Abstract
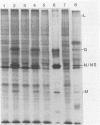
We examined the inductive signals necessary to render B lymphocytes capable of supporting a productive vesicular stomatitis virus infection. Small murine splenic B cells in the G0 phase of the cell cycle were cultured with stimulators which allow progression through various stages in the activation and/or differentiation pathway leading to antibody secretion. We found that vesicular stomatitis virus expression is dependent on the state of B-cell activation and that three distinct phases can be defined. A nonsupportive state, which is defined by the failure to produce infection centers, viral proteins, or PFUs, is characteristic of freshly isolated small B cells, B cells cultured 48 h without further stimulation, or B cells in the G1 phase of the cell cycle induced by culture with T-cell-derived lymphokines. This refractory state was not due to a failure of virus uptake. Activation of G0 B cells with anti-immunoglobulin at doses which allow entry into the S phase rendered them capable of synthesizing viral proteins and increased the number of B cells producing infection centers, without enhancing PFU production on a per cell basis. In contrast, B cells stimulated with multiple inductive signals provided by anti-immunoglobulin and lymphokines showed increased infectious particle production (7 PFU per infection center). Lipopolysaccharide stimulation, acting through another induction pathway, caused the maximum increase in the number of infected B cells and production of infectious particles (25 PFU per infection center).
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biron C. A., Welsh R. M. Blastogenesis of natural killer cells during viral infection in vivo. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2788–2795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom B. R., Jimenez L., Marcus P. I. A plaque assay for enumerating antigen-sensitive cells in delayed-type hypersensitivity. J Exp Med. 1970 Jul 1;132(1):16–30. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.1.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom B. R., Senik A., Stoner G., Ju G., Nowakowski M., Kano S., Jimenez L. Studies on the interactions between viruses and lymphocytes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1977;41(Pt 1):73–83. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1977.041.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce J., Symington F. W., McKearn T. J., Sprent J. A monoclonal antibody discriminating between subsets of T and B cells. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2496–2501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casali P., Notkins A. L. Probing the human B-cell repertoire with EBV: polyreactive antibodies and CD5+ B lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:513–535. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.002501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatis P. A., Morrison T. G. Mutational changes in the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein affect the requirement of carbohydrate in morphogenesis. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):307–316. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.307-316.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman R. L., Weissman I. L. B220: a B cell-specific member of th T200 glycoprotein family. Nature. 1981 Feb 19;289(5799):681–683. doi: 10.1038/289681a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper N. R., Moore M. D., Nemerow G. R. Immunobiology of CR2, the B lymphocyte receptor for Epstein-Barr virus and the C3d complement fragment. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:85–113. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.000505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford D. H., Ando I. EB virus induction is associated with B-cell maturation. Immunology. 1986 Nov;59(3):405–409. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creager R. S., Cardamone J. J., Jr, Youngner J. S. Human lymphoblastoid cell lines of B- and T-cell origin: different responses to infection with vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1981 May;111(1):211–222. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90666-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFranco A. L. Molecular aspects of B-lymphocyte activation. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:143–178. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.001043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defranco A. L., Raveche E. S., Asofsky R., Paul W. E. Frequency of B lymphocytes responsive to anti-immunoglobulin. J Exp Med. 1982 May 1;155(5):1523–1536. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.5.1523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman R., Wheelock E. F. Vesicular stomatitis virus replication in human leukocyte cultures: enhancement by phytohemagglutinin. Science. 1966 Nov 25;154(3752):1053–1055. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3752.1053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flahart R. E., Lawton A. R. Mechanism of suppression of lipopolysaccharide-driven B cell differentiation by anti-mu antibodies. Evidence for a trans-acting repressor of transcription. J Exp Med. 1987 Oct 1;166(4):864–873. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.4.864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard M., Farrar J., Hilfiker M., Johnson B., Takatsu K., Hamaoka T., Paul W. E. Identification of a T cell-derived b cell growth factor distinct from interleukin 2. J Exp Med. 1982 Mar 1;155(3):914–923. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.3.914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez L., Bloom B. R., Blume M. R., Oettgen H. F. On the number and nature of antigen-sensitive lymphocytes in the blood of delayed-hypersensitive human donors. J Exp Med. 1971 Apr 1;133(4):740–751. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.4.740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kano S., Bloom B. R., Howe M. L. Enumeration of activated thymus-derived lymphocytes by the virus plaque assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2299–2303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kincade P. W., Lee G., Watanabe T., Sun L., Scheid M. P. Antigens displayed on murine B lymphocyte precursors. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2262–2268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurt-Jones E. A., Hamberg S., Ohara J., Paul W. E., Abbas A. K. Heterogeneity of helper/inducer T lymphocytes. I. Lymphokine production and lymphokine responsiveness. J Exp Med. 1987 Dec 1;166(6):1774–1787. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.6.1774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landolfo S., Gariglio M., Gribaudo G., Jemma C., Giovarelli M., Cavallo G. Interferon-gamma is not an antiviral, but a growth-promoting factor for T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Apr;18(4):503–509. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshak-Rothstein A., Fink P., Gridley T., Raulet D. H., Bevan M. J., Gefter M. L. Properties and applications of monoclonal antibodies directed against determinants of the Thy-1 locus. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2491–2497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshak-Rothstein A., Siekevitz M., Margolies M. N., Mudgett-Hunter M., Gefter M. L. Hybridoma proteins expressing the predominant idiotype of the antiazophenylarsonate response of A/J mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1120–1124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McChesney M. B., Oldstone M. B. Viruses perturb lymphocyte functions: selected principles characterizing virus-induced immunosuppression. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:279–304. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.001431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Cherwinski H., Bond M. W., Giedlin M. A., Coffman R. L. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2348–2357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowakowski M., Bloom B. R., Ehrenfeld E., Summers D. F. Restricted replication of vesicular stomatitis virus in human lymphoblastoid cells. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1272–1278. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1272-1278.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowakowski M., Feldman J. D., Kano S., Bloom B. R. The production of vesicular stomatitis virus by antigen- or mitogen-stimulated lymphocytes and continuous lymphoblastoid lines. J Exp Med. 1973 Apr 1;137(4):1042–1059. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.4.1042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Garra A., Umland S., De France T., Christiansen J. 'B-cell factors' are pleiotropic. Immunol Today. 1988 Feb;9(2):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91259-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olding L. B., Jensen F. C., Oldstone M. B. Pathogenesis of of cytomegalovirus infection. I. Activation of virus from bone marrow-derived lymphocytes by in vitro allogenic reaction. J Exp Med. 1975 Mar 1;141(3):561–572. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.3.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozato K., Mayer N., Sachs D. H. Hybridoma cell lines secreting monoclonal antibodies to mouse H-2 and Ia antigens. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):533–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker D. C., Wadsworth D. C., Schneider G. B. Activation of murine B lymphocytes by anti-immunoglobulin is an inductive signal leading to immunoglobulin secretion. J Exp Med. 1980 Jul 1;152(1):138–150. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.1.138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W. E. Pleiotropy and redundancy: T cell-derived lymphokines in the immune response. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):521–524. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90121-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips N. E., Parker D. C. Cross-linking of B lymphocyte Fc gamma receptors and membrane immunoglobulin inhibits anti-immunoglobulin-induced blastogenesis. J Immunol. 1984 Feb;132(2):627–632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snapper C. M., Finkelman F. D., Paul W. E. Regulation of IgG1 and IgE production by interleukin 4. Immunol Rev. 1988 Feb;102:51–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1988.tb00741.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tony H. P., Phillips N. E., Parker D. C. Role of membrane immunoglobulin (Ig) crosslinking in membrane Ig-mediated, major histocompatibility-restricted T cell-B cell cooperation. J Exp Med. 1985 Nov 1;162(5):1695–1708. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.5.1695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tovey M. G., Lenoir G., Begon-Lours J. Activation of latent Epstein-Barr virus by antibody to human IgM. Nature. 1978 Nov 16;276(5685):270–272. doi: 10.1038/276270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb D. R., Munshi S., Banerjee A. K. Replication of vesicular stomatitis virus in murine spleen cells: enrichment of the virus-replicating lymphocytes and analysis of replication restriction. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):169–172. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.169-172.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weck P. K., Wagner R. R. Inhibition of RNA synthesis in mouse myeloma cells infected with vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1978 Mar;25(3):770–780. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.3.770-780.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheelock E. F., Toy S. T. Participation of lymphocytes in viral infections. Adv Immunol. 1973;16:123–184. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60297-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]