Abstract
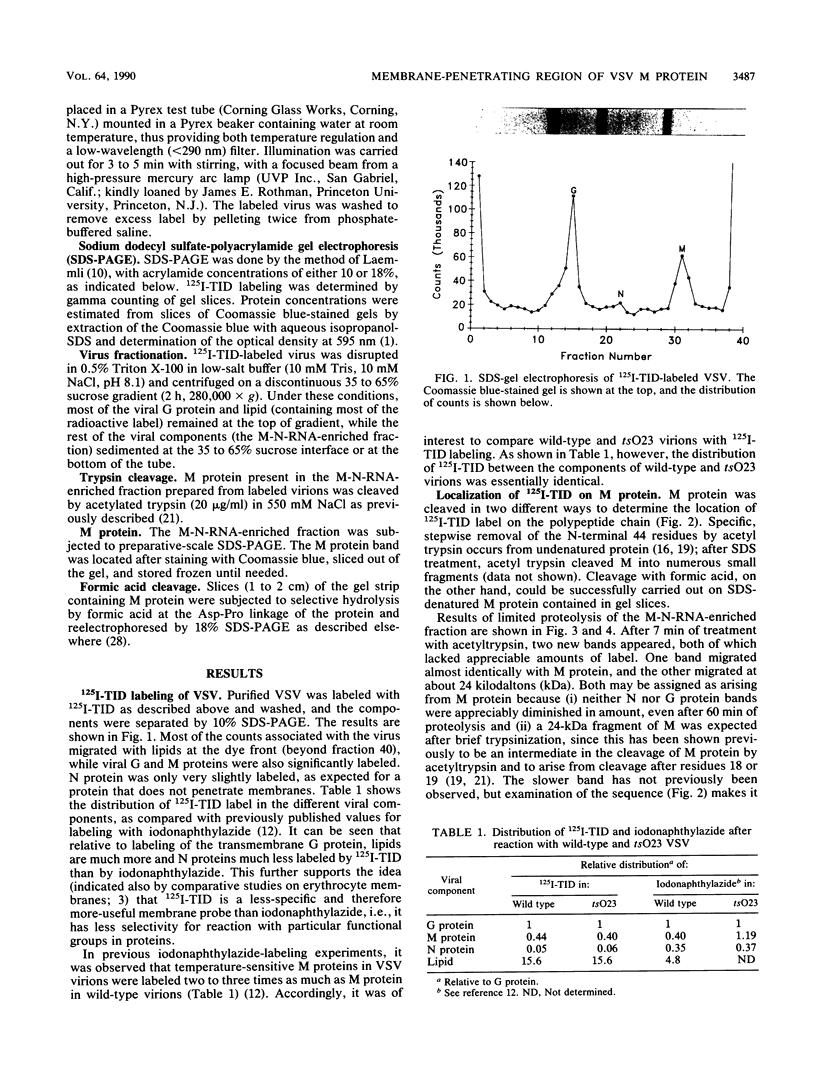
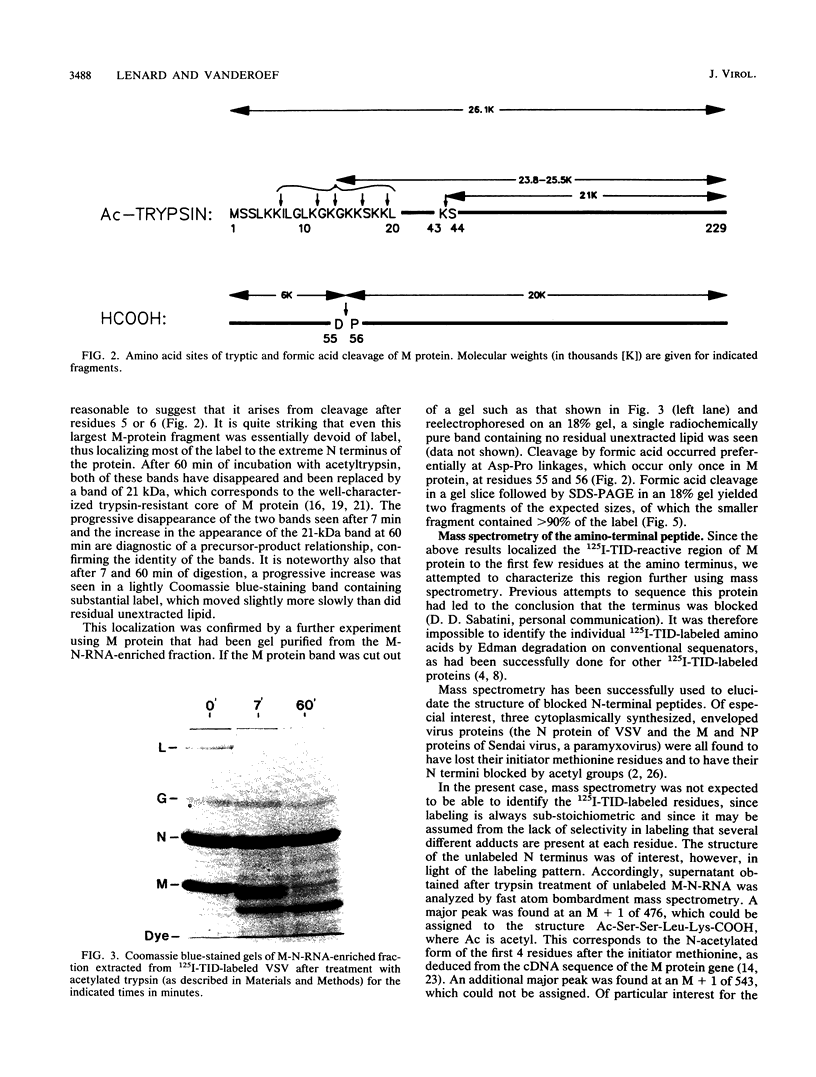
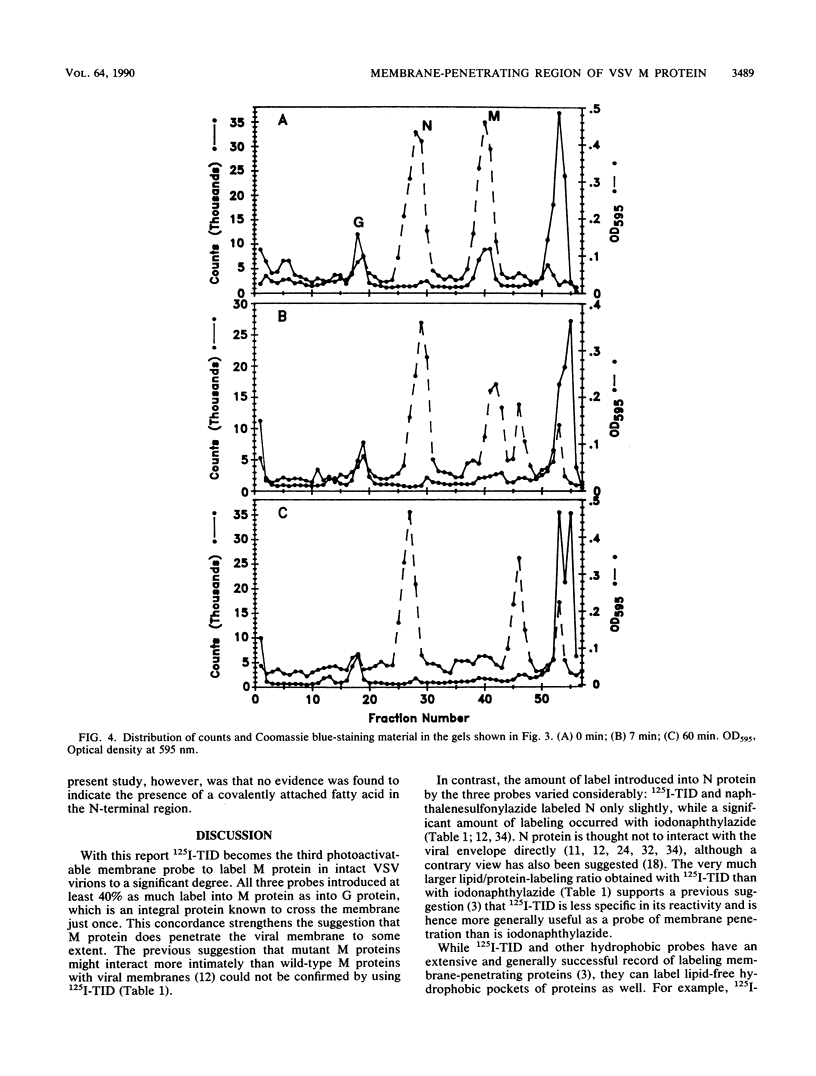
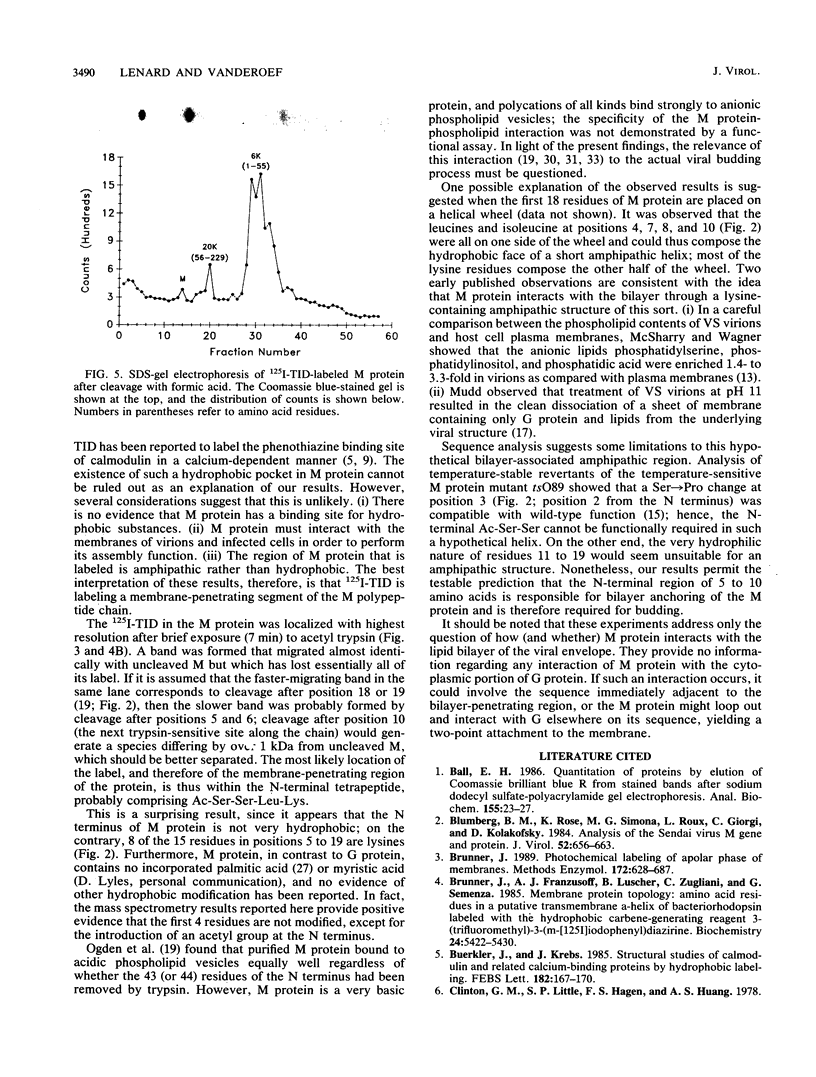
The membrane-reactive, photoactivatable probe 125I-TID [3-(trifluoromethyl)-3-(m-[125I]iodophenyl)-3H-diazirine] was found to label the M protein of vesicular stomatitis virus about 40% as much as G protein in intact virions, in agreement with labeling studies with other probes. By analyzing limited tryptic digestion and specific chemical cleavage products, the label was essentially entirely localized within the first 19, and probably within the first 5 to 10, amino acid residues at the N terminus, identifying this short amphipathic segment as the likely site of interaction of M protein with the viral bilayer.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ball E. H. Quantitation of proteins by elution of Coomassie brilliant blue R from stained bands after sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1986 May 15;155(1):23–27. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90218-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg B. M., Rose K., Simona M. G., Roux L., Giorgi C., Kolakofsky D. Analysis of the Sendai virus M gene and protein. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):656–663. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.656-663.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner J. Photochemical labeling of apolar phase of membranes. Methods Enzymol. 1989;172:628–687. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(89)72037-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harter C., James P., Bächi T., Semenza G., Brunner J. Hydrophobic binding of the ectodomain of influenza hemagglutinin to membranes occurs through the "fusion peptide". J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6459–6464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs J., Buerkler J., Guerini D., Brunner J., Carafoli E. 3-(Trifluoromethyl)-3-(m-[125I]iodophenyl)diazirine, a hydrophobic, photoreactive probe, labels calmodulin and calmodulin fragments in a Ca2+-dependent way. Biochemistry. 1984 Jan 31;23(3):400–403. doi: 10.1021/bi00298a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F., Porter M. Heterogeneity of vesicular stomatitis virus particles: implications for virion assembly. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):52–58. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.52-58.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancarella D. A., Lenard J. Interactions of wild-type and mutant M protein of vesicular stomatitis virus with viral nucleocapsid and envelope in intact virions. Evidence from [125I]iodonaphthyl azide labeling and specific cross-linking. Biochemistry. 1981 Nov 24;20(24):6872–6877. doi: 10.1021/bi00527a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSharry J. J., Wagner R. R. Lipid composition of purified vesicular stomatitis viruses. J Virol. 1971 Jan;7(1):59–70. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.1.59-70.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. K., Lenard J. Inhibition of vesicular stomatitis virus infection by spike glycoprotein. Evidence for an intracellular, G protein-requiring step. J Cell Biol. 1980 Feb;84(2):430–437. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.2.430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita K., Vanderoef R., Lenard J. Phenotypic revertants of temperature-sensitive M protein mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus: sequence analysis and functional characterization. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):256–263. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.256-263.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison T. G., McQuain C. O. Assembly of viral membranes: nature of the association of vesicular stomatitis virus proteins to membranes. J Virol. 1978 Apr;26(1):115–125. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.1.115-125.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudd J. A. Effects of pH on the structure of vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1973 Oct;55(2):546–549. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90200-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odenwald W. F., Arnheiter H., Dubois-Dalcq M., Lazzarini R. A. Stereo images of vesicular stomatitis virus assembly. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):922–932. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.922-932.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogden J. R., Pal R., Wagner R. R. Mapping regions of the matrix protein of vesicular stomatitis virus which bind to ribonucleocapsids, liposomes, and monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):860–868. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.860-868.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono K., Dubois-Dalcq M. E., Schubert M., Lazzarini R. A. A mutated membrane protein of vesicular stomatitis virus has an abnormal distribution within the infected cell and causes defective budding. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1332–1341. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1332-1341.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pal R., Grinnell B. W., Snyder R. M., Wiener J. R., Volk W. A., Wagner R. R. Monoclonal antibodies to the M protein of vesicular stomatitis virus (Indiana serotype) and to a cDNA M gene expression product. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):298–306. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.298-306.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepinsky R. B., Vogt V. M. Identification of retrovirus matrix proteins by lipid-protein cross-linking. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jul 15;131(4):819–837. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90203-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle C. R. Conditional lethal mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1975;69:85–116. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-50112-8_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reidler J. A., Keller P. M., Elson E. L., Lenard J. A fluorescence photobleaching study of vesicular stomatitis virus infected BHK cells. Modulation of G protein mobility by M protein. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 3;20(5):1345–1349. doi: 10.1021/bi00508a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Gallione C. J. Nucleotide sequences of the mRNA's encoding the vesicular stomatitis virus G and M proteins determined from cDNA clones containing the complete coding regions. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):519–528. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.519-528.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose K., Kocher H. P., Blumberg B. M., Kolakofsky D. An improved procedure, involving mass spectrometry, for N-terminal amino acid sequence determination of proteins which are N alpha-blocked. Biochem J. 1984 Jan 1;217(1):253–257. doi: 10.1042/bj2170253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. F., Schlesinger M. J. Fatty acid binding to vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein: a new type of post-translational modification of the viral glycoprotein. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):813–819. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90321-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonderegger P., Jaussi R., Gehring H., Brunschweiler K., Christen P. Peptide mapping of protein bands from polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis by chemical cleavage in gel pieces and re-electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1982 May 15;122(2):298–301. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90285-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoffel W., Schreiber C., Scheefers H. Lipids with photosensitive groups as chemical probes for the structural analysis of biological membranes. On the localization of the G- and M-protein of vesicular stomatitis virus. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1978 Aug;359(8):923–931. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1978.359.2.923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener J. R., Pal R., Barenholz Y., Wagner R. R. Effect of the vesicular stomatitis virus matrix protein on the lateral organization of lipid bilayers containing phosphatidylglycerol: use of fluorescent phospholipid analogues. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 17;24(26):7651–7658. doi: 10.1021/bi00347a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener J. R., Pal R., Barenholz Y., Wagner R. R. Influence of the peripheral matrix protein of vesicular stomatitis virus on the membrane dynamics of mixed phospholipid vesicles: fluorescence studies. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 26;22(9):2162–2170. doi: 10.1021/bi00278a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T., Lenard J. Interaction of wild-type and mutant M protein vesicular stomatitis virus with nucleocapsids in vitro. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 3;20(5):1349–1354. doi: 10.1021/bi00508a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakowski J. J., Petri W. A., Jr, Wagner R. R. Role of matrix protein in assembling the membrane of vesicular stomatitis virus: reconstitution of matrix protein with negatively charged phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry. 1981 Jun 23;20(13):3902–3907. doi: 10.1021/bi00516a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakowski J. J., Wagner R. R. Localization of membrane-associated proteins in vesicular stomatitis virus by use of hydrophobic membrane probes and cross-linking reagents. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):93–102. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.93-102.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]