Abstract
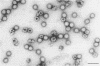
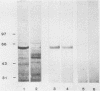
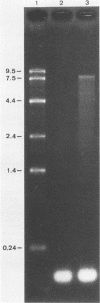
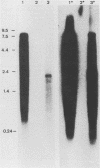
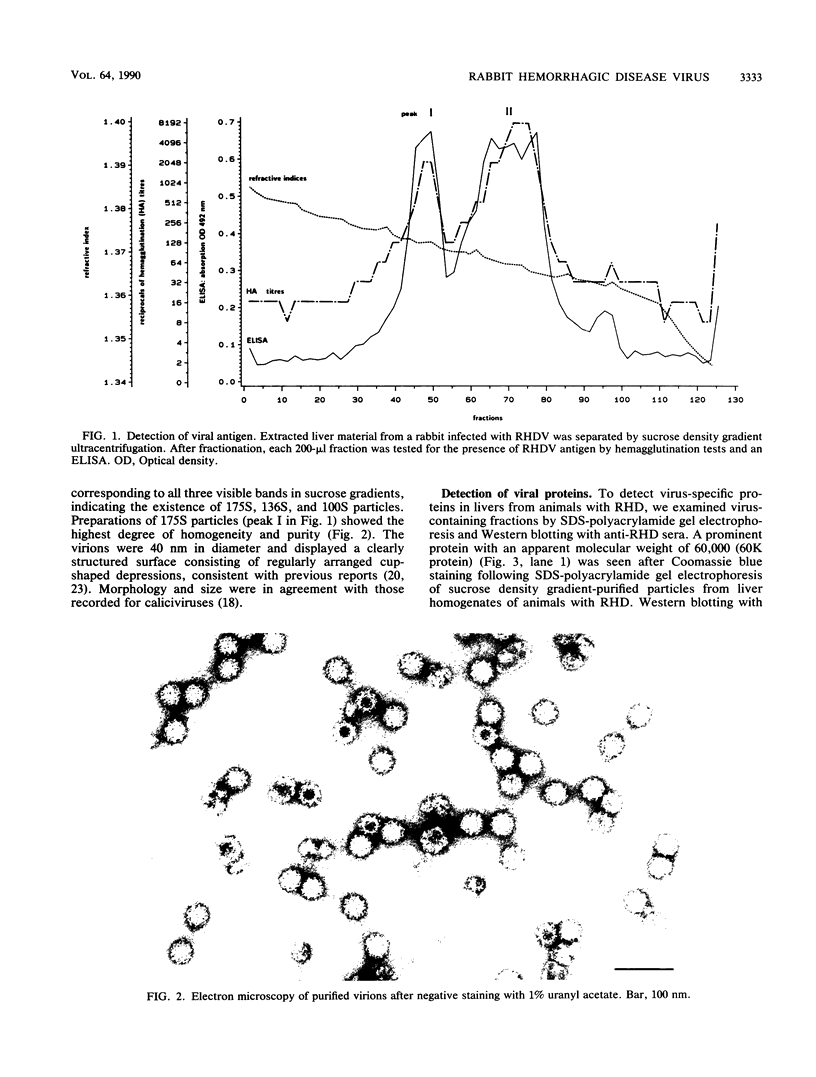
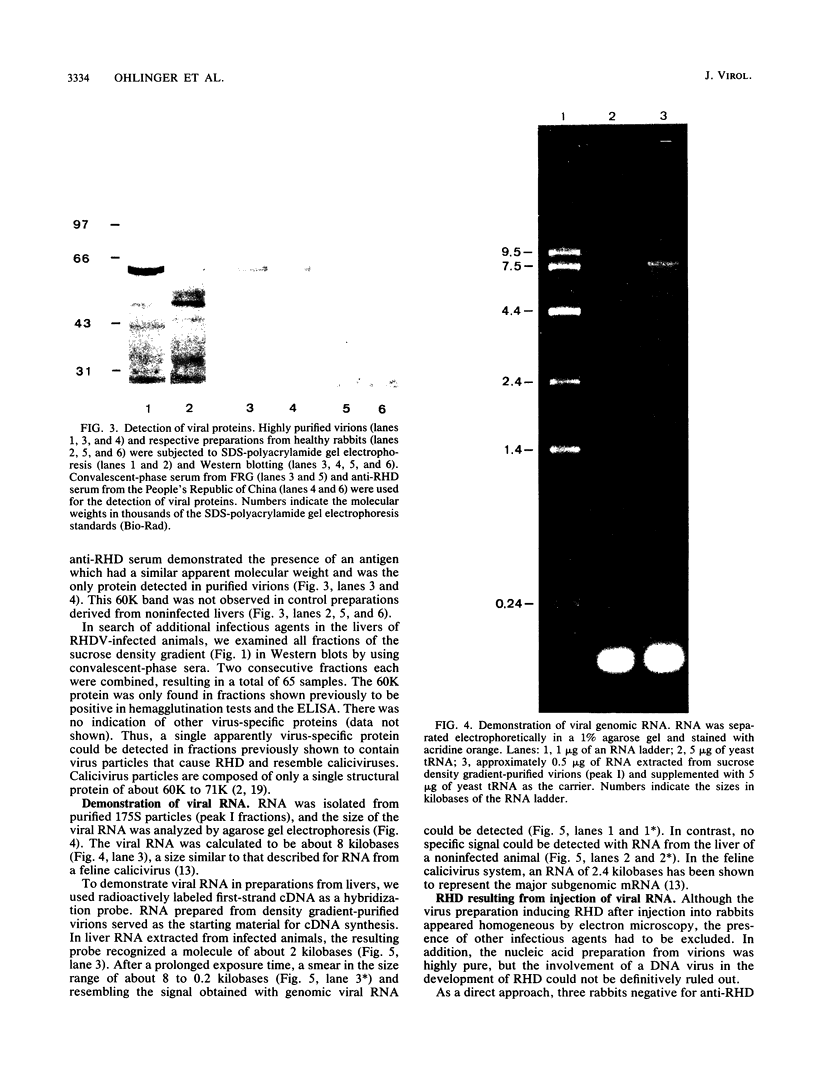
Liver tissue from animals that died of rabbit hemorrhagic disease (RHD) was used to identify the causative agent. After extraction of liver homogenates and sucrose density gradient ultracentrifugation, distinct bands were obtained. The respective gradient fractions reacted positively in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay as well as in hemagglutination assays and were infective for rabbits. These fractions contained virions which had a diameter of 40 nm and resembled morphologically those of the family Caliciviridae. By immunoblotting, a major structural protein with a molecular weight of 60,000 was identified. Highly pure RNA of about 8 kilobases was isolated from virions. Labeled cDNA synthesized from virion RNA detected two RNAs of 8 and 2 kilobases in Northern (RNA) blots of liver RNA from animals infected with RHD virus. Finally, isolated virion RNA injected into the liver of rabbits produced a disease with clinical symptoms and pathological findings typical of RHD. We conclude that a calicivirus represents the causative agent of RHD.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burroughs J. N., Doel T. R., Smale C. J., Brown F. A model for vesicular exanthema virus, the prototype of the calicivirus group. J Gen Virol. 1978 Jul;40(1):161–174. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-40-1-161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael G. G., McMaster G. K. The analysis of nucleic acids in gels using glyoxal and acridine orange. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):380–391. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregg D. A., House C. Necrotic hepatitis of rabbits in Mexico: a parvovirus. Vet Rec. 1989 Dec 9;125(24):603–604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Love D. N., Jones R. F. Studies on the buoyant density of a feline calicivirus. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1974;44(2):142–143. doi: 10.1007/BF01250222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEwen C. R. Tables for estimating sedimentation through linear concentration gradients of sucrose solution. Anal Biochem. 1967 Jul;20(1):114–149. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90271-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neill J. D., Mengeling W. L. Further characterization of the virus-specific RNAs in feline calicivirus infected cells. Virus Res. 1988 Aug;11(1):59–72. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(88)90067-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowlands D. J., Sangar D. V., Brown F. Buoyant density of picornaviruses in caesium salts. J Gen Virol. 1971 Oct;13(1):141–152. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-13-1-141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer F. L., Soergel M. E. Single major polypeptide of a calicivirus: characterization by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and stabilization of virions by cross-linking with dimethyl suberimidate. J Virol. 1976 Sep;19(3):925–931. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.3.925-931.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smíd B., Valícek L., Stepánek J., Jurák E., Rodák L. Experimental transmission and electron microscopic demonstration of the virus of haemorrhagic disease of rabbits in Czechoslovakia. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1989 May;36(3):237–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.1989.tb00597.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Z. J., Chen W. X. Viral haemorrhagic disease in rabbits: a review. Vet Res Commun. 1989;13(3):205–212. doi: 10.1007/BF00142046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Werf S., Bradley J., Wimmer E., Studier F. W., Dunn J. J. Synthesis of infectious poliovirus RNA by purified T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]