Abstract
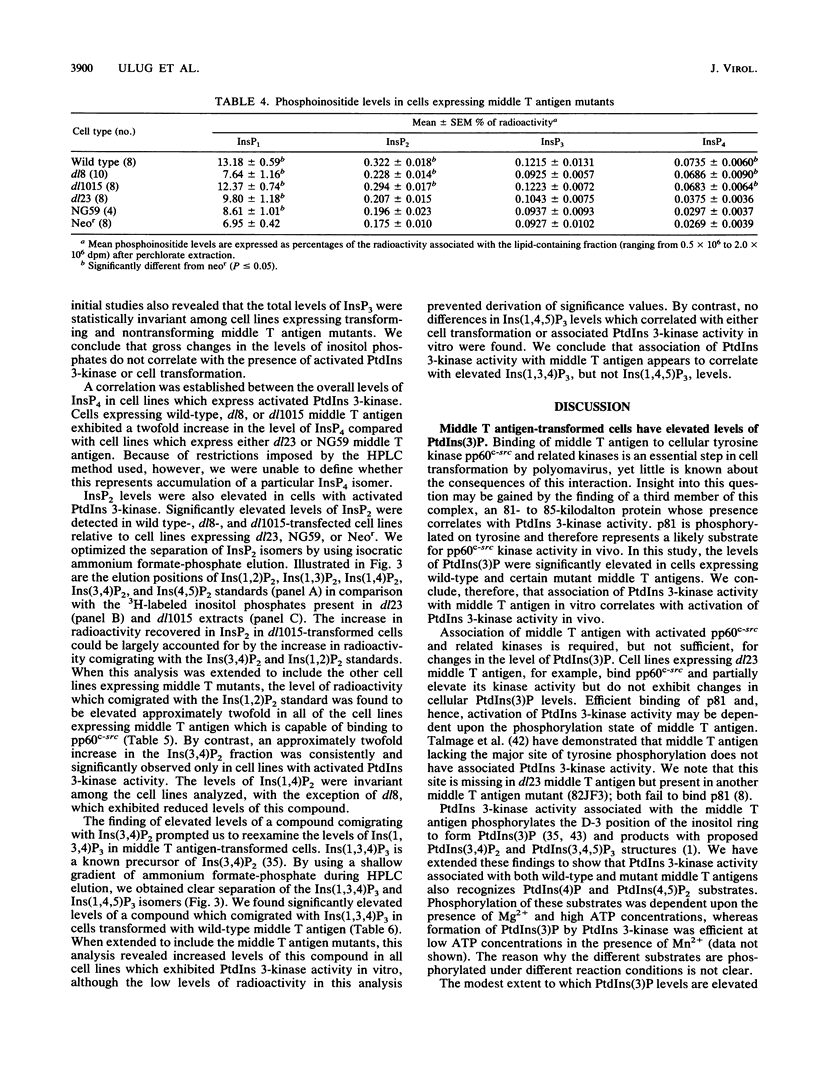
Associated with the middle T antigen of polyomavirus is a novel phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns) kinase activity which phosphorylates PtdIns at the D-3 position of the inositol ring. We have undertaken an analysis of myo-[3H]inositol-containing compounds in a panel of NIH 3T3 cell lines stably transfected with transforming and nontransforming middle T antigen mutants. All cell lines from which PtdIns 3-kinase activity coprecipitated with middle T antigen exhibited modestly elevated levels of PtdIns(3)P and compounds with predicted PtdIns(3,4)P2 and PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 structures. Complex formation between middle T antigen and PtdIns 3-kinase correlated not with an increase in total inositol phosphate levels but rather with elevated levels of InsP2 and InsP4. A specific increase in the level of an InsP2 species which comigrated in high-pressure liquid chromatography analysis with Ins(3,4)P2 was observed. These results suggest that association of the polyomavirus middle T antigen with PtdIns 3-kinase activates a distinct inositol metabolic pathway.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auger K. R., Serunian L. A., Soltoff S. P., Libby P., Cantley L. C. PDGF-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation stimulates production of novel polyphosphoinositides in intact cells. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):167–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90182-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol: two interacting second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:159–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. B., Thiele C. J., Israel M. A., Yonemoto W., Lipsich L. A., Brugge J. S. Enhancement of cellular src gene product associated tyrosyl kinase activity following polyoma virus infection and transformation. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):767–777. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90272-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. H., Harvey R., Espino P. C., Semba K., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K., Smith A. E. Peptide antibodies to the human c-fyn gene product demonstrate pp59c-fyn is capable of complex formation with the middle-T antigen of polyomavirus. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3845–3855. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03270.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiarugi V., Porciatti F., Pasquali F., Magnelli L., Giannelli S., Ruggiero M. Polyphosphoinositide metabolism is rapidly stimulated by activation of a temperature-sensitive mutant of Rous sarcoma virus in rat fibroblasts. Oncogene. 1987;2(1):37–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Heber A. An 81 kd protein complexed with middle T antigen and pp60c-src: a possible phosphatidylinositol kinase. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1031–1037. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90169-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Kypta R. M., Ulug E. T. Interactions between the middle T antigen of polyomavirus and host cell proteins. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 1):153–160. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Read M., Wilson J. B., Fried M. Cytoplasmic interaction between pp60c-src and a truncated polyoma virus middle T antigen. Oncogene Res. 1989;4(1):75–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Smith A. E. Polyoma virus transforming protein associates with the product of the c-src cellular gene. Nature. 1983 Jun 2;303(5916):435–439. doi: 10.1038/303435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Hawkins P. T., Irvine R. F. Inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate and not phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate is the probable precursor of inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in agonist-stimulated parotid gland. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 1;238(2):501–506. doi: 10.1042/bj2380501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endemann G., Yonezawa K., Roth R. A. Phosphatidylinositol kinase or an associated protein is a substrate for the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):396–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry M. J., Gebhardt A., Parker P. J., Foulkes J. G. Phosphatidylinositol turnover and transformation of cells by Abelson murine leukaemia virus. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3173–3178. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04061.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukami K., Matsuoka K., Nakanishi O., Yamakawa A., Kawai S., Takenawa T. Antibody to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate inhibits oncogene-induced mitogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9057–9061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., Hanafusa H. Phosphatidylinositol kinase activity associates with viral p60src protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1651–1658. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., Kornbluth S., Jong S. M., Wang L. H., Hanafusa H. Phosphatidylinositol kinase type I activity associates with various oncogene products. Oncogene Res. 1989;4(4):283–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorga F. R., Riney C. E., Benjamin T. L. Inositol trisphosphate levels in cells expressing wild-type and mutant polyomavirus middle T antigens: evidence for activation of phospholipase C via activation of pp60c-src. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):105–112. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.105-112.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins P. T., Michell R. H., Kirk C. J. Analysis of the metabolic turnover of the individual phosphate groups of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Validation of novel analytical techniques by using 32P-labelled lipids from erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1984 Mar 15;218(3):785–793. doi: 10.1042/bj2180785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins P. T., Stephens L., Downes C. P. Rapid formation of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate and inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in rat parotid glands may both result indirectly from receptor-stimulated release of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate from phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 1;238(2):507–516. doi: 10.1042/bj2380507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. M., Wasilenko W. J., Mattingly R. R., Weber M. J., Garrison J. C. Fibroblasts transformed with v-src show enhanced formation of an inositol tetrakisphosphate. Science. 1989 Oct 6;246(4926):121–124. doi: 10.1126/science.2506643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Whitman M., Schaffhausen B., Pallas D. C., White M., Cantley L., Roberts T. M. Common elements in growth factor stimulation and oncogenic transformation: 85 kd phosphoprotein and phosphatidylinositol kinase activity. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1021–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90168-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Whitman M., Schaffhausen B., Raptis L., Garcea R. L., Pallas D., Roberts T. M., Cantley L. Phosphatidylinositol metabolism and polyoma-mediated transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3624–3628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato M., Kawai S., Takenawa T. Altered signal transduction in erbB-transformed cells. Implication of enhanced inositol phospholipid metabolism in erbB-induced transformation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5696–5704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornbluth S., Sudol M., Hanafusa H. Association of the polyomavirus middle-T antigen with c-yes protein. Nature. 1987 Jan 8;325(7000):171–173. doi: 10.1038/325171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kypta R. M., Hemming A., Courtneidge S. A. Identification and characterization of p59fyn (a src-like protein tyrosine kinase) in normal and polyoma virus transformed cells. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3837–3844. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03269.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lips D. L., Majerus P. W., Gorga F. R., Young A. T., Benjamin T. L. Phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate is present in normal and transformed fibroblasts and is resistant to hydrolysis by bovine brain phospholipase C II. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8759–8763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lips D. L., Majerus P. W. The discovery of a 3-phosphomonoesterase that hydrolyzes phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate in NIH 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19911–19915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macara I. G., Marinetti G. V., Balduzzi P. C. Transforming protein of avian sarcoma virus UR2 is associated with phosphatidylinositol kinase activity: possible role in tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2728–2732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majerus P. W., Connolly T. M., Deckmyn H., Ross T. S., Bross T. E., Ishii H., Bansal V. S., Wilson D. B. The metabolism of phosphoinositide-derived messenger molecules. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1519–1526. doi: 10.1126/science.3024320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martins T. J., Sugimoto Y., Erikson R. L. Dissociation of inositol trisphosphate from diacylglycerol production in Rous sarcoma virus-transformed fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):683–691. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallas D. C., Cherington V., Morgan W., DeAnda J., Kaplan D., Schaffhausen B., Roberts T. M. Cellular proteins that associate with the middle and small T antigens of polyomavirus. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):3934–3940. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.3934-3940.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang D. T., Sharma B. R., Shafer J. A. Purification of the catalytically active phosphorylated form of insulin receptor kinase by affinity chromatography with O-phosphotyrosyl-binding antibodies. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Oct;242(1):176–186. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90491-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross A. H., Baltimore D., Eisen H. N. Phosphotyrosine-containing proteins isolated by affinity chromatography with antibodies to a synthetic hapten. Nature. 1981 Dec 17;294(5842):654–656. doi: 10.1038/294654a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman N. B., Kapeller R., White M. F., Cantley L. C. Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase by insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1411–1415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serunian L. A., Haber M. T., Fukui T., Kim J. W., Rhee S. G., Lowenstein J. M., Cantley L. C. Polyphosphoinositides produced by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase are poor substrates for phospholipases C from rat liver and bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17809–17815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shears S. B. Metabolism of the inositol phosphates produced upon receptor activation. Biochem J. 1989 Jun 1;260(2):313–324. doi: 10.1042/bj2600313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L., Hawkins P. T., Carter N., Chahwala S. B., Morris A. J., Whetton A. D., Downes P. C. L-myo-inositol 1,4,5,6-tetrakisphosphate is present in both mammalian and avian cells. Biochem J. 1988 Jan 1;249(1):271–282. doi: 10.1042/bj2490271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L., Hawkins P. T., Downes C. P. Metabolic and structural evidence for the existence of a third species of polyphosphoinositide in cells: D-phosphatidyl-myo-inositol 3-phosphate. Biochem J. 1989 Apr 1;259(1):267–276. doi: 10.1042/bj2590267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto Y., Erikson R. L. Phosphatidylinositol kinase activities in normal and Rous sarcoma virus-transformed cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3194–3198. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto Y., Whitman M., Cantley L. C., Erikson R. L. Evidence that the Rous sarcoma virus transforming gene product phosphorylates phosphatidylinositol and diacylglycerol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2117–2121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talmage D. A., Freund R., Young A. T., Dahl J., Dawe C. J., Benjamin T. L. Phosphorylation of middle T by pp60c-src: a switch for binding of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and optimal tumorigenesis. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):55–65. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90869-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilly B. C., van Paridon P. A., Verlaan I., de Laat S. W., Moolenaar W. H. Epidermal-growth-factor-induced formation of inositol phosphates in human A431 cells. Differences from the effect of bradykinin. Biochem J. 1988 Jun 15;252(3):857–863. doi: 10.1042/bj2520857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varticovski L., Druker B., Morrison D., Cantley L., Roberts T. The colony stimulating factor-1 receptor associates with and activates phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):699–702. doi: 10.1038/342699a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman M., Downes C. P., Keeler M., Keller T., Cantley L. Type I phosphatidylinositol kinase makes a novel inositol phospholipid, phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate. Nature. 1988 Apr 14;332(6165):644–646. doi: 10.1038/332644a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman M., Kaplan D. R., Schaffhausen B., Cantley L., Roberts T. M. Association of phosphatidylinositol kinase activity with polyoma middle-T competent for transformation. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):239–242. doi: 10.1038/315239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman M., Kaplan D., Roberts T., Cantley L. Evidence for two distinct phosphatidylinositol kinases in fibroblasts. Implications for cellular regulation. Biochem J. 1987 Oct 1;247(1):165–174. doi: 10.1042/bj2470165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




