Abstract
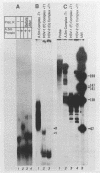
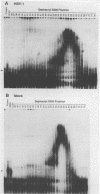
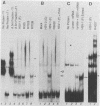
Herpes simplex virus 1- and 2 (HSV-1 and HSV-2)-infected cell extracts but not uninfected cell extracts contain an RNA-binding activity for an in vitro-transcribed sequence from the domains of the HSV-1 US11 and alpha 47 genes. The transcript of this sequence has not been detected in infected cells. The binding is sequence and secondary structure specific and protects approximately 95 nucleotides from RNase digestion. Analyses of HSV-1 x HSV-2 recombinants and HSV-1 deletion mutants mapped the function necessary for activity to the US11 or alpha 47 open reading frame. The alpha 47 gene was excluded, since the RNA-binding activity is a late (gamma 2) function dependent on viral DNA synthesis for its expression. The US11 function is the only viral function required, since translation in rabbit reticulocyte lysate of an in vitro-synthesized US11 mRNA resulted in the appearance of the RNA-binding activity. The product of the US11 open reading frame is associated with the RNA probe-protein complex inasmuch as insertion of a sequence encoding in frame 15 additional amino acids at the C terminus of the US11 protein caused a corresponding decrease in the electrophoretic mobility of the binding complex.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackermann M., Chou J., Sarmiento M., Lerner R. A., Roizman B. Identification by antibody to a synthetic peptide of a protein specified by a diploid gene located in the terminal repeats of the L component of herpes simplex virus genome. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):843–850. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.843-850.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. P., Frink R. J., Devi G. B., Gaylord B. H., Costa R. H., Wagner E. K. Detailed characterization of the mRNA mapping in the HindIII fragment K region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome. J Virol. 1981 Mar;37(3):1011–1027. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.3.1011-1027.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J., Roizman B. Characterization of DNA sequence-common and sequence-specific proteins binding to cis-acting sites for cleavage of the terminal a sequence of the herpes simplex virus 1 genome. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1059–1068. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1059-1068.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J., Roizman B. The herpes simplex virus 1 gene for ICP34.5, which maps in inverted repeats, is conserved in several limited-passage isolates but not in strain 17syn+. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1014–1020. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1014-1020.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J., Roizman B. The terminal a sequence of the herpes simplex virus genome contains the promoter of a gene located in the repeat sequences of the L component. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):629–637. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.629-637.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalziel R. G., Marsden H. S. Identification of two herpes simplex virus type 1-induced proteins (21K and 22K) which interact specifically with the a sequence of herpes simplex virus DNA. J Gen Virol. 1984 Sep;65(Pt 9):1467–1475. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-9-1467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ejercito P. M., Kieff E. D., Roizman B. Characterization of herpes simplex virus strains differing in their effects on social behaviour of infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1968 May;2(3):357–364. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-2-3-357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland L. E., Sandri-Goldin R. M., Goldin A. L., Glorioso J. C., Levine M. Transcriptional and genetic analyses of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome: coordinates 0.29 to 0.45. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):947–959. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.947-959.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. I. Cascade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.8-19.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis: sequential transition of polypeptide synthesis requires functional viral polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1276–1280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubenthal-Voss J., Houghten R. A., Pereira L., Roizman B. Mapping of functional and antigenic domains of the alpha 4 protein of herpes simplex virus 1. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):454–462. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.454-462.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. A., MacLean C., Marsden H. S., Dalziel R. G., Everett R. D. The product of gene US11 of herpes simplex virus type 1 is expressed as a true late gene. J Gen Virol. 1986 May;67(Pt 5):871–883. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-5-871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Alpha 4, the major regulatory protein of herpes simplex virus type 1, is stably and specifically associated with promoter-regulatory domains of alpha genes and of selected other viral genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3218–3222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwong A. D., Kruper J. A., Frenkel N. Herpes simplex virus virion host shutoff function. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):912–921. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.912-921.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Bindereif A., Green M. R. A small-scale procedure for preparation of nuclear extracts that support efficient transcription and pre-mRNA splicing. Gene Anal Tech. 1988 Mar-Apr;5(2):22–31. doi: 10.1016/0735-0651(88)90023-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibold E. A., Munro H. N. Cytoplasmic protein binds in vitro to a highly conserved sequence in the 5' untranslated region of ferritin heavy- and light-subunit mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2171–2175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker R., Roizman B. Clustering of genes dispensable for growth in culture in the S component of the HSV-1 genome. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):573–576. doi: 10.1126/science.3033823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLean C. A., Rixon F. J., Marsden H. S. The products of gene US11 of herpes simplex virus type 1 are DNA-binding and localize to the nucleoli of infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jul;68(Pt 7):1921–1937. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-7-1921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavromara-Nazos P., Ackermann M., Roizman B. Construction and properties of a viable herpes simplex virus 1 recombinant lacking coding sequences of the alpha 47 gene. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):807–812. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.807-812.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Davison A. J., Dolan A., Frame M. C., McNab D., Perry L. J., Scott J. E., Taylor P. The complete DNA sequence of the long unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1531–1574. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dolan A., Donald S., Rixon F. J. Sequence determination and genetic content of the short unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 5;181(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90320-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan J., Simpson S., Clements J. B. Herpes simplex virus induces a processing factor that stimulates poly(A) site usage. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1093–1105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90765-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meignier B., Longnecker R., Mavromara-Nazos P., Sears A. E., Roizman B. Virulence of and establishment of latency by genetically engineered deletion mutants of herpes simplex virus 1. Virology. 1988 Jan;162(1):251–254. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90417-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen D. A., Shapiro D. J. Preparation of capped RNA transcripts using T7 RNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 25;14(14):5936–5936. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.14.5936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Roizman B. A generalized technique for deletion of specific genes in large genomes: alpha gene 22 of herpes simplex virus 1 is not essential for growth. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):227–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90247-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puvion-Dutilleul F., Pichard E., Sheldrick P., Amalric F., Puvion E. Appearance of host-specific nucleolar proteins in intranuclear "dense bodies" following herpes simplex infection. Eur J Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;39(2):458–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read G. S., Frenkel N. Herpes simplex virus mutants defective in the virion-associated shutoff of host polypeptide synthesis and exhibiting abnormal synthesis of alpha (immediate early) viral polypeptides. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):498–512. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.498-512.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rixon F. J., Atkinson M. A., Hay J. Intranuclear distribution of herpes simplex virus type 2 DNA synthesis: examination by light and electron microscopy. J Gen Virol. 1983 Sep;64(Pt 9):2087–2092. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-9-2087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rixon F. J., McGeoch D. J. A 3' co-terminal family of mRNAs from the herpes simplex virus type 1 short region: two overlapping reading frames encode unrelated polypeptide one of which has highly reiterated amino acid sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 12;12(5):2473–2487. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.5.2473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roizman B., Spear P. G. Preparation of herpes simplex virus of high titer. J Virol. 1968 Jan;2(1):83–84. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.1.83-84.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roller R. J., McCormick A. L., Roizman B. Cellular proteins specifically bind single- and double-stranded DNA and RNA from the initiation site of a transcript that crosses the origin of DNA replication of herpes simplex virus 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6518–6522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J., Kobs G., Brewer G., Peltz S. W. Properties of the exonuclease activity that degrades H4 histone mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9374–9381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J., Kobs G. H4 histone messenger RNA decay in cell-free extracts initiates at or near the 3' terminus and proceeds 3' to 5'. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 20;188(4):579–593. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(86)80008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillero A., Ribeiro J. M. Isoelectric points of proteins: theoretical determination. Anal Biochem. 1989 Jun;179(2):319–325. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90136-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlazny D. A., Kwong A., Frenkel N. Site-specific cleavage/packaging of herpes simplex virus DNA and the selective maturation of nucleocapsids containing full-length viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1423–1427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadsworth S., Jacob R. J., Roizman B. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA. II. Size, composition, and arrangement of inverted terminal repetitions. J Virol. 1975 Jun;15(6):1487–1497. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.6.1487-1497.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner E. K., Roizman B. Ribonucleic acid synthesis in cells infected with herpes simplex virus. I. Patterns of ribonucleic acid synthesis in productively infected cells. J Virol. 1969 Jul;4(1):36–46. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.1.36-46.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. G., Koprowski H., Lonsdale D. M., Brown S. M., Subak-Sharpe J. H. The polypeptide and the DNA restriction enzyme profiles of spontaneous isolates of herpes simplex virus type 1 from explants of human trigeminal, superior cervical and vagus ganglia. J Gen Virol. 1979 Apr;43(1):151–171. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-43-1-151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Vande Woude G. F. DNA sequence of an immediate-early gene (IEmRNA-5) of herpes simplex virus type I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 11;10(3):979–991. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.3.979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]