Abstract
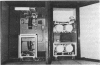
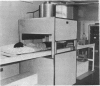
Total-body counters designed for clinical use have considerable advantage and application over other methods for the measurement of iron metabolism. An investigation may be performed on an out-patient basis and the need for faecal collections avoided.
Although the initial cost of their installation is high, this can be off-set by the saving of in-patient costs in 2 or 3 years of operation.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. A., Warner G. T. Estimation of the standard error of retention in whole-body counter studies and its relevance to counter design. Phys Med Biol. 1970 Apr;15(2):281–287. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/15/2/004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BADENOCH J., CALLENDER S. T. Iron metabolism in steatorrhea; the use of radioactive iron in studies of absorption and utilization. Blood. 1954 Feb;9(2):123–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAIRD I. M., WILSON G. M. The pathogenesis of anaemia after partial gastrectomy. II. Iron absorption after partial gastrectomy. Q J Med. 1959 Jan;28(109):35–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOOTH C. C., MOLLIN D. L. Plasma, tissue and urinary radioactivity after oral administration of 56Co-labelled vitamin B12. Br J Haematol. 1956 Jul;2(3):223–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1956.tb06695.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURCH P. R., SPIERS F. W. Measurement of the gamma-radiation from the human body. Nature. 1953 Sep 19;172(4377):519–521. doi: 10.1038/172519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnaby C. F., Smith T. Calibration of a whole-body counter suitable for use in routine clinical investigations. Phys Med Biol. 1971 Jan;16(1):97–104. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/16/1/008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boddy K. The development and performance of a prototype shadow-shield whole body monitor. Phys Med Biol. 1967 Jan;12(1):43–50. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/12/1/305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CALLENDER S. T. Iron metabolism using iron 59 (59Fe) as a tracer. Proc R Soc Med. 1962 Feb;55:145–146. doi: 10.1177/003591576205500213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CALLENDER S. T., MALLETT B. J., SMITH M. D. Absorption of haemoglobin iron. Br J Haematol. 1957 Apr;3(2):186–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1957.tb05785.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTIAN J. E., KESSLER W. V., ZIEMER P. L. A 2 pi liquid scintillation counter for determining the radioactivity of large samples including man and animals. Int J Appl Radiat Isot. 1962 Oct;13:557–564. doi: 10.1016/0020-708x(62)90128-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAPHAM W. F., HAYTER C. J. The measurement of gammaemitting isotopes in faeces. Phys Med Biol. 1962 Dec;7:313–317. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/7/3/303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOK J. D., VALBERG L. S. Evaluation and use of a large plastic scintillator for gamma counting. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Feb;61:317–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callender S. T., Marney S. R., Jr, Warner G. T. Eggs and iron absorption. Br J Haematol. 1970 Dec;19(6):657–665. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1970.tb07010.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callender S. T., Warner G. T. Absorption of "slow Fe" measured with a total body counter. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 1971 Sep;13(9):591–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callender S. T., Warner G. T., Cope E. Treatment of menorrhagia with tranexamic acid. A double-blind trial. Br Med J. 1970 Oct 24;4(5729):214–216. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5729.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callender S. T., Warner G. T. Iron absorption from bread. Am J Clin Nutr. 1968 Oct;21(10):1170–1174. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/21.10.1170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callender S. T., Warner G. T. Iron absorption from brown bread. Lancet. 1970 Mar 14;1(7646):546–547. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90772-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callender S. T., Witts L. J., Warner G. T., Oliver R. The use of a simple whole-body counter for haematological investigations. Br J Haematol. 1966 May;12(3):276–282. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1966.tb05634.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook J. D., Palmer H. E., Pailthorp K. G., Finch C. A. The measurement of iron absorption by whole-body counting. Phys Med Biol. 1970 Jul;15(3):467–473. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/15/3/007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DERN R. J., HART W. L. Studies with doubly labeled iron. II. Separation of iron from blood samples and preparation of ferrous perchlorate for liquid scintillation counting. J Lab Clin Med. 1961 Mar;57:460–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBACH R., MOORE C. V., CALLENDER S. Studies in iron transportation and metabolism. IX. The excretion of iron as measured by the isotope technique. J Lab Clin Med. 1955 Apr;45(4):599–615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dymock I. W., Godfrey B. E., Williams R. A comparison of methods for the determination of iron absorption using a whole-body counter. Phys Med Biol. 1971 Apr;16(2):269–272. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/16/2/309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINCH C. A. Body iron exchange in man. J Clin Invest. 1959 Feb;38(2):392–396. doi: 10.1172/JCI103813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANCOIS P. E., SZUR L. Use of iron-52 as a radioactive tracer. Nature. 1958 Dec 13;182(4650):1665–1667. doi: 10.1038/1821665b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLASS H. I., CLARKSON D. G., BURNS H. G. A WHOLE-BODY COUNTER FOR CLINICAL APPLICATIONS. Phys Med Biol. 1964 Jan;9:57–63. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/9/1/305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALLBERG L., BRISE H. Determination of Fe55 and Fe59 in blood. Int J Appl Radiat Isot. 1960 Dec;9:100–108. doi: 10.1016/0020-708x(60)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn P. F., Bale W. F., Lawrence E. O., Whipple G. H. RADIOACTIVE IRON AND ITS METABOLISM IN ANEMIA : ITS ABSORPTION, TRANSPORTATION, AND UTILIZATION. J Exp Med. 1939 Apr 30;69(5):739–753. doi: 10.1084/jem.69.5.739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallberg L., Björn-Rasmussen E. Determination of iron absorption from whole diet. A new two-pool model using two radioiron isotopes given as haem and non-haem iron. Scand J Haematol. 1972;9(3):193–197. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1972.tb00930.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt J. M., Gear M. W., Warner G. T. The role of chronic blood loss in the pathogenesis of postgastrectomy iron-deficiency anaemia. Gut. 1970 Oct;11(10):847–850. doi: 10.1136/gut.11.10.847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt J. M., Mayet F. G., Warner G. T., Callender S. T., Gunning A. J. Iron absorption and blood loss in patients with hiatus hernia. Br Med J. 1968 Jul 6;3(5609):22–25. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5609.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt J. M., Mayet F. G., Warner G. T., Callender S. T. Measurement of blood loss by means of a whole-body counter. Br Med J. 1967 Oct 14;4(5571):86–88. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5571.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOSEPHS H. W. Absorption of iron as a problem in human physiology; a critical review. Blood. 1958 Jan;13(1):1–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOEVINGER R., BERMAN M. Efficiency criteria in radioactivity counting. Nucleonics. 1951 Jul;9(1):26–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBlanc A. D., Johnson P. C. 60 Co a constant contaminant of pharmaceutically prepared 59 Fe. Phys Med Biol. 1972 May;17(3):418–419. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/17/3/009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLIVER R. Use of a scintillation gamma counter for the estimation of iodine 131 in liquid samples. Br J Radiol. 1953 Dec;26(312):663–664. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-26-312-663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver R., Warner G. T. Some factors affecting spatial uniformity of response in whole-body counters. Br J Radiol. 1966 Jul;39(463):554–556. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-39-463-554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERRY S. W., WARNER G. T. A METHOD OF SAMPLE PREPARATION FOR THE ESTIMATION OF FE55 IN WHOLE BLOOD BY THE LIQUID SCINTILLATION COUNTING TECHNIQUE. Int J Appl Radiat Isot. 1963 Sep;14:397–400. doi: 10.1016/0020-708x(63)90020-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PIRCHER F. J., HORN E. G., REEVES R. J., BUFFALO T. DESIGN AND PROPERTIES OF THE WHOLE BODY SCANNER AT DUKE. J Nucl Med. 1965 Jun;6:389–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRICE D. C., COHN S. H., WASSERMAN L. R., REIZENSTEIN P. G., CRONKITE E. P. The determination of iron absorption and loss by whole body counting. Blood. 1962 Nov;20:517–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRICE D. C., FORSYTH E. M., COHN S. H., CRONKITE E. P. THE STUDY OF MENSTRUAL AND OTHER BLOOD LOSS, AND CONSEQUENT IRON DEFICIENCY, BY FE59 WHOLE-BODY COUNTING. Can Med Assoc J. 1964 Jan 11;90:51–54. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paix D., Davis A. E., Blagonravoff L. Radioactive assay of bulky samples. J Coll Radiol Australas. 1965 Oct;9(3):268–271. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1673.1965.tb01036.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer H. E., Cook J. D., Pailthorp K. G., Finch C. A. A whole-body counter for precision in vivo measurement of radio-iron. Phys Med Biol. 1970 Jul;15(3):457–465. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/15/3/006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock W. C., Evans R. D., Irvine J. W., Good W. M., Kip A. F., Weiss S., Gibson J. G. THE USE OF TWO RADIOACTIVE ISOTOPES OF IRON IN TRACER STUDIES OF ERYTHROCYTES. J Clin Invest. 1946 Jul;25(4):605–615. doi: 10.1172/JCI101743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAITO H., SARGENT T., 3rd, PARKER H. G., LAWRENCE J. H. WHOLE-BODY IRON LOSS IN NORMAL MAN MEASURED WITH A GAMMA SPECTROMETER. J Nucl Med. 1964 Aug;5:571–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHIFFER L. M., PRICE D. C., CUTTNER J., COHN S. H., CRONKITE E. P. A NOTE CONCERNING THE "100 PER CENT VALUE" IN IRON ABSORPTION STUDIES BY WHOLE BODY COUNTING. Blood. 1964 Jun;23:757–760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH M. D., MALLETT B. Iron absorption before and after partial gastrectomy. Clin Sci. 1957 Feb;16(1):23–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAPPIN J. W. THE CONVERSION OF A SMALL LABORATORY INTO A LOW BACKGROUND ROOM SUITABLE FOR COUNTING WHOLE BODY RADIATION. Br J Radiol. 1963 Aug;36:608–609. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-36-428-608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TROTT N. G., PARNELL C. J., HODT H. J., ENTWISTLE R. F. STUDIES IN THE DESIGN AND APPLICATIONS OF A CLINICAL LOW BACKGROUND COUNTING ROOM. Br J Radiol. 1963 Aug;36:592–607. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-36-428-592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tothill P., Galt J. M. Quantitative profile scanning for the measurement of organ radioactivity. Phys Med Biol. 1971 Oct;16(4):625–634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valberg L. S., Ludwig J., Olatunbosun D. Alteration in cobalt absorption in patients with disorders of iron metabolism. Gastroenterology. 1969 Feb;56(2):241–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner G. T., Oliver R. A whole-body counter for clinical measurements utilizing the 'shadow shield' technique. Phys Med Biol. 1966 Jan;11(1):83–94. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/11/1/307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Will G., Boddy K. Iron turnover estimated by a whole body monitor. Scott Med J. 1967 Apr;12(4):157–162. doi: 10.1177/003693306701200404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]