Abstract
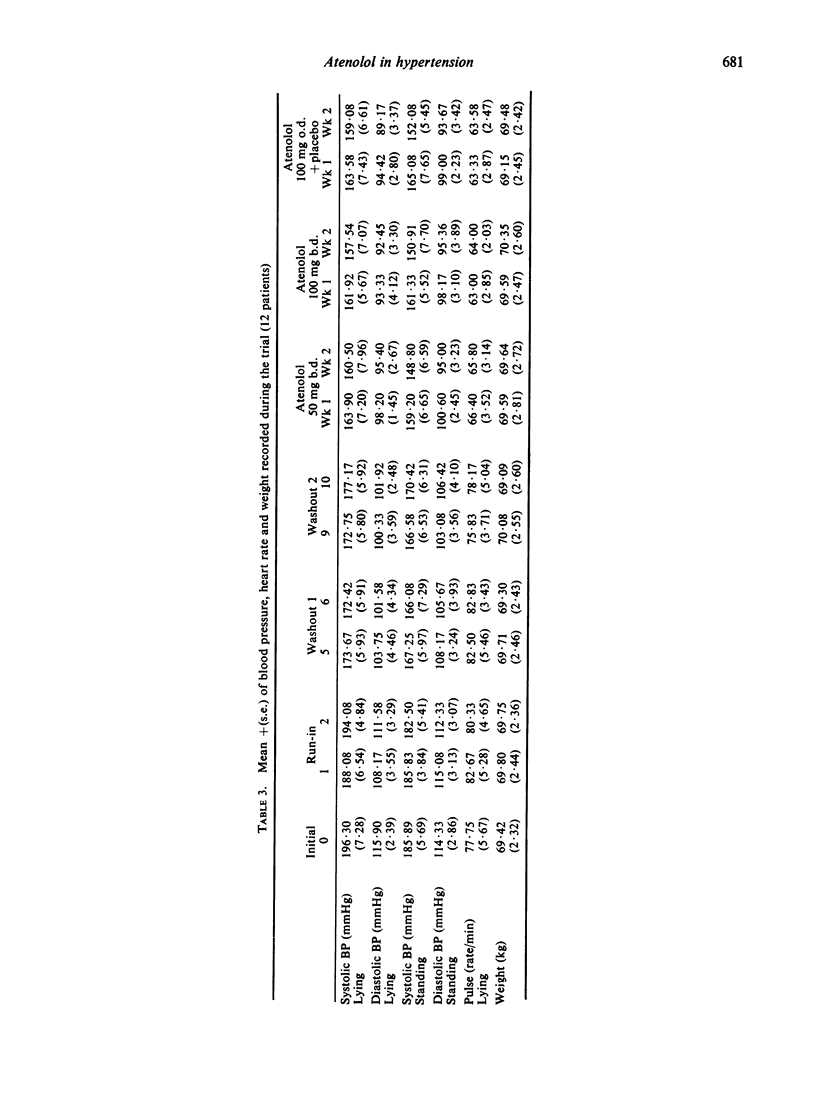
The hypertensive action of atenolol has been studied in a randomized double-blind crossover comparison. Twelve patients showed a highly significant reduction in average supine systolic and diastolic blood pressures from pre-treatment values of 196.3/115.9 to 159.1/89.2 mmHg (26.1/15.4 kPa to 22.2/11.9 kPa) after 2 weeks on once daily atenolol. No dose-related reduction in blood pressure was seen and the single 100 mg daily dose was as effective as 100 mg twice daily or 50 mg twice daily. Blood pressures recorded after 2 weeks' atenolol were lower than those obtained at 7 days irrespective of dose.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amery A., De Plaen J. F., Fagard R., Linjen P., Reybrouck T. The relationship between beta-blockade, hyporeninaemic and hypotensive effect of two beta-blocking agents. Postgrad Med J. 1976;52 (Suppl 4):102–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway F. J., Fitzgerald J. D., McAinsh J., Rowlands D. J., Simpson W. T. Human pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies on the atenolo (ICI 66,082), a new cardioselective beta-adrenoceptor blocking drug. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1976 Apr;3(2):267–272. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1976.tb00602.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas-Jones A. P., Cruickshank J. M. Once-daily dosing with Atenolol in patients with mild or moderate hypertension. Br Med J. 1976 Apr 24;1(6016):990–991. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6016.990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall A. J., Roberts C. J., Barritt D. W. Raynaud's phenomenon as side effect of beta-blockers in hypertension. Br Med J. 1976 Jun 19;1(6024):1498–1499. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6024.1498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers M. G., Lewis G. R., Steiner J., Dollery C. T. Atenolol in essential hypertension. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1976 May;19(5 Pt 1):502–507. doi: 10.1002/cpt1976195part1502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



