Abstract
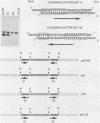
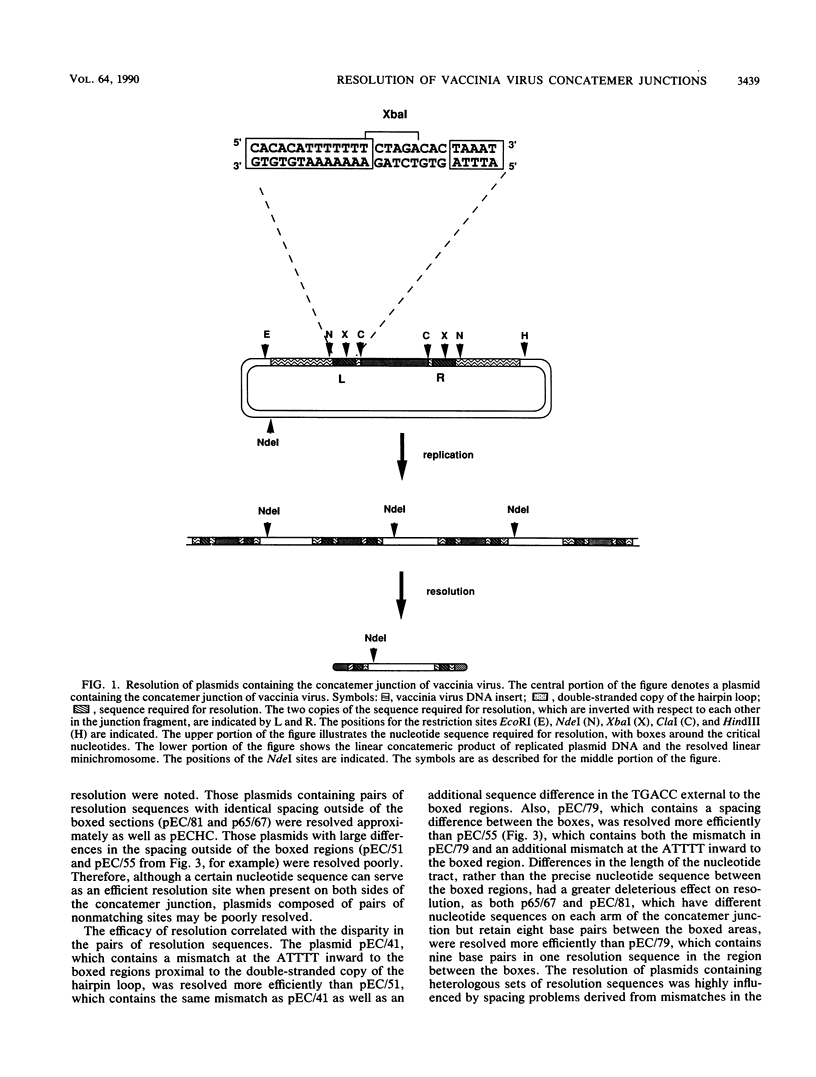
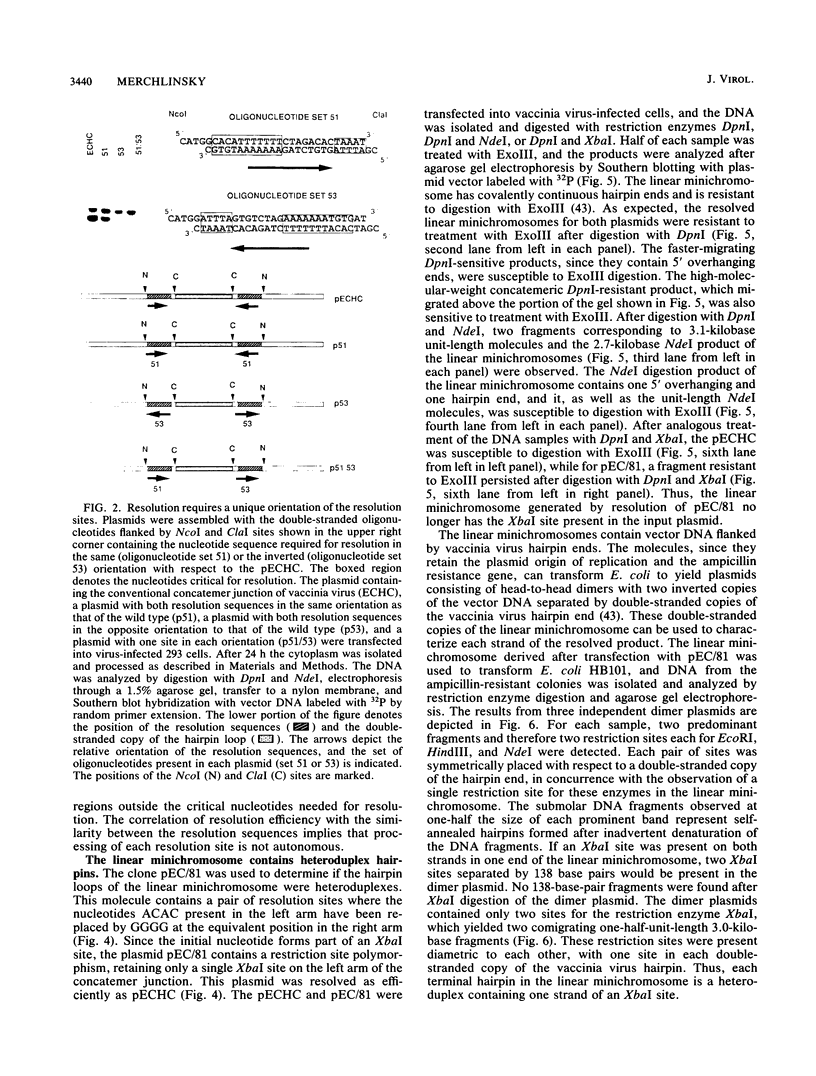
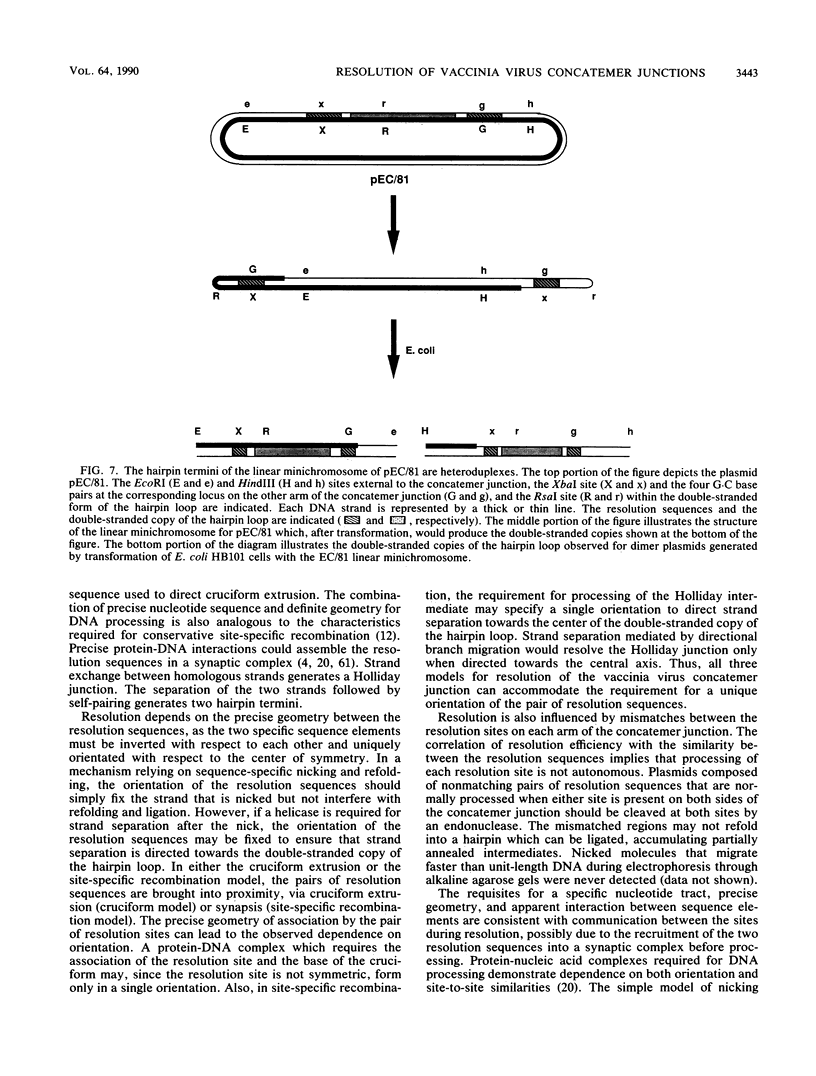
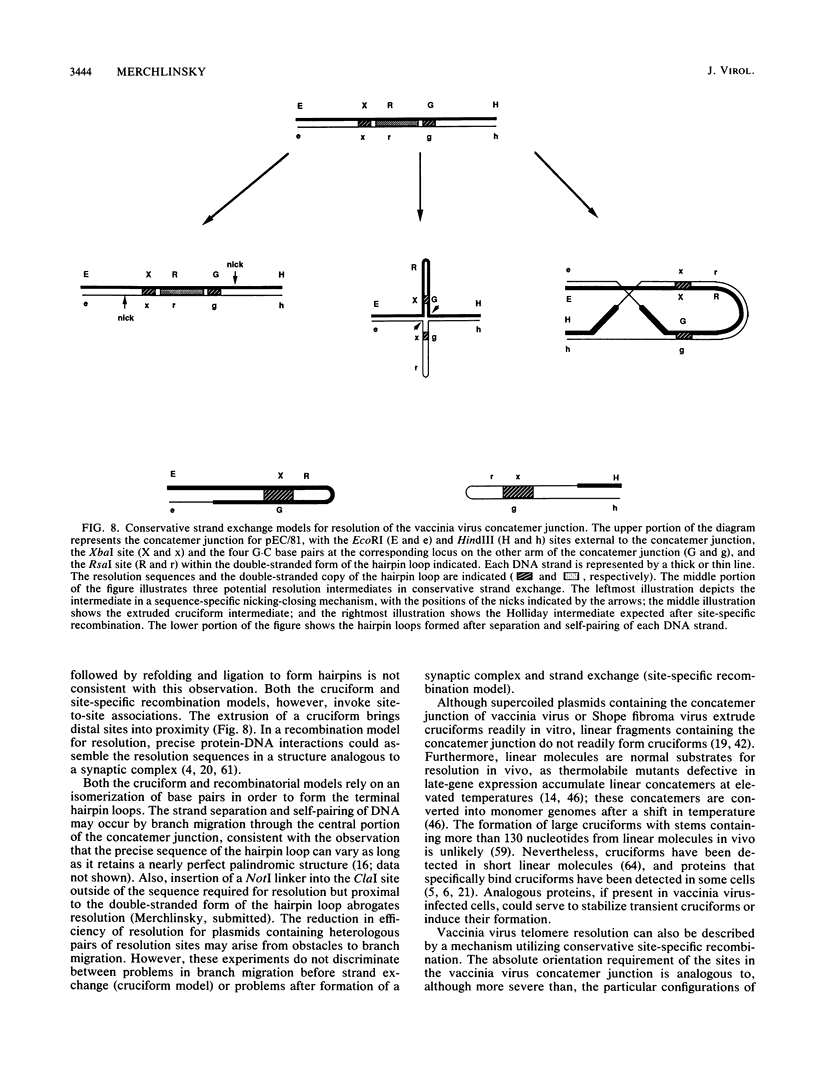
The replication of vaccinia virus proceeds through concatemeric intermediates which are resolved into unit-length DNA. In vaccinia virus-infected cells, plasmids containing the vaccinia virus DNA junction fragment that connects concatemers are resolved into linear minichromosomes of vector DNA flanked by hairpin loops. Resolution requires two copies of a specific nucleotide sequence conserved among poxviruses and found proximal to the hairpin loop. This study demonstrates that orientation of each sequence with respect to the other as well as to the axis of symmetry is critical for resolution, the processing of plasmids containing heterologous pairs of resolution sites is influenced by mismatched nucleotides between the sites, and the vaccinia virus hairpin in the linear minichromosome is a heteroduplex composed of DNA from each strand of the concatemer junction. A model incorporating site-specific recombination and orientated branch migration is proposed to account for resolution of the vaccinia virus concatemer junction.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baroudy B. M., Venkatesan S., Moss B. Incompletely base-paired flip-flop terminal loops link the two DNA strands of the vaccinia virus genome into one uninterrupted polynucleotide chain. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):315–324. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90349-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baroudy B. M., Venkatesan S., Moss B. Structure and replication of vaccinia virus telomeres. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):723–729. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bateman A. J. Letter: Simplification of palindromic telomere theory. Nature. 1975 Jan 31;253(5490):379–380. doi: 10.1038/253379a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin H. W., Cozzarelli N. R. Isolation and characterization of the Tn3 resolvase synaptic intermediate. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1897–1905. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03023.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi M. E., Beltrame M., Paonessa G. Specific recognition of cruciform DNA by nuclear protein HMG1. Science. 1989 Feb 24;243(4894 Pt 1):1056–1059. doi: 10.1126/science.2922595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi M. E. Interaction of a protein from rat liver nuclei with cruciform DNA. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):843–849. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02883.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. Telomeres: do the ends justify the means? Cell. 1984 May;37(1):7–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90295-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn E. H. The molecular structure of centromeres and telomeres. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:163–194. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalier-Smith T. Palindromic base sequences and replication of eukaryote chromosome ends. Nature. 1974 Aug 9;250(5466):467–470. doi: 10.1038/250467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. G-strings at chromosome ends. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):777–778. doi: 10.1038/332777a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D., Kelly T. J. Animal virus DNA replication. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:671–717. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig N. L., Nash H. A. The mechanism of phage lambda site-specific recombination: site-specific breakage of DNA by Int topoisomerase. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):795–803. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90112-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig N. L. The mechanism of conservative site-specific recombination. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:77–105. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.000453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLange A. M. Identification of temperature-sensitive mutants of vaccinia virus that are defective in conversion of concatemeric replicative intermediates to the mature linear DNA genome. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2437–2444. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2437-2444.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLange A. M., McFadden G. Efficient resolution of replicated poxvirus telomeres to native hairpin structures requires two inverted symmetrical copies of a core target DNA sequence. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):1957–1963. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.1957-1963.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLange A. M., McFadden G. Sequence-nonspecific replication of transfected plasmid DNA in poxvirus-infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):614–618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLange A. M., Reddy M., Scraba D., Upton C., McFadden G. Replication and resolution of cloned poxvirus telomeres in vivo generates linear minichromosomes with intact viral hairpin termini. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):249–259. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.249-259.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickie P., Morgan A. R., McFadden G. Cruciform extrusion in plasmids bearing the replicative intermediate configuration of a poxvirus telomere. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 5;196(3):541–558. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echols H. Multiple DNA-protein interactions governing high-precision DNA transactions. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1050–1056. doi: 10.1126/science.2943018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elborough K. M., West S. C. Specific binding of cruciform DNA structures by a protein from human extracts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 11;16(9):3603–3616. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.9.3603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis T. H., Day A. A hairpin plastid genome in barley. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2769–2774. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04566.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. H., Kolodner R. Effect of DNA structure and nucleotide sequence on Holliday junction resolution by a Saccharomyces cerevisiae endonuclease. J Mol Biol. 1988 May 5;201(1):69–80. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90439-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geshelin P., Berns K. I. Characterization and localization of the naturally occurring cross-links in vaccinia virus DNA. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 5;88(4):785–796. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90399-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González A., Talavera A., Almendral J. M., Viñuela E. Hairpin loop structure of African swine fever virus DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):6835–6844. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.17.6835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. A telomeric sequence in the RNA of Tetrahymena telomerase required for telomere repeat synthesis. Nature. 1989 Jan 26;337(6205):331–337. doi: 10.1038/337331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. Identification of a specific telomere terminal transferase activity in Tetrahymena extracts. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):405–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Sakaki Y. Dideoxy sequencing method using denatured plasmid templates. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90403-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauswirth W. W., Berns K. I. Adeno-associated virus DNA replication: nonunit-length molecules. Virology. 1979 Feb;93(1):57–68. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90275-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoess R. H., Abremski K. Mechanism of strand cleavage and exchange in the Cre-lox site-specific recombination system. J Mol Biol. 1985 Feb 5;181(3):351–362. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90224-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Simon M. I. Hin-mediated site-specific recombination requires two 26 bp recombination sites and a 60 bp recombinational enhancer. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):781–791. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi Y., Hirai K., Gunge N., Hishinuma F. Hairpin plasmid--a novel linear DNA of perfect hairpin structure. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1881–1886. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03864.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitts P. A., Symington L. S., Dyson P., Sherratt D. J. Transposon-encoded site-specific recombination: nature of the Tn3 DNA sequences which constitute the recombination site res. EMBO J. 1983;2(7):1055–1060. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01545.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasnow M. A., Cozzarelli N. R. Site-specific relaxation and recombination by the Tn3 resolvase: recognition of the DNA path between oriented res sites. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1313–1324. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90312-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakritz N., Foglesong P. D., Reddy M., Baum S., Hurwitz J., Bauer W. R. A vaccinia virus DNase preparation which cross-links superhelical DNA. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):935–943. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.935-943.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M., Kemper B. Cruciform-resolvase interactions in supercoiled DNA. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):413–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90234-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod M., Craft S., Broach J. R. Identification of the crossover site during FLP-mediated recombination in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae plasmid 2 microns circle. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3357–3367. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merchlinsky M., Garon C. F., Moss B. Molecular cloning and sequence of the concatemer junction from vaccinia virus replicative DNA. Viral nuclease cleavage sites in cruciform structures. J Mol Biol. 1988 Feb 5;199(3):399–413. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90613-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merchlinsky M. Intramolecular homologous recombination in cells infected with temperature-sensitive mutants of vaccinia virus. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2030–2035. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2030-2035.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merchlinsky M., Moss B. Nucleotide sequence required for resolution of the concatemer junction of vaccinia virus DNA. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4354–4361. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4354-4361.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merchlinsky M., Moss B. Resolution of linear minichromosomes with hairpin ends from circular plasmids containing vaccinia virus concatemer junctions. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):879–884. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90562-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merchlinsky M., Moss B. Resolution of vaccinia virus DNA concatemer junctions requires late-gene expression. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1595–1603. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1595-1603.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Kemper B., Hays J., Weisberg R. A. T4 endonuclease VII cleaves holliday structures. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):357–365. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90152-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyer R. W., Graves R. L. The mechanism of cytoplasmic orthopoxvirus DNA replication. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):391–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90422-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A., Robertson C. A. Heteroduplex substrates for bacteriophage lambda site-specific recombination: cleavage and strand transfer products. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3523–3533. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08518.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunes-Düby S. E., Matsumoto L., Landy A. Half-att site substrates reveal the homology independence and minimal protein requirements for productive synapsis in lambda excisive recombination. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):197–206. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90881-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons C. A., West S. C. Resolution of model Holliday junctions by yeast endonuclease is dependent upon homologous DNA sequences. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):621–629. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90474-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard A. E., Cummings D. J. Replication of linear mitochondrial DNA from Paramecium: sequence and structure of the initiation-end crosslink. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7341–7345. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy M. K., Bauer W. R. Activation of the vaccinia virus nicking-joining enzyme by trypsinization. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):443–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. R. Transposon-mediated site-specific recombination: a defined in vitro system. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):713–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90178-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman S., Golder M., Moss B. Insertional mutagenesis of the vaccinia virus gene encoding a type I DNA topoisomerase: evidence that the gene is essential for virus growth. Virology. 1989 May;170(1):302–306. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90384-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman S., Moss B. Identification of a vaccinia virus gene encoding a type I DNA topoisomerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7478–7482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman S. Vaccinia DNA topoisomerase I promotes illegitimate recombination in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3489–3493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinden R. R., Broyles S. S., Pettijohn D. E. Perfect palindromic lac operator DNA sequence exists as a stable cruciform structure in supercoiled DNA in vitro but not in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1797–1801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus S. E., Sebring E. D., Rose J. A. Concatemers of alternating plus and minus strands are intermediates in adenovirus-associated virus DNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):742–746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surette M. G., Buch S. J., Chaconas G. Transpososomes: stable protein-DNA complexes involved in the in vitro transposition of bacteriophage Mu DNA. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90566-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tattersall P., Ward D. C. Rolling hairpin model for replication of parvovirus and linear chromosomal DNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 9;263(5573):106–109. doi: 10.1038/263106a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittek R., Menna A., Müller H. K., Schümperli D., Boseley P. G., Wyler R. Inverted terminal repeats in rabbit poxvirus and vaccinia virus DNA. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):171–181. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.171-181.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xodo L. E., Manzini G., Quadrifoglio F., Yathindra N., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H. A facile duplex-hairpin interconversion through a cruciform intermediate in a linear DNA fragment. J Mol Biol. 1989 Feb 20;205(4):777–781. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90322-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Massy B., Studier F. W., Dorgai L., Appelbaum E., Weisberg R. A. Enzymes and sites of genetic recombination: studies with gene-3 endonuclease of phage T7 and with site-affinity mutants of phage lambda. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:715–726. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]