Abstract
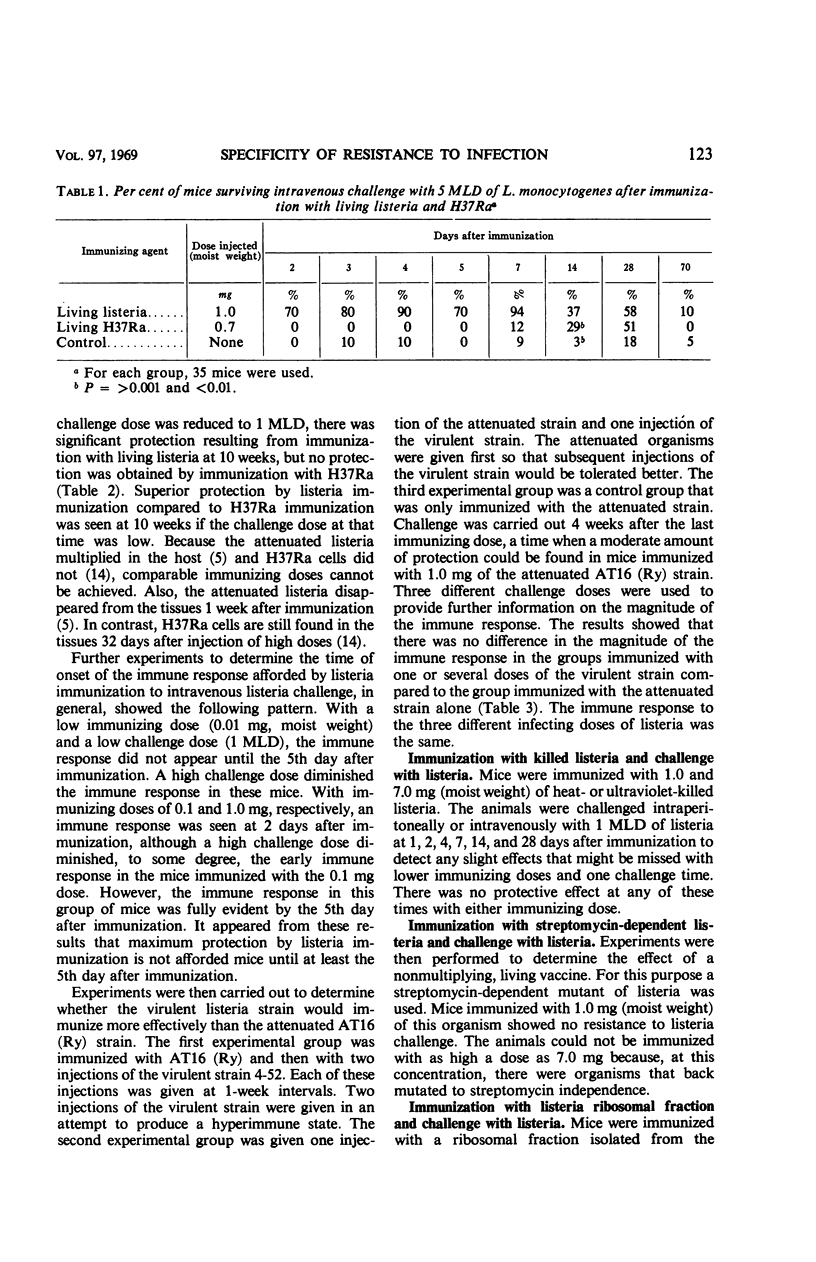
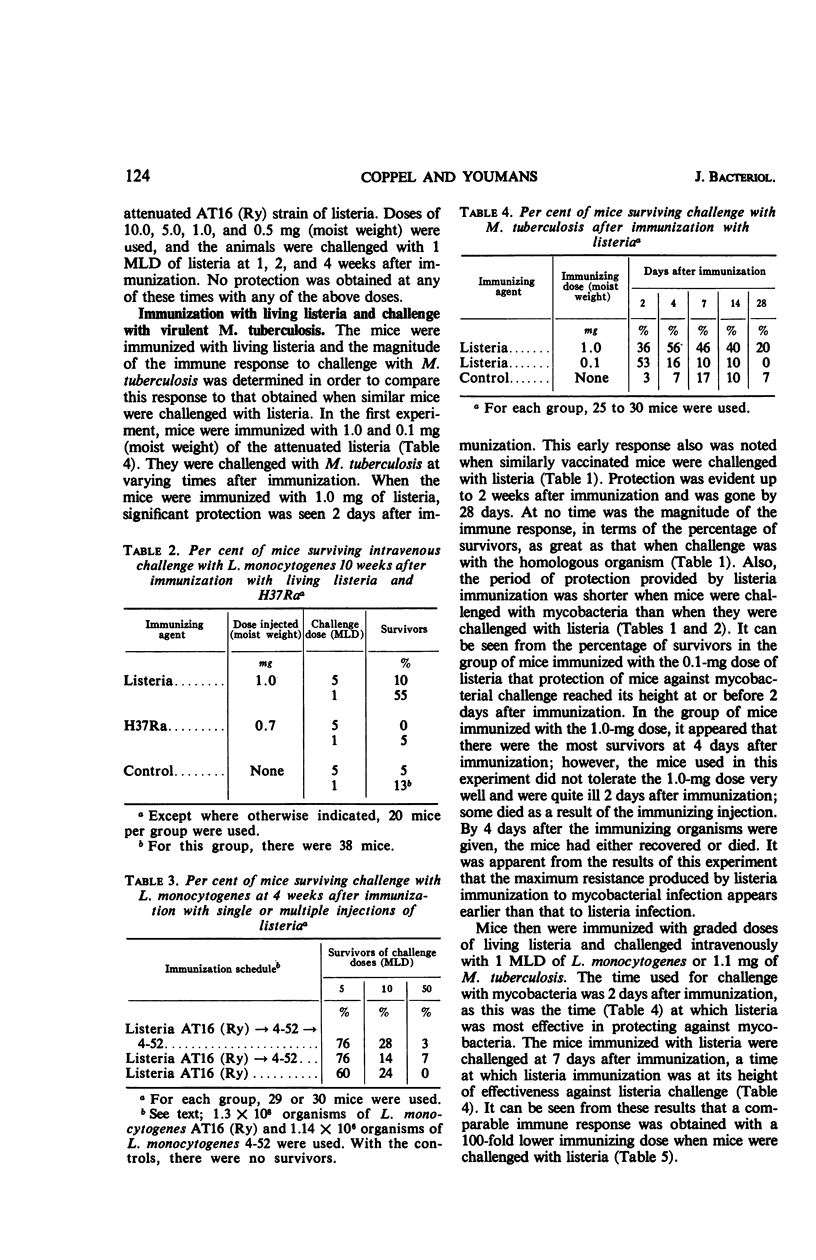
Mice were immunized with 1.0 mg of an attenuated strain of Listeria monocytogenes to determine the period of protection afforded by this strain when the mice were challenged intravenously with 5 MLD of listeria. Protection appeared 2 days after immunization and was still apparent 4 weeks after immunization. If the challenge dose was decreased to 1 MLD, protection was apparent at 10 weeks. Mice immunized with a comparable dose of mycobacterial cells and challenged intravenously with 1 MLD of listeria showed no protection at 10 weeks. The magnitude of the immune response to listeria challenge was not increased in mice immunized with the same virulent strain as that used for challenge. It was also found that resistance to listeria challenge appeared early after listeria immunization if the immunizing dose was large. As the immunizing dose was decreased and the challenge dose increased, resistance appeared later. Listeria killed by heat or ultraviolet irradiation, living but nonmultiplying streptomycin-dependent listeria, or listeria ribosomal fraction gave no protection against listeria challenge. The magnitude of the immune responses after listeria immunization to listeria challenge and to mycobacteria challenge were compared. It was found that protection after listeria challenge was of longer duration. In addition, a 100-fold larger vaccinating dose was required to give comparable protection against tuberculous infection.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARMSTRONG A. S., SWORD C. P. CELLULAR RESISTANCE IN LISTERIOSIS. J Infect Dis. 1964 Jun;114:258–264. doi: 10.1093/infdis/114.3.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanden R. V., Mackaness G. B., Collins F. M. Mechanisms of acquired resistance in mouse typhoid. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):585–600. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppel S., Youmans G. P. Specificity of acquired resistance produced by immunization with mycobacterial cells and mycobacterial fractions. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):114–120. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.114-120.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppel S., Youmans G. P. Specificity of the anamnestic response produced by Listeria monocytogenes or Mycobacterium tuberculosis to challenge with Listeria monocytogenes. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):127–133. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.127-133.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOS R. J., SCHAEDLER R. W., BOHME D. Effects of bacterial endotoxins on susceptibility to infection with gram-positive and acid-fast bacteria. Fed Proc. 1957 Sep;16(3):856–857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauve R. M., Bouanchaud D., Delaunay A. Résistance cellulaire à l'infection bactérienne. IV. Immunisation active et résistance des macrophages de souris NCS à la multiplication intracellulaire de Listeria monocytogenes, Corynebacterium kutscheri et Brucella melitensis. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1966 Mar;110(3 Suppl):106–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOOK E. W., WAGNER R. R. The resistance-promoting activity of endotoxins and other microbial products. I. Their effect on Salmonella typhosa infections of mice. J Immunol. 1959 Sep;83:302–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klasky S., Pickett M. J. Immunogenicity and specificity of Listeria monocytogenes cell walls. J Infect Dis. 1968 Feb;118(1):65–75. doi: 10.1093/infdis/118.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. THE IMMUNOLOGICAL BASIS OF ACQUIRED CELLULAR RESISTANCE. J Exp Med. 1964 Jul 1;120:105–120. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NJOKU-OBI A. N., OSEBOLD J. W. Studies on mechanisms of immunity in listeriosis. I. Interaction of peritoneal exudate cells from sheep with Listeria monocytogenes in vitro. J Immunol. 1962 Aug;89:187–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L., YOUMANS G. P. The enumeration of nonpathogenic viable tubercle bacilli from the organs of mice. Am Rev Tuberc. 1957 Feb;75(2):280–294. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1957.75.2.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUMANS A. S., YOUMANS G. P. IMMUNOGENIC ACTIVITY OF A RIBOSOMAL FRACTION OBTAINED FROM MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1291–1298. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1291-1298.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUMANS A. S., YOUMANS G. P. NATURE OF THE LABILE IMMUNOGENIC SUBSTANCE IN THE PARTICULATE FRACTION ISOLATED FROM MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1030–1037. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1030-1037.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUMANS G. P., YOUMANS A. S. The measurement of the response of immunized mice to infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis va. hominis. J Immunol. 1957 May;78(5):318–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans A. S., Youmans G. P. Preparation and effect of different adjuvants on the immunogenic activity of mycobacterial ribosomal fraction. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):836–843. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.836-843.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans A. S., Youmans G. P. Preparation of highly immunogenic ribosomal fractions of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by use of sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2139–2145. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2139-2145.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans G. P., Youmans A. S. Nonspecific factors in resistance of mice to experimental tuberculosis. J Bacteriol. 1965 Dec;90(6):1675–1681. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.6.1675-1681.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



