Abstract
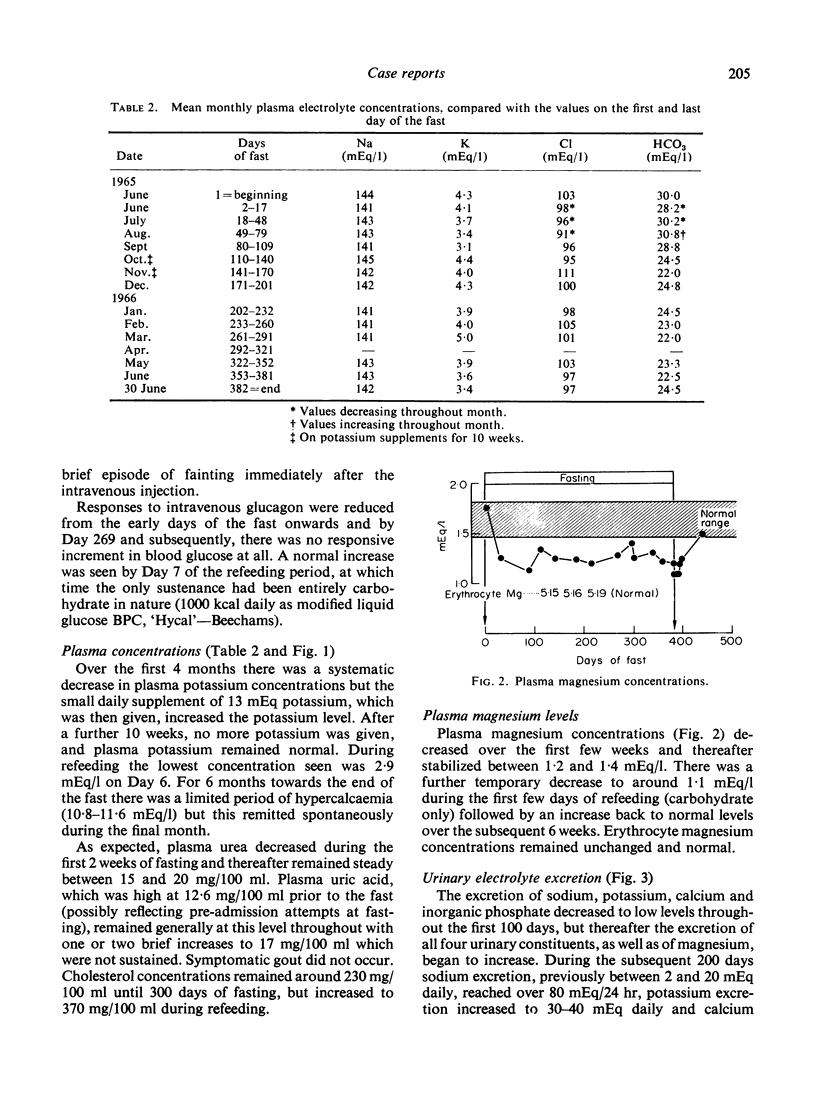
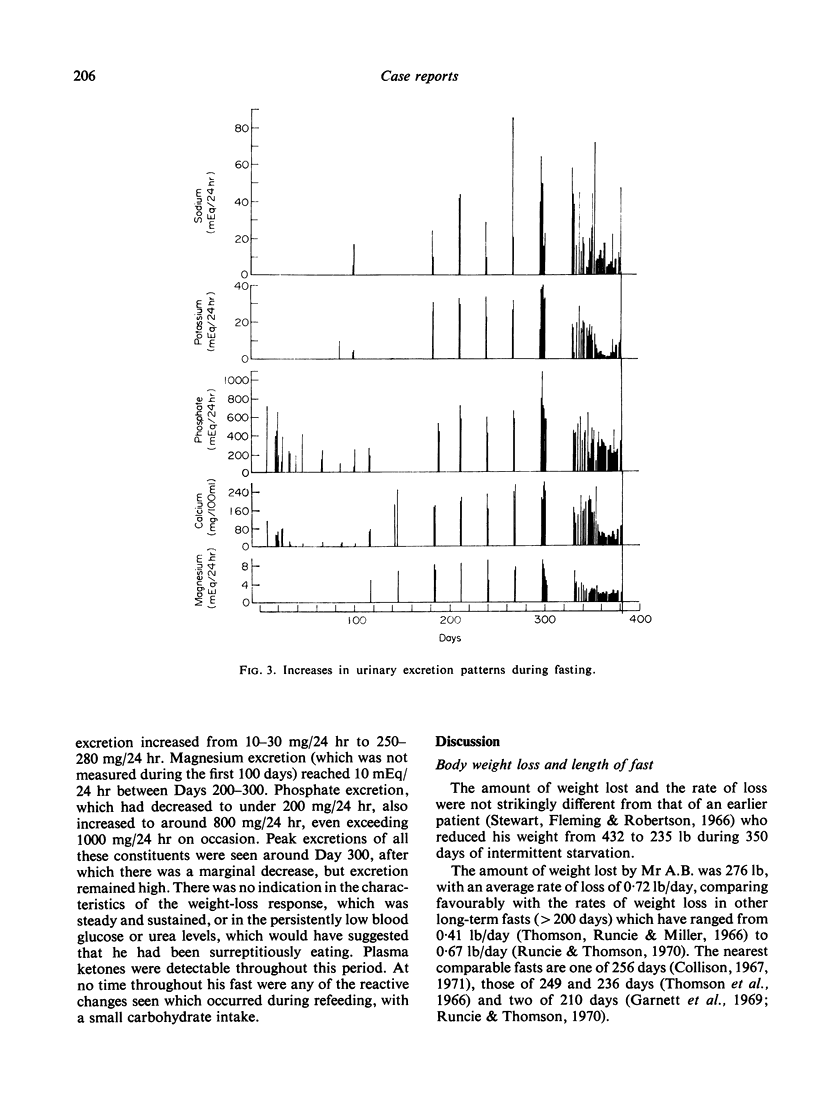
A 27-year-old male patient fasted under supervision for 382 days and has subsequently maintained his normal weight. Blood glucose concentrations around 30 mg/100 ml were recorded consistently during the last 8 months, although the patient was ambulant and attending as an out-patient. Responses to glucose and tolbutamide tolerance tests remained normal. The hyperglycaemic response to glucagon was reduced and latterly absent, but promptly returned to normal during carbohydrate refeeding. After an initial decrease was corrected, plasma potassium levels remained normal without supplementation. A temporary period of hypercalcaemia occurred towards the end of the fast. Decreased plasma magnesium concentrations were a consistent feature from the first month onwards. After 100 days of fasting there was a marked and persistent increase in the excretion of urinary cations and inorganic phosphate, which until then had been minimal. These increases may be due to dissolution of excessive soft tissue and skeletal mass. Prolonged fasting in this patient had no ill-effects.
Full text
PDF
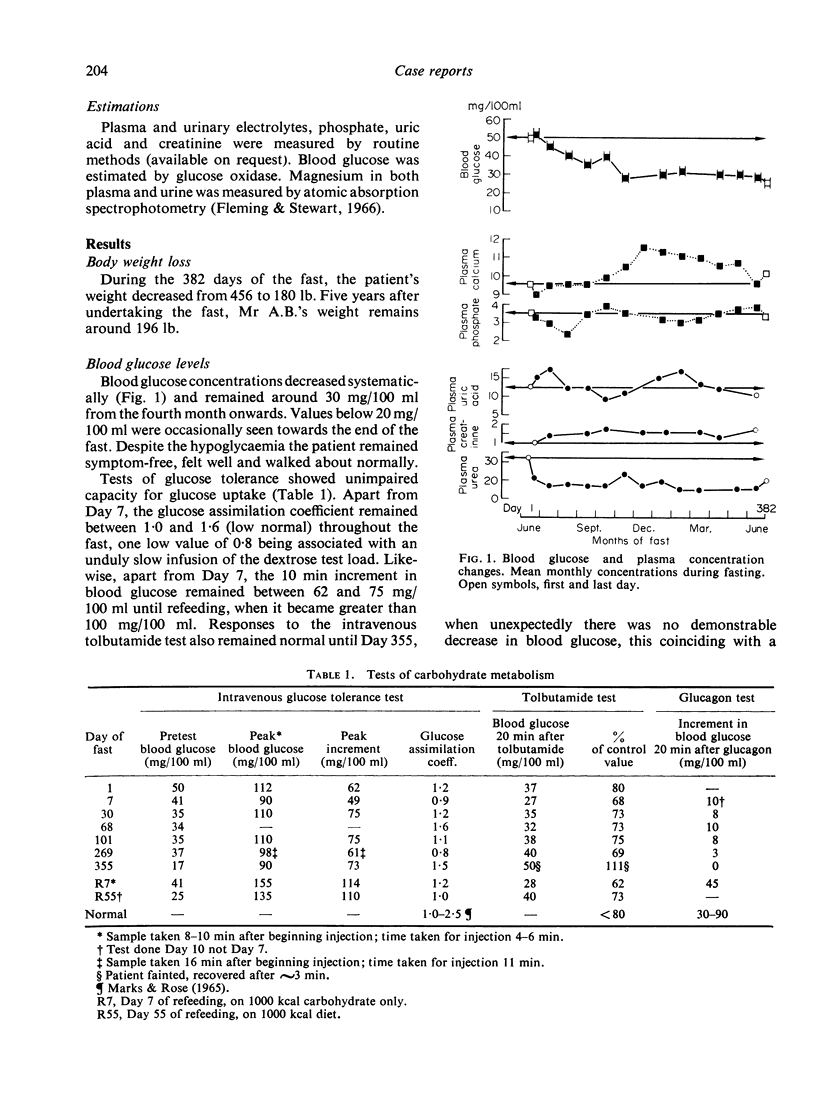



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. W., Herman R. H., Newcomer K. L. Improvement in glucose tolerance of fasting obese patients given oral potassium. Am J Clin Nutr. 1969 Dec;22(12):1589–1596. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/22.12.1589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUBBERLEY P. T., POLSTER S. A., SCHULMAN C. L. LACTIC ACIDOSIS AND DEATH AFTER THE TREATMENT OF OBESITY BY FASTING. N Engl J Med. 1965 Mar 25;272:628–630. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196503252721208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRENICK E. J., SWENDSEID M. E., BLAHD W. H., TUTTLE S. G. PROLONGED STARVATION AS TREATMENT FOR SEVERE OBESITY. JAMA. 1964 Jan 11;187:100–105. doi: 10.1001/jama.1964.03060150024006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drenick E. J., Hunt I. F., Swendseid M. E. Magnesium depletion during prolonged fasting of obese males. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 Oct;29(10):1341–1348. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-10-1341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming L. W., Stewart W. K. The effect of the atomiser on the estimation of magnesium by atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Clin Chim Acta. 1966 Jul;14(1):131–134. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(66)90075-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnett E. S., Barnard D. L., Ford J., Goodbody R. A., Woodehouse M. A. Gross fragmentation of cardiac myofibrils after therapeutic starvation for obesity. Lancet. 1969 May 3;1(7601):914–916. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)92546-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson I. M., McKiddie M. T., Buchanan K. D. Effect of fasting on glucose and insulin metabolism of obese patients. Lancet. 1969 Feb 8;1(7589):285–287. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson I. M., McKiddie M. T., Buchanan K. D. The effect of prolonged fasting on carbohydrate metabolism: evidence for heterogeneity in obesity. J Endocrinol. 1968 Feb;40(2):259–260. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0400259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawlor T., Wells D. G. Fasting as a treatment of obesity. Postgrad Med J. 1971 Jun;47(Suppl):452–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro J. F., Maccuish A. C., Goodall J. A., Fraser J., Duncan L. J. Further experience with prolon- ged therapeutic starvation in gross refractory obesity. Br Med J. 1970 Dec 19;4(5737):712–714. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5737.712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPOPORT A., FROM G. L., HUSDAN H. METABOLIC STUDIES IN PROLONGED FASTING. I. INORGANIC METABOLISM AND KIDNEY FUNCTION. Metabolism. 1965 Jan;14:31–46. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(65)90079-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooth G., Carlström S. Therapeutic fasting. Acta Med Scand. 1970 Jun;187(6):455–463. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1970.tb02970.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runcie J., Thomson T. J. Prolonged starvation--a dangerous procedure? Br Med J. 1970 Aug 22;3(5720):432–435. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5720.432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schless G. L., Duncan G. G. The beneficial effect of intermittent total fasts on the glucose tolerance in obese diabetic patients. Metabolism. 1966 Feb;15(2):98–102. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(66)90029-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer I. O. Death during therapeutic starvation for obesity. Lancet. 1968 Jun 15;1(7555):1288–1290. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92299-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart W. K., Fleming L. W. Fragmentation of cardiac myofibrils after therapeutic starvation. Lancet. 1969 Jun 7;1(7606):1154–1154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart W. K., Fleming L. W., Robertson P. C. Massive obesity treated by intermittent fasting. A metabolic and clinical study. Am J Med. 1966 Jun;40(6):967–986. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(66)90209-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson T. J., Runcie J., Miller V. Treatment of obesity by total fasting for up to 249 days. Lancet. 1966 Nov 5;2(7471):992–996. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)92925-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildenhoff K. E., Dalsager H. H., Schwartz Sorensen N. Ketonstoffer i blod og urin hos overvaegtige patienter behandlet med absolut faste. Nord Med. 1969 Sep 25;82(39):1201–1208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



