Abstract
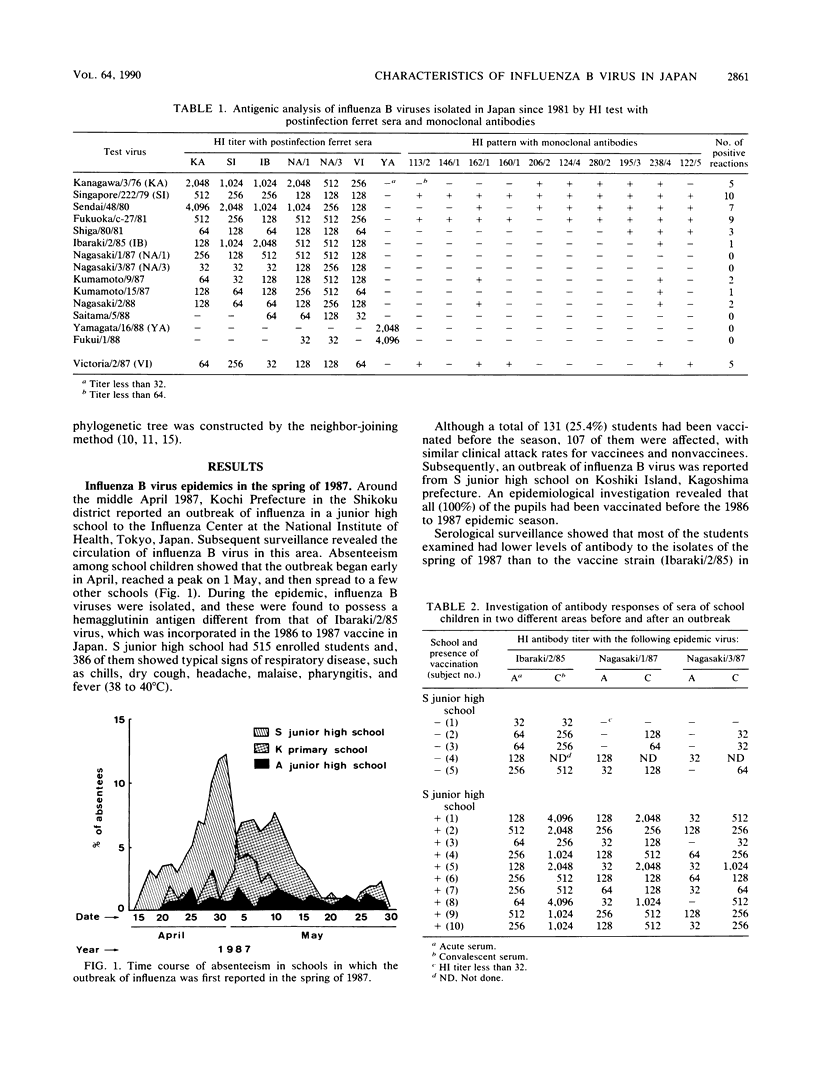
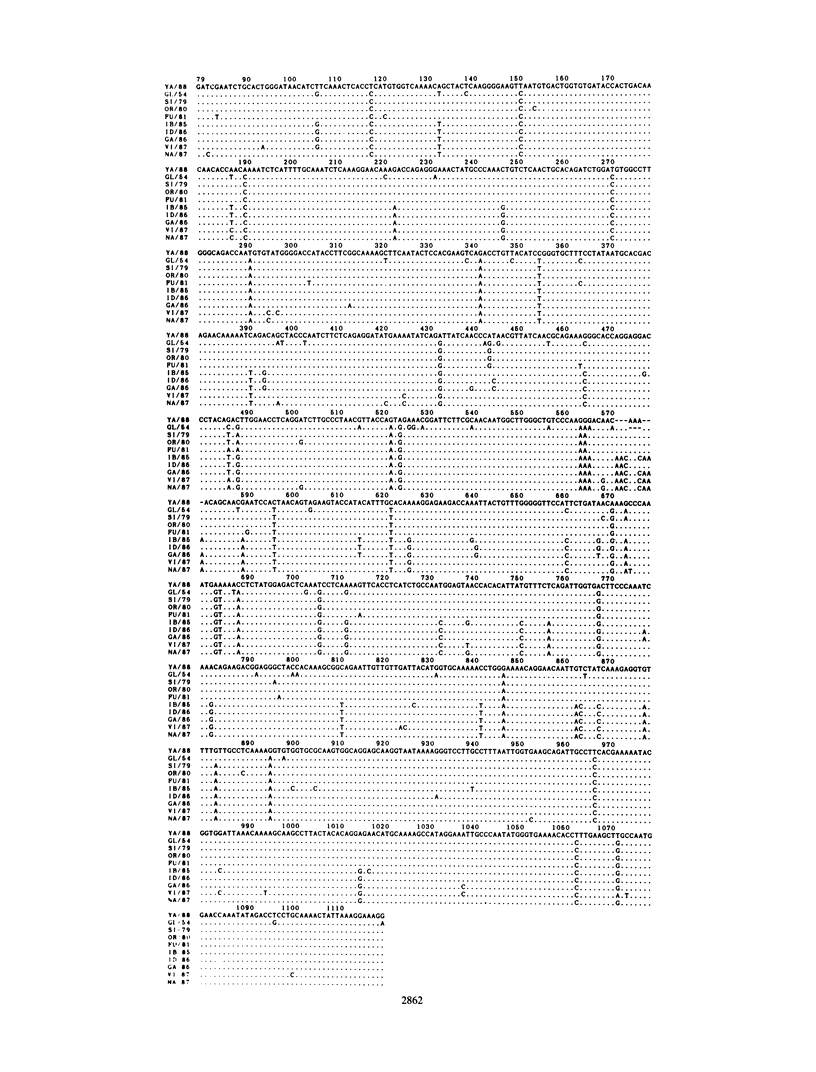
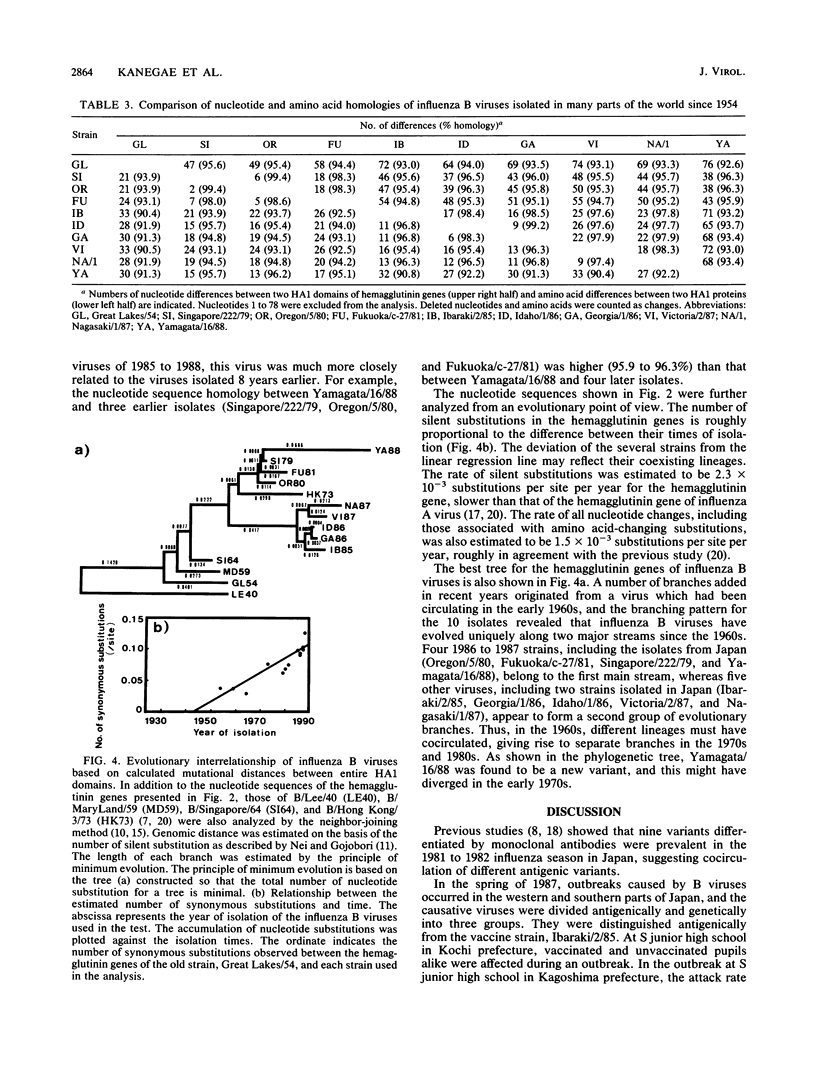
The unexpectedly low efficacy of influenza vaccine during school outbreaks of influenza B virus in the spring of 1987 in Japan was probably attributable to a poor antibody response of vaccinees to the epidemic viruses. An antigenic analysis of the causative B viruses isolated in 1987 and 1988 showed much variation in hemagglutination inhibition patterns. The nucleotide sequences that code for the HA1 domain of B/Fukuoka/c-27/81, B/Ibaraki/2/85, B/Nagasaki/1/87, and B/Yamagata/16/88 viruses were determined and compared with those of the previously reported hemagglutinin genes. The nucleotide sequences of the hemagglutinin gene of a new variant, B/Yamagata/16/88, had only 93.4% homology with those of two other viruses from the same epidemic. An analysis of nucleotide and amino acid substitutions of the hemagglutinin genes of influenza B viruses revealed that new and some old variants could cocirculate in the same epidemic. A phylogenetic tree constructed by the neighbor-joining method allowed estimation of an evolutionary rate of 2.3 x 10(-3) synonymous (silent) substitutions per nucleotide site per year in the hemagglutinin gene.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bao-Lan L., Webster R. G., Brown L. E., Nerome K. Heterogeneity of influenza B viruses. Bull World Health Organ. 1983;61(4):681–687. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berton M. T., Naeve C. W., Webster R. G. Antigenic structure of the influenza B virus hemagglutinin: nucleotide sequence analysis of antigenic variants selected with monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):919–927. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.919-927.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Both G. W., Sleigh M. J., Cox N. J., Kendal A. P. Antigenic drift in influenza virus H3 hemagglutinin from 1968 to 1980: multiple evolutionary pathways and sequential amino acid changes at key antigenic sites. J Virol. 1983 Oct;48(1):52–60. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.1.52-60.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox N. J., Black R. A., Kendal A. P. Pathways of evolution of influenza A (H1N1) viruses from 1977 to 1986 as determined by oligonucleotide mapping and sequencing studies. J Gen Virol. 1989 Feb;70(Pt 2):299–313. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-2-299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovanec D. L., Air G. M. Antigenic structure of the hemagglutinin of influenza virus B/Hong Kong/8/73 as determined from gene sequence analysis of variants selected with monoclonal antibodies. Virology. 1984 Dec;139(2):384–392. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90384-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystal M., Buonagurio D., Young J. F., Palese P. Sequential mutations in the NS genes of influenza virus field strains. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):547–554. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.547-554.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystal M., Young J. F., Palese P., Wilson I. A., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Sequential mutations in hemagglutinins of influenza B virus isolates: definition of antigenic domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4527–4531. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima K., Desselberger U., Palese P. Recent human influenza A (H1N1) viruses are closely related genetically to strains isolated in 1950. Nature. 1978 Jul 27;274(5669):334–339. doi: 10.1038/274334a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M., Gojobori T. Simple methods for estimating the numbers of synonymous and nonsynonymous nucleotide substitutions. Mol Biol Evol. 1986 Sep;3(5):418–426. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nerome K., Sakamoto S., Yano N., Yamamoto T., Kobayashi S., Webster R. G., Oya A. Antigenic characteristics and genome composition of a naturally occurring recombinant influenza virus isolated from a pig in Japan. J Gen Virol. 1983 Dec;64(Pt 12):2611–2620. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-12-2611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond F. L., Caton A. J., Cox N. J., Kendal A. P., Brownlee G. G. The antigenicity and evolution of influenza H1 haemagglutinin, from 1950-1957 and 1977-1983: two pathways from one gene. Virology. 1986 Jan 30;148(2):275–287. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90325-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitou N., Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 Jul;4(4):406–425. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoeyen M., Van Rompuy L., Jou W. M., Huylebroeck D., Fiers W. Complete nucleotide sequence of the influenza B/Singapore/222/79 virus hemagglutinin gene and comparison with the B/Lee/40 hemagglutinin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 25;11(14):4703–4712. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.14.4703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. G., Berton M. T. Analysis of antigenic drift in the haemagglutinin molecule of influenza B virus with monoclonal antibodies. J Gen Virol. 1981 Jun;54(Pt 2):243–251. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-54-2-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita M., Krystal M., Fitch W. M., Palese P. Influenza B virus evolution: co-circulating lineages and comparison of evolutionary pattern with those of influenza A and C viruses. Virology. 1988 Mar;163(1):112–122. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90238-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yewdell J. W., Webster R. G., Gerhard W. U. Antigenic variation in three distinct determinants of an influenza type A haemagglutinin molecule. Nature. 1979 May 17;279(5710):246–248. doi: 10.1038/279246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


