Abstract
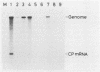
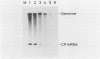
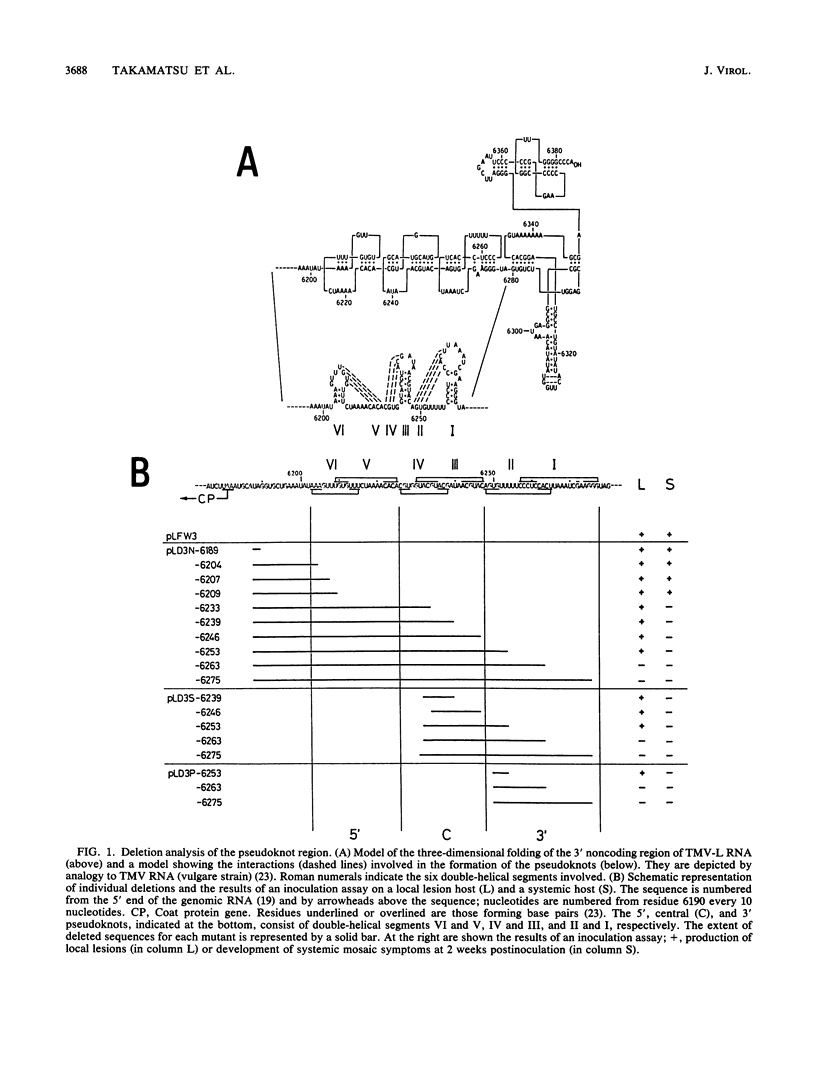
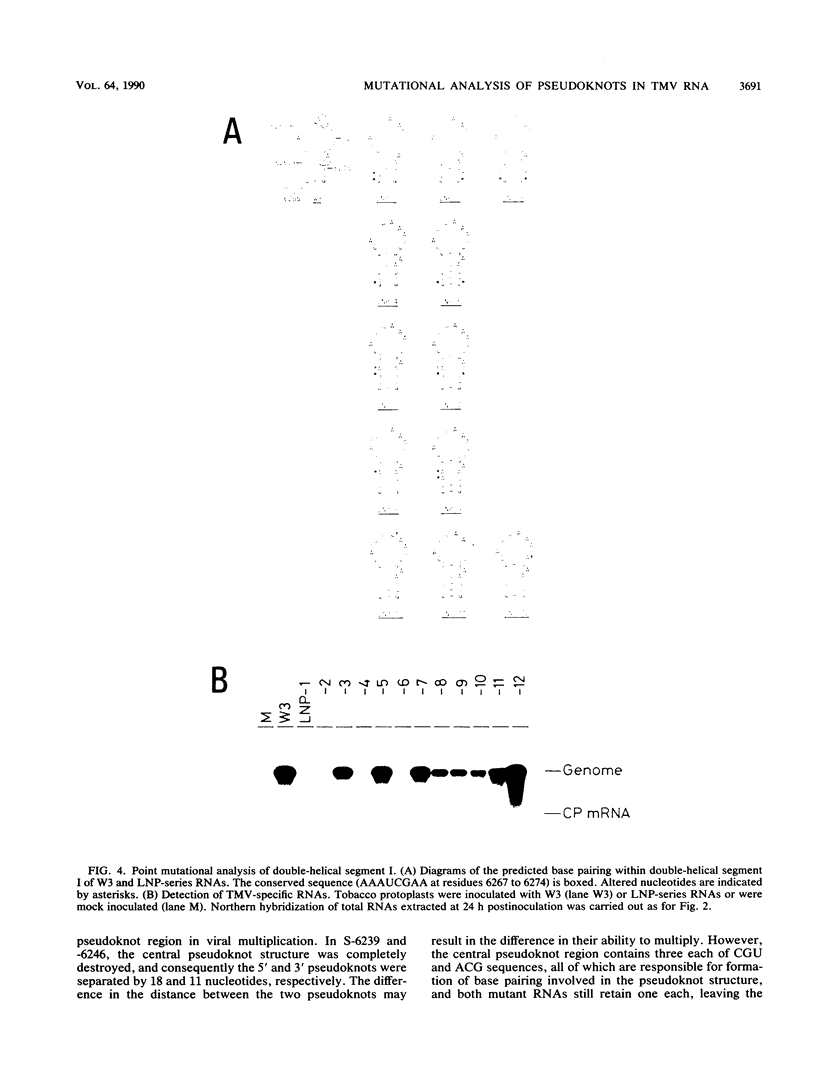
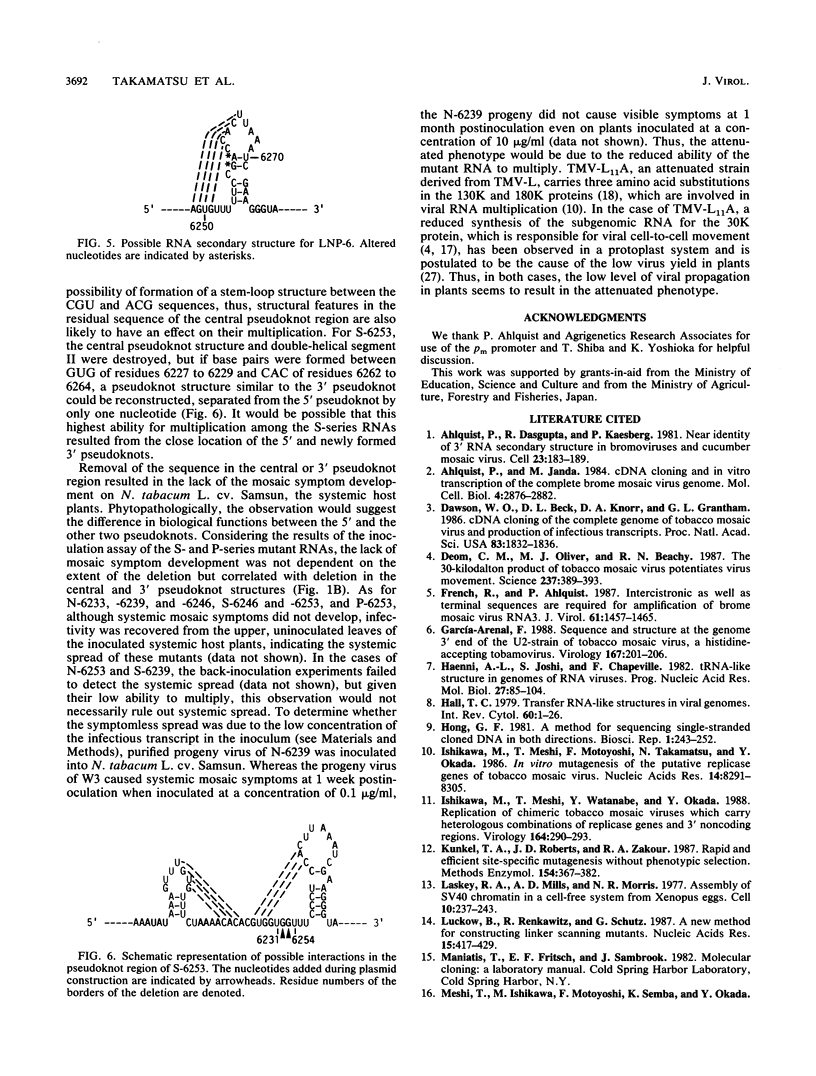
The approximately 200-nucleotide-long 3'-terminal noncoding region of tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) RNA contains a tRNA-like structure and, in its immediate upstream region, three consecutive pseudoknots, each of which is composed of two double-helical segments. To elucidate the biological functions of the pseudoknot region, we constructed several deletion mutant TMV-L (a tomato strain) RNAs by using an in vitro transcription system and tested their ability to multiply in both tobacco plants and protoplasts. When deletions were introduced just downstream of the termination codon of the coat protein gene in the 5'-to-3' direction progressively, five of six double-helical segments were dispensable for viral multiplication, indicating that the pseudoknot structures are not essential for multiplication. However, extension of the deletion into the central pseudoknot region resulted in reduction in viral multiplication, accompanied by loss of development of mosaic symptoms on systemic tobacco plants. Cessation of multiplication was observed when the sequence involved in formation of double-helical segment I just upstream of the tRNA-like structure was deleted irrespective of the start point and extent of deletion. Point mutations that destabilized double-helical segment I resulted in a loss or great reduction of viral multiplication, whereas the double mutants in which the double helix was restored by additional compensating base substitutions restored multiplication to nearly the wild-type level. Thus, double-helical segment I just upstream of the tRNA-like structure is a structural feature essential for viral multiplication.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahlquist P., Dasgupta R., Kaesberg P. Near identity of 3- RNA secondary structure in bromoviruses and cucumber mosaic virus. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):183–189. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90283-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahlquist P., Janda M. cDNA cloning and in vitro transcription of the complete brome mosaic virus genome. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2876–2882. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson W. O., Beck D. L., Knorr D. A., Grantham G. L. cDNA cloning of the complete genome of tobacco mosaic virus and production of infectious transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1832–1836. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deom C. M., Oliver M. J., Beachy R. N. The 30-kilodalton gene product of tobacco mosaic virus potentiates virus movement. Science. 1987 Jul 24;237(4813):389–394. doi: 10.1126/science.237.4813.389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French R., Ahlquist P. Intercistronic as well as terminal sequences are required for efficient amplification of brome mosaic virus RNA3. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1457–1465. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1457-1465.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Arenal F. Sequence and structure at the genome 3' end of the U2-strain of tobacco mosaic virus, a histidine-accepting tobamovirus. Virology. 1988 Nov;167(1):201–206. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90070-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haenni A. L., Joshi S., Chapeville F. tRNA-like structures in the genomes of RNA viruses. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1982;27:85–104. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60598-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall T. C. Transfer RNA-like structures in viral genomes. Int Rev Cytol. 1979;60:1–26. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61257-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong G. F. A method for sequencing single-stranded cloned DNA in both directions. Biosci Rep. 1981 Mar;1(3):243–252. doi: 10.1007/BF01114911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa M., Meshi T., Motoyoshi F., Takamatsu N., Okada Y. In vitro mutagenesis of the putative replicase genes of tobacco mosaic virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 11;14(21):8291–8305. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.21.8291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa M., Meshi T., Watanabe Y., Okada Y. Replication of chimeric tobacco mosaic viruses which carry heterologous combinations of replicase genes and 3' noncoding regions. Virology. 1988 May;164(1):290–293. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90648-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D., Morris N. R. Assembly of SV40 chromatin in a cell-free system from Xenopus eggs. Cell. 1977 Feb;10(2):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Renkawitz R., Schütz G. A new method for constructing linker scanning mutants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):417–429. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meshi T., Watanabe Y., Saito T., Sugimoto A., Maeda T., Okada Y. Function of the 30 kd protein of tobacco mosaic virus: involvement in cell-to-cell movement and dispensability for replication. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2557–2563. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02544.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiguchi M., Kikuchi S., Kiho Y., Ohno T., Meshi T., Okada Y. Molecular basis of plant viral virulence; the complete nucleotide sequence of an attenuated strain of tobacco mosaic virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 12;13(15):5585–5590. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.15.5585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno T., Aoyagi M., Yamanashi Y., Saito H., Ikawa S., Meshi T., Okada Y. Nucleotide sequence of the tobacco mosaic virus (tomato strain) genome and comparison with the common strain genome. J Biochem. 1984 Dec;96(6):1915–1923. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuki Y., Takebe I., Ohno T., Fukuda M., Okada Y. Reconstitution of tobacco mosaic virus rods occurs bidirectionally from an internal initiation region: demonstration by electron microscopic serology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):1913–1917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.1913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pleij C. W., Rietveld K., Bosch L. A new principle of RNA folding based on pseudoknotting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1717–1731. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietveld K., Linschooten K., Pleij C. W., Bosch L. The three-dimensional folding of the tRNA-like structure of tobacco mosaic virus RNA. A new building principle applied twice. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2613–2619. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02182.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y., Morita N., Nishiguchi M., Okada Y. Attenuated strains of tobacco mosaic virus. Reduced synthesis of a viral protein with a cell-to-cell movement function. J Mol Biol. 1987 Apr 20;194(4):699–704. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90247-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Belkum A., Abrahams J. P., Pleij C. W., Bosch L. Five pseudoknots are present at the 204 nucleotides long 3' noncoding region of tobacco mosaic virus RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 11;13(21):7673–7686. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.21.7673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]