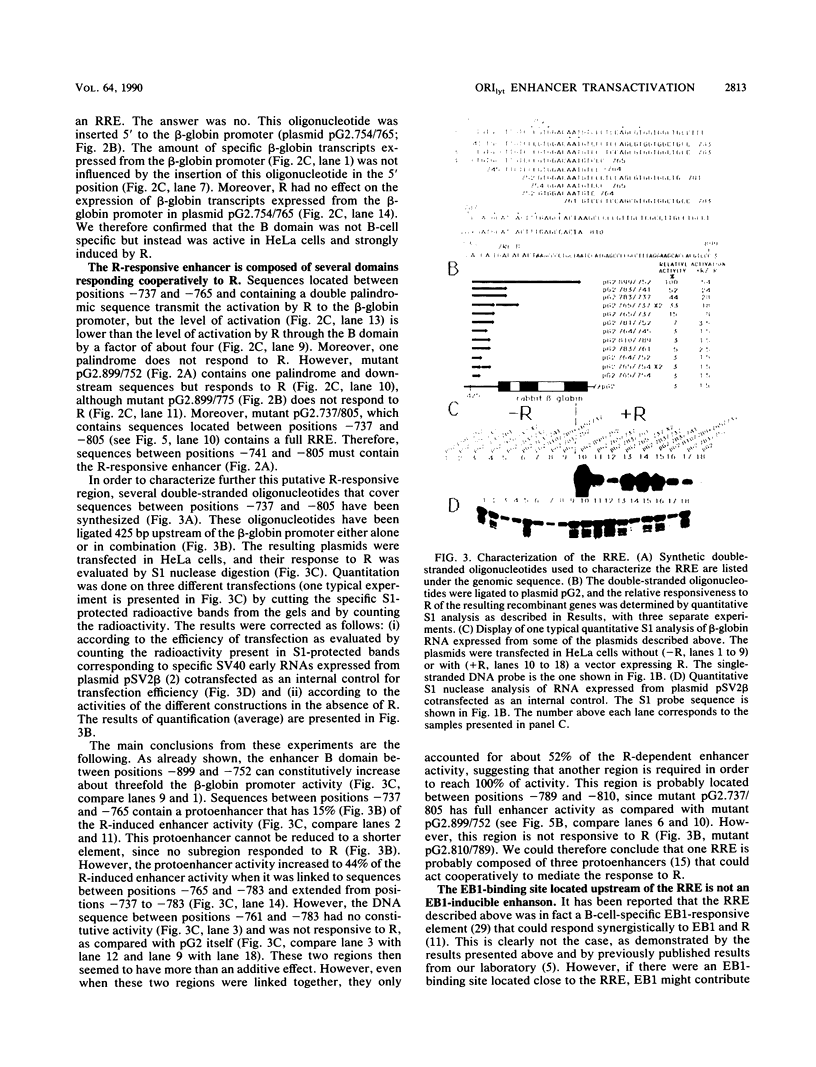
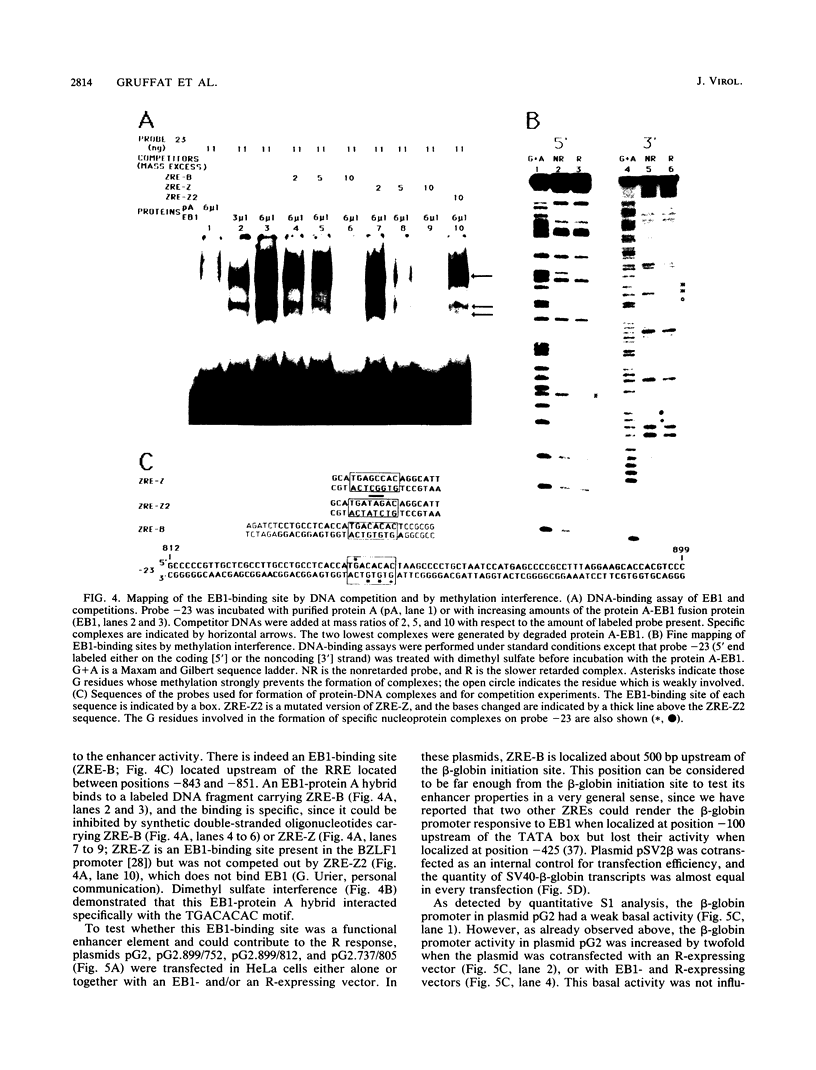
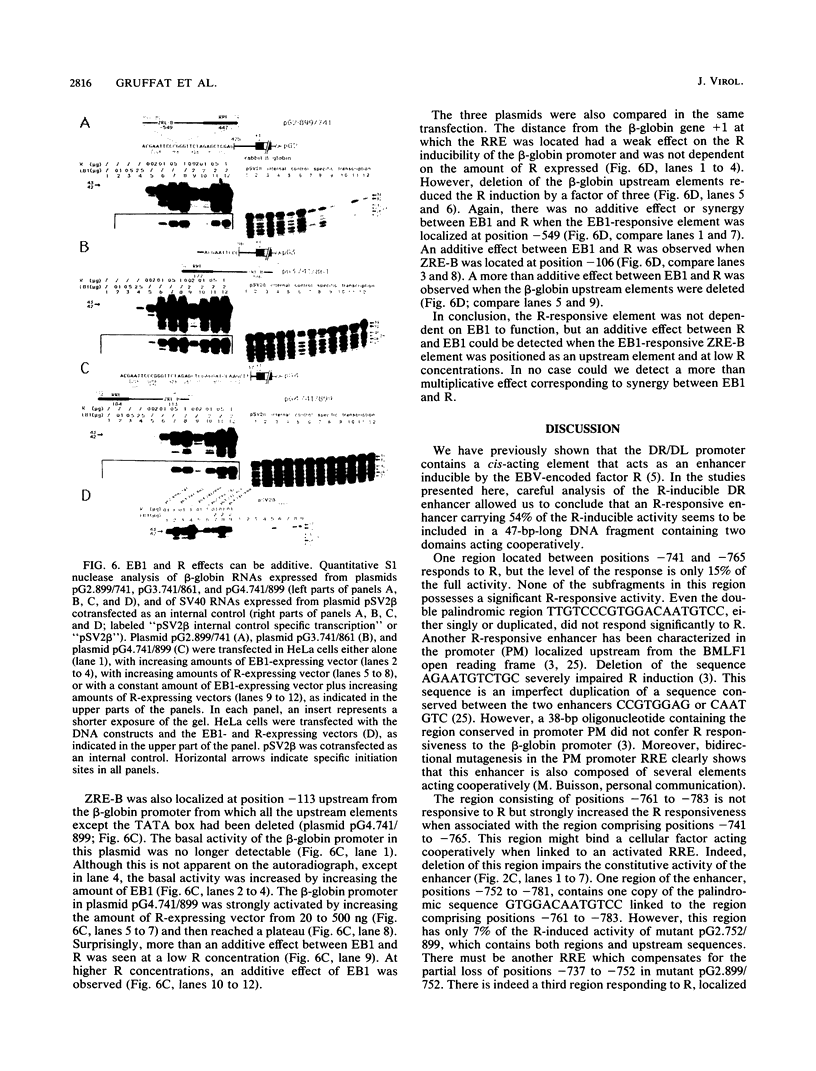
The Epstein-Barr virus DR promoter is located upstream of the PstI repeats, and in addition to the TATA box, it contains an upstream region (positions -69 to -220) responsive to EB1 (Z) (the BZLF1-encoded transcription factor) and an enhancer with two functionally distinct domains, A and B. Domain B has been described as a B-cell-specific EB1-responsive element (P. M. Lieberman, J. M. Hardwick, and S. D. Hayward, J. Virol. 63:3040-3050, 1989) activated synergistically by EB1 and R, an EBV early product encoded by the open reading frame BRLF1 (M. A. Cox, J. Leahy, and J. M. Hardwick, J. Virol. 64:313-321, 1990). We show here that domain B is an R-responsive element in HeLa cells and is therefore not an EB1-responsive B-cell-specific element. However, there is an EB1-binding site (ZRE-B) located within the R-responsive enhancer region. ZRE-B can be deleted without affecting the R-dependent enhancer activity. Moreover, there is no cooperation or synergy between R and EB1 when activating the B domain (ZRE-B plus the R-responsive element) positioned as an enhancer. ZRE-B is therefore not part of the R-inducible enhancer. We have tested several subregions of the DR enhancer B domain, either alone or in combination, for their capacity to transmit the R-activating signal to the rabbit beta-globin promoter. We found that the R-responsive element is composed of four protoenhancers that span the whole B domain. These protoenhancers alone are weakly or not responsive to R. One of the protoenhancers contains the overlapping palindromes 5'-TTGTCCcgtGGACAAaTGTCC-3'. However, one palindrome, either alone or duplicated, or the overlapping palindromes did not respond to R.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodescot M., Perricaudet M. Epstein-Barr virus mRNAs produced by alternative splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):7103–7114. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.17.7103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buisson M., Manet E., Trescol-Biemont M. C., Gruffat H., Durand B., Sergeant A. The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) early protein EB2 is a posttranscriptional activator expressed under the control of EBV transcription factors EB1 and R. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5276–5284. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5276-5284.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Gruffat H., Chevallier-Greco A., Buisson M., Sergeant A. The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) early promoter DR contains a cis-acting element responsive to the EBV transactivator EB1 and an enhancer with constitutive and inducible activities. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):607–614. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.607-614.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chevallier-Greco A., Gruffat H., Manet E., Calender A., Sergeant A. The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DR enhancer contains two functionally different domains: domain A is constitutive and cell specific, domain B is transactivated by the EBV early protein R. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):615–623. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.615-623.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chevallier-Greco A., Manet E., Chavrier P., Mosnier C., Daillie J., Sergeant A. Both Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-encoded trans-acting factors, EB1 and EB2, are required to activate transcription from an EBV early promoter. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3243–3249. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04635.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho M. S., Jeang K. T., Hayward S. D. Localization of the coding region for an Epstein-Barr virus early antigen and inducible expression of this 60-kilodalton nuclear protein in transfected fibroblast cell lines. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):852–859. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.852-859.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Countryman J., Miller G. Activation of expression of latent Epstein-Barr herpesvirus after gene transfer with a small cloned subfragment of heterogeneous viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4085–4089. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox M. A., Leahy J., Hardwick J. M. An enhancer within the divergent promoter of Epstein-Barr virus responds synergistically to the R and Z transactivators. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):313–321. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.313-321.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dambaugh T. R., Kieff E. Identification and nucleotide sequences of two similar tandem direct repeats in Epstein-Barr virus DNA. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):823–833. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.823-833.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Rowe D. T., Rooney C. M., Kouzarides T. Epstein-Barr virus BZLF1 trans-activator specifically binds to a consensus AP-1 site and is related to c-fos. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):127–132. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03356.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freese U. K., Laux G., Hudewentz J., Schwarz E., Bornkamm G. W. Two distant clusters of partially homologous small repeats of Epstein-Barr virus are transcribed upon induction of an abortive or lytic cycle of the virus. J Virol. 1983 Dec;48(3):731–743. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.3.731-743.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromental C., Kanno M., Nomiyama H., Chambon P. Cooperativity and hierarchical levels of functional organization in the SV40 enhancer. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):943–953. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90109-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt W., Sugden B. Identification and characterization of oriLyt, a lytic origin of DNA replication of Epstein-Barr virus. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):427–433. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90028-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardwick J. M., Lieberman P. M., Hayward S. D. A new Epstein-Barr virus transactivator, R, induces expression of a cytoplasmic early antigen. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2274–2284. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2274-2284.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward S. D., Lazarowitz S. G., Hayward G. S. Organization of the Epstein-Barr virus DNA molecule. II. Fine mapping of the boundaries of the internal repeat cluster of B95-8 and identification of additional small tandem repeats adjacent to the HR-1 deletion. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):201–212. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.201-212.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Fennewald S., Hummel M., Cole T., Kieff E. A membrane protein encoded by Epstein-Barr virus in latent growth-transforming infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7207–7211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudewentz J., Delius H., Freese U. K., Zimber U., Bornkamm G. W. Two distant regions of the Epstein-Barr virus genome with sequence homologies have the same orientation and involve small tandem repeats. EMBO J. 1982;1(1):21–26. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01118.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalinot P., Kédinger C. Negative regulatory sequences in the EIa-inducible enhancer of the adenovirus-2 early EIIa promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2651–2669. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeang K. T., Hayward S. D. Organization of the Epstein-Barr virus DNA molecule. III. Location of the P3HR-1 deletion junction and characterization of the NotI repeat units that form part of the template for an abundant 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced mRNA transcript. J Virol. 1983 Oct;48(1):135–148. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.1.135-148.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. D., Griffin B. E. Clustered repeat sequences in the genome of Epstein Barr virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):3919–3937. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.3919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney S., Holley-Guthrie E., Mar E. C., Smith M. The Epstein-Barr virus BMLF1 promoter contains an enhancer element that is responsive to the BZLF1 and BRLF1 transactivators. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3878–3883. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3878-3883.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laux G., Freese U. K., Bornkamm G. W. Structure and evolution of two related transcription units of Epstein-Barr virus carrying small tandem repeats. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):987–995. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.987-995.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laux G., Perricaudet M., Farrell P. J. A spliced Epstein-Barr virus gene expressed in immortalized lymphocytes is created by circularization of the linear viral genome. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):769–774. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02874.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Andrews N. C., Miller G., Steitz J. A. Two small RNAs encoded by Epstein-Barr virus and complexed with protein are precipitated by antibodies from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):805–809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman P. M., Hardwick J. M., Hayward S. D. Responsiveness of the Epstein-Barr virus NotI repeat promoter to the Z transactivator is mediated in a cell-type-specific manner by two independent signal regions. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3040–3050. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3040-3050.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manet E., Gruffat H., Trescol-Biemont M. C., Moreno N., Chambard P., Giot J. F., Sergeant A. Epstein-Barr virus bicistronic mRNAs generated by facultative splicing code for two transcriptional trans-activators. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1819–1826. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03576.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Rabson M., Heston L. Epstein-Barr virus with heterogeneous DNA disrupts latency. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):174–182. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.174-182.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson B., Abrahmsén L., Uhlén M. Immobilization and purification of enzymes with staphylococcal protein A gene fusion vectors. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):1075–1080. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03741.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ondek B., Gloss L., Herr W. The SV40 enhancer contains two distinct levels of organization. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):40–45. doi: 10.1038/333040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sample J., Liebowitz D., Kieff E. Two related Epstein-Barr virus membrane proteins are encoded by separate genes. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):933–937. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.933-937.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada K., Shimizu N., Sakuma S., Ono Y. trans activation of the latent Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) genome after transfection of the EBV DNA fragment. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1016–1022. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1016-1022.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urier G., Buisson M., Chambard P., Sergeant A. The Epstein-Barr virus early protein EB1 activates transcription from different responsive elements including AP-1 binding sites. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1447–1453. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03527.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H., O'Neill F. J., Freese U. K., Hecker E. Persisting oncogenic herpesvirus induced by the tumour promotor TPA. Nature. 1978 Mar 23;272(5651):373–375. doi: 10.1038/272373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]