Abstract
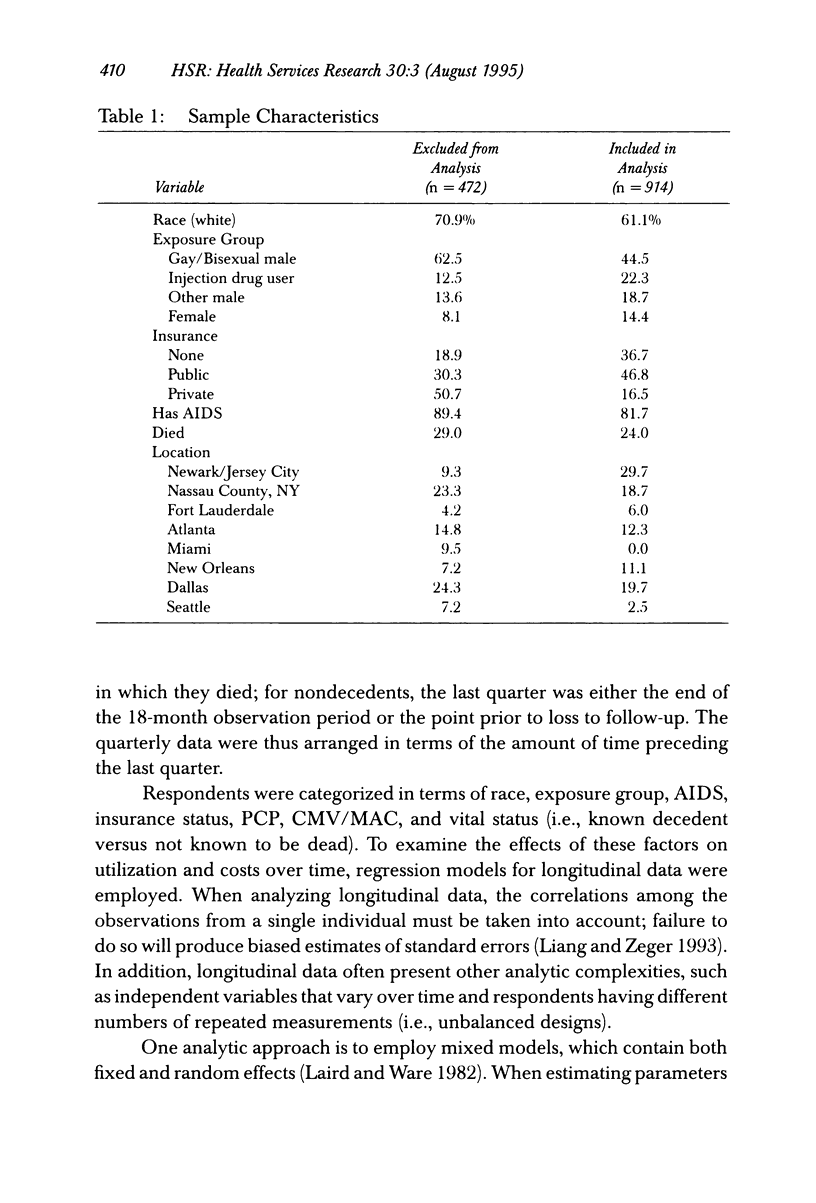
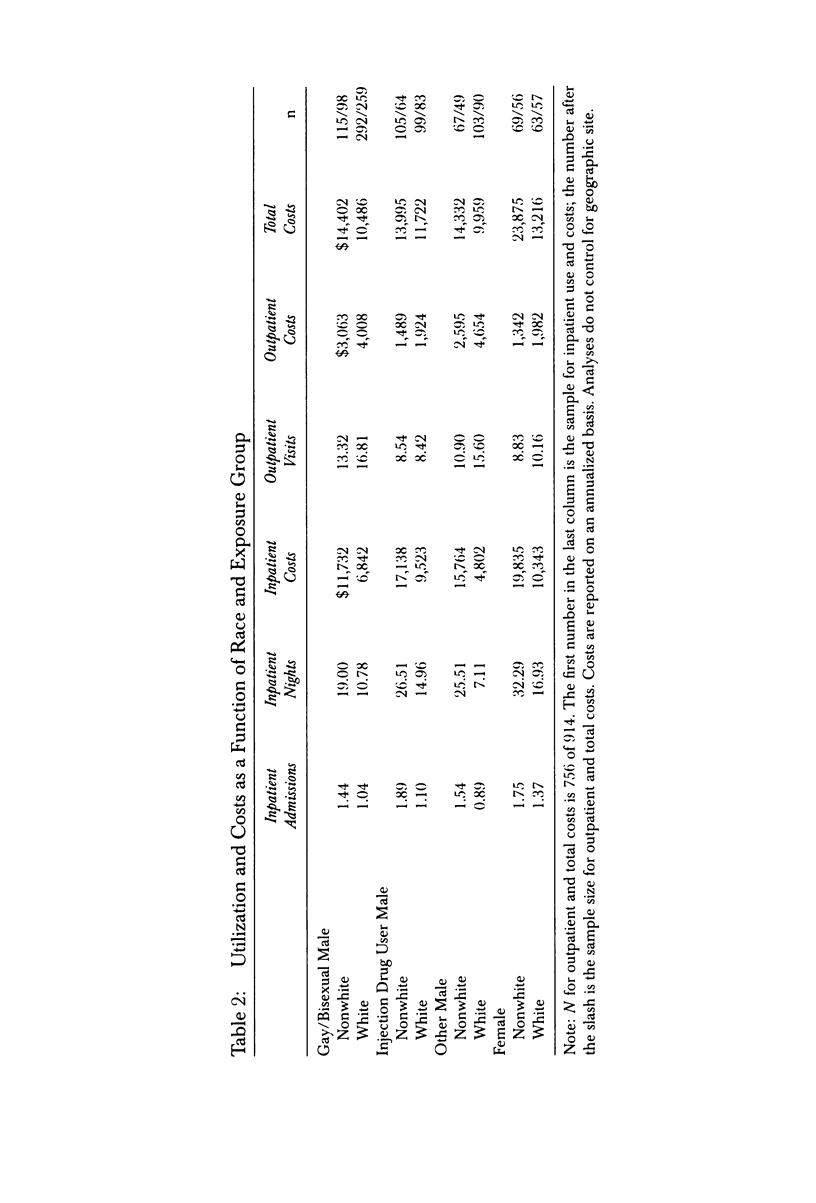
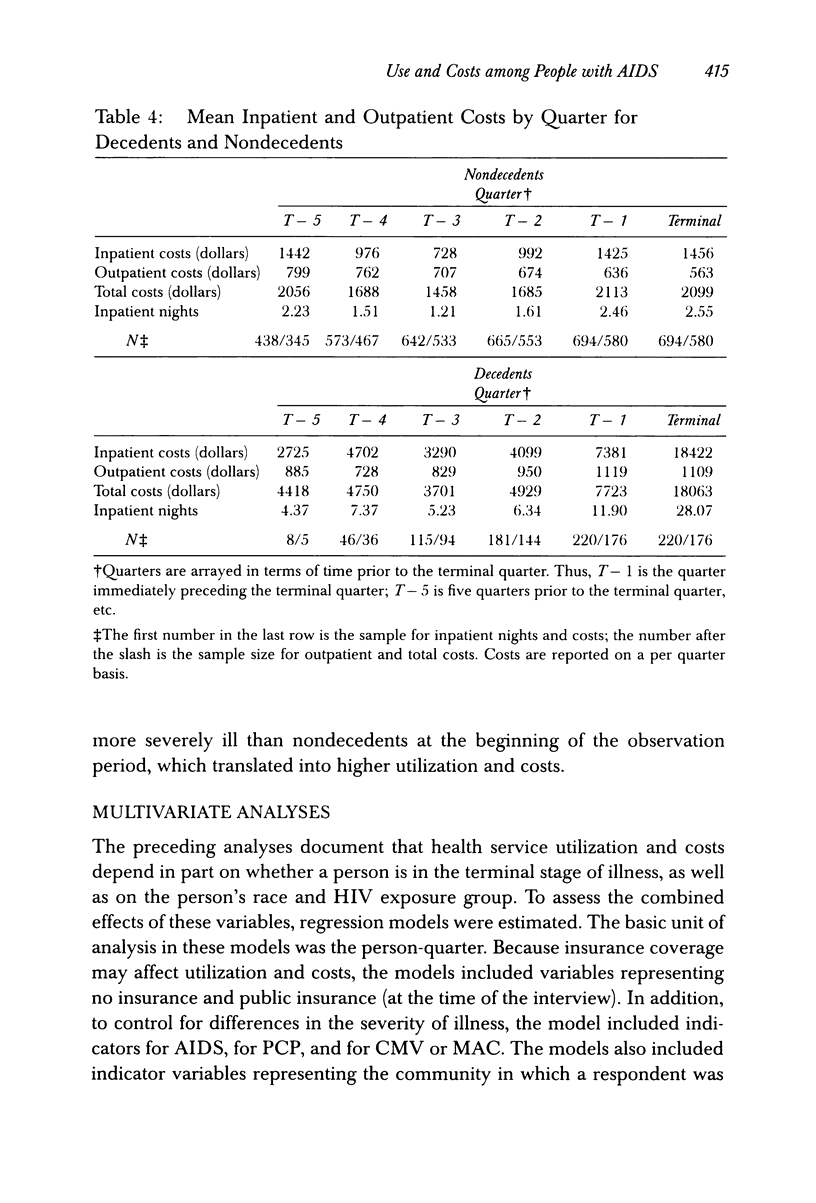
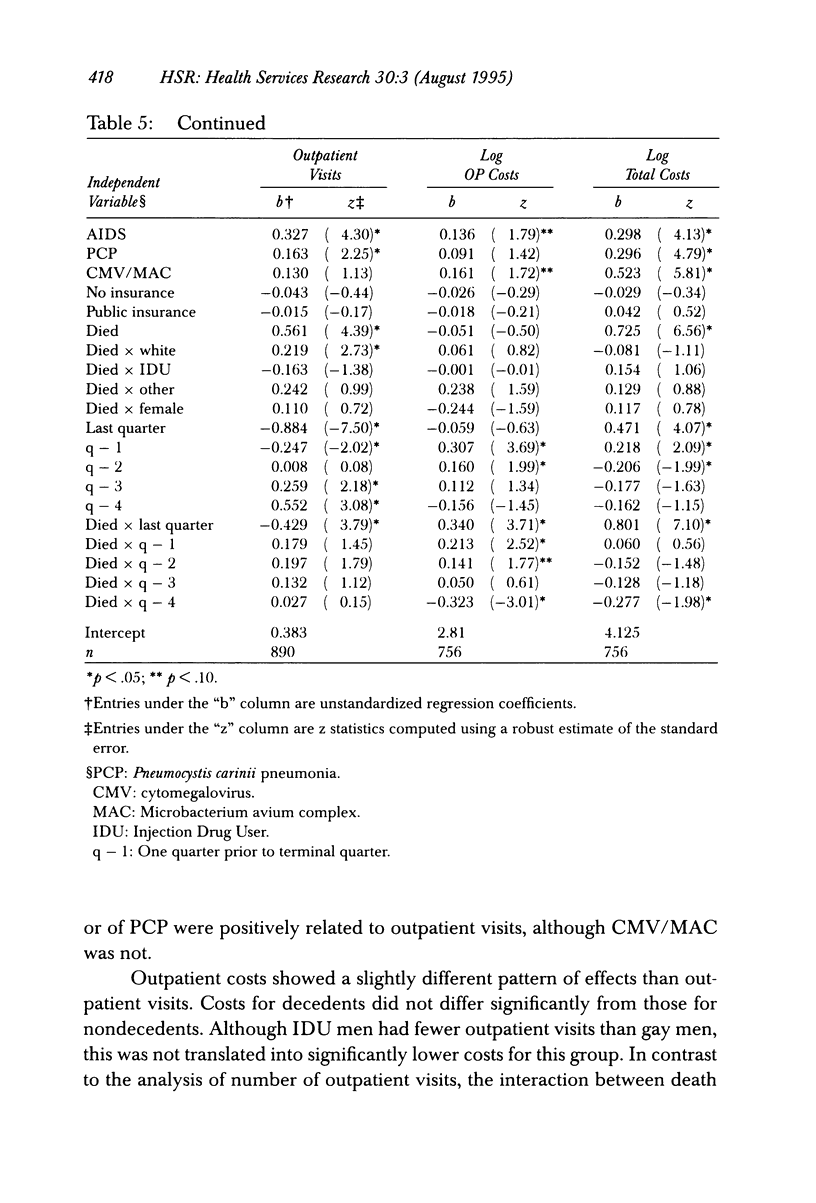
OBJECTIVE. This study examines the effect of race, HIV transmission group, and decedent status on the use and cost of inpatient and outpatient care among people with AIDS. DATA SOURCES. Data come from 914 people with AIDS who were receiving services in nine cities across the United States in 1990-1991 and who indicated that a hospital clinic was their usual source of care. Review of hospital medical and billing records provided data on use and costs of medical services over an 18-month period. Vital status was determined from hospital records and death certificates. STUDY DESIGN. Data from each respondent were aggregated into three-month intervals, beginning with the last quarter of data and working backward. Regression analyses using random-effect models and generalized estimating equations were conducted to assess temporal patterns of inpatient and outpatient use and costs. PRINCIPAL FINDINGS. Inpatient utilization and costs were higher for decedents than for nondecedents. However, differences between decedents and nondecedents varied as a function of race. Nonwhites had more inpatient use and higher costs than whites, but lower outpatient use, and these differences were greater among decedents. Inpatient nights and costs rose sharply in the six months prior to death. Outpatient use and costs did not display as strong a temporal trend. CONCLUSIONS. Much of the cost of treating HIV infection is concentrated in the period immediately preceding death. The intensity of service use in the terminal period should be considered when developing estimates of annual costs of care and when designing programs to provide community-based treatment.
Full text
PDF

















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews R., Keyes M., Pine P. Longitudinal patterns of California Medicaid recipients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Health Care Financ Rev. 1991 Winter;13(2):1–12. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin A. E. Long-term care and AIDS: perspectives from experience with the elderly. Milbank Q. 1988;66(3):415–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett C. L., Cvitanic M., Pascal A. The costs of AIDS in Los Angeles. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1991;4(2):197–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleishman J. A., Hsia D. C., Hellinger F. J. Correlates of medical service utilization among people with HIV infection. Health Serv Res. 1994 Dec;29(5):527–548. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleishman J. A., Mor V., Cwi J. S., Piette J. D. Sampling and accessing people with AIDS. Implications for program evaluation. Eval Health Prof. 1992 Dec;15(4):385–404. doi: 10.1177/016327879201500403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleishman J. A., Mor V. Insurance status among people with AIDS: relationships with sociodemographic characteristics and service use. Inquiry. 1993 Summer;30(2):180–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J., Arno P. S. The 'Medicaidization' of AIDS. Trends in the financing of HIV-related medical care. JAMA. 1990 Sep 12;264(10):1261–1266. doi: 10.1001/jama.264.10.1261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellinger F. J., Fleishman J. A., Hsia D. C. AIDS treatment costs during the last months of life: evidence from the ACSUS. Health Serv Res. 1994 Dec;29(5):569–581. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellinger F. J. The lifetime cost of treating a person with HIV. JAMA. 1993 Jul 28;270(4):474–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jellinek P. S. Case-managing AIDS. Issues Sci Technol. 1988 Summer;4(4):59–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. J., Chu S. Y., Buehler J. W. AIDS deaths shift from hospital to home. AIDS Mortality Project Group. Am J Public Health. 1993 Oct;83(10):1433–1437. doi: 10.2105/ajph.83.10.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird N. M., Ware J. H. Random-effects models for longitudinal data. Biometrics. 1982 Dec;38(4):963–974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubitz J. D., Riley G. F. Trends in Medicare payments in the last year of life. N Engl J Med. 1993 Apr 15;328(15):1092–1096. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199304153281506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merzel C., Crystal S., Sambamoorthi U., Karus D., Kurland C. New Jersey's Medicaid waiver for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Health Care Financ Rev. 1992 Spring;13(3):27–44. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. D., Hidalgo J., Sugland B. W., Chaisson R. E. Zidovudine and the natural history of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1991 May 16;324(20):1412–1416. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199105163242006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mor V., Fleishman J. A., Dresser M., Piette J. Variation in health service use among HIV-infected patients. Med Care. 1992 Jan;30(1):17–29. doi: 10.1097/00005650-199201000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mor V., Wilcox V., Rakowski W., Hiris J. Functional transitions among the elderly: patterns, predictors, and related hospital use. Am J Public Health. 1994 Aug;84(8):1274–1280. doi: 10.2105/ajph.84.8.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piette J. D., Mor V., Mayer K., Zierler S., Wachtel T. The effects of immune status and race on health service use among people with HIV disease. Am J Public Health. 1993 Apr;83(4):510–514. doi: 10.2105/ajph.83.4.510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scitovsky A. A., Cline M., Lee P. R. Medical care costs of patients with AIDS in San Francisco. JAMA. 1986 Dec 12;256(22):3103–3106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon D. J., Hogan A. J. HIV infection treatment costs under Medicaid in Michigan. Public Health Rep. 1992 Jul-Aug;107(4):461–468. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector W. D., Mor V. Utilization and charges for terminal cancer patients in Rhode Island. Inquiry. 1984 Winter;21(4):328–337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein M. D., Piette J., Mor V., Wachtel T. J., Fleishman J., Mayer K. H., Carpenter C. C. Differences in access to zidovudine (AZT) among symptomatic HIV-infected persons. J Gen Intern Med. 1991 Jan-Feb;6(1):35–40. doi: 10.1007/BF02599388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temkin-Greener H., Meiners M. R., Petty E. A., Szydlowski J. S. The use and cost of health services prior to death: a comparison of the Medicare-only and the Medicare-Medicaid elderly populations. Milbank Q. 1992;70(4):679–701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeger S. L., Liang K. Y., Albert P. S. Models for longitudinal data: a generalized estimating equation approach. Biometrics. 1988 Dec;44(4):1049–1060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


