Abstract
The pulmonary circuit receives the whole of the cardiac output, and the flow through it is governed by events in the systemic circulation. Its function is gaseous exchange, and the low resistance and high capacitance of the circuit is subservient to this function. Local flow is affected by intra-alveolar oxygen tension, and regional flow by passive hydrostatic effects due to gravity. The distribution of ventilation is also affected by gravity owing to the effect of the latter on regional compliance. When the cardiac output falls, as it does in most methods of induced hypotension, there is an accompanying increase in physiological dead space owing to an increase in the alveolar component.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ECKENHOFF J. E., ENDERBY G. E., LARSON A., EDRIDGE A., JUDEVINE D. E. PULMONARY GAS EXCHANGE DURING DELIBERATE HYPOTENSION. Br J Anaesth. 1963 Dec;35:750–759. doi: 10.1093/bja/35.12.750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOBOL B. J., BOTTEX G., EMIRGIL C., GISSEN H. GASEOUS DIFFUSION FROM ALVEOLI TO PULMONARY VESSELS OF CONSIDERABLE SIZE. Circ Res. 1963 Jul;13:71–79. doi: 10.1161/01.res.13.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
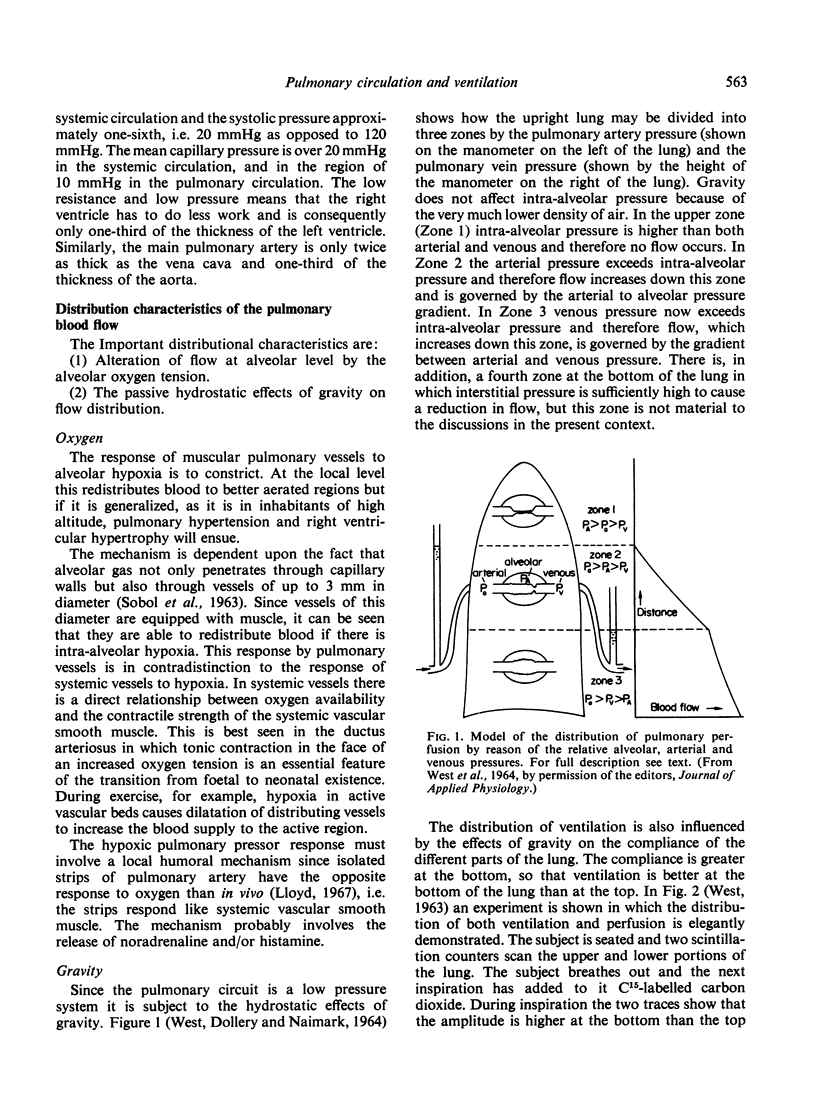
- WEST J. B., DOLLERY C. T., NAIMARK A. DISTRIBUTION OF BLOOD FLOW IN ISOLATED LUNG; RELATION TO VASCULAR AND ALVEOLAR PRESSURES. J Appl Physiol. 1964 Jul;19:713–724. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1964.19.4.713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEST J. B. Distribution of gas and blood in the normal lungs. Br Med Bull. 1963 Jan;19:53–58. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON L. G. The transformation of ancient concepts of respiration in the seventeenth century. Isis. 1960 Jun;51:161–172. doi: 10.1086/348871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


