Abstract
Normal hepatocytes express very few class I major histocompatibility complex (MHC I) molecules, but MHC I expression is elevated in hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. We report here that hepatoblastoma cells with replicating HBV genomes express three- to fourfold-higher levels of MHC I protein and mRNA than do parent cells without HBV DNA. Transient transfection assays demonstrated that the HBV X protein trans activated transcription from an MHC I promoter and allowed identification of cis elements important for trans activation.
Full text
PDF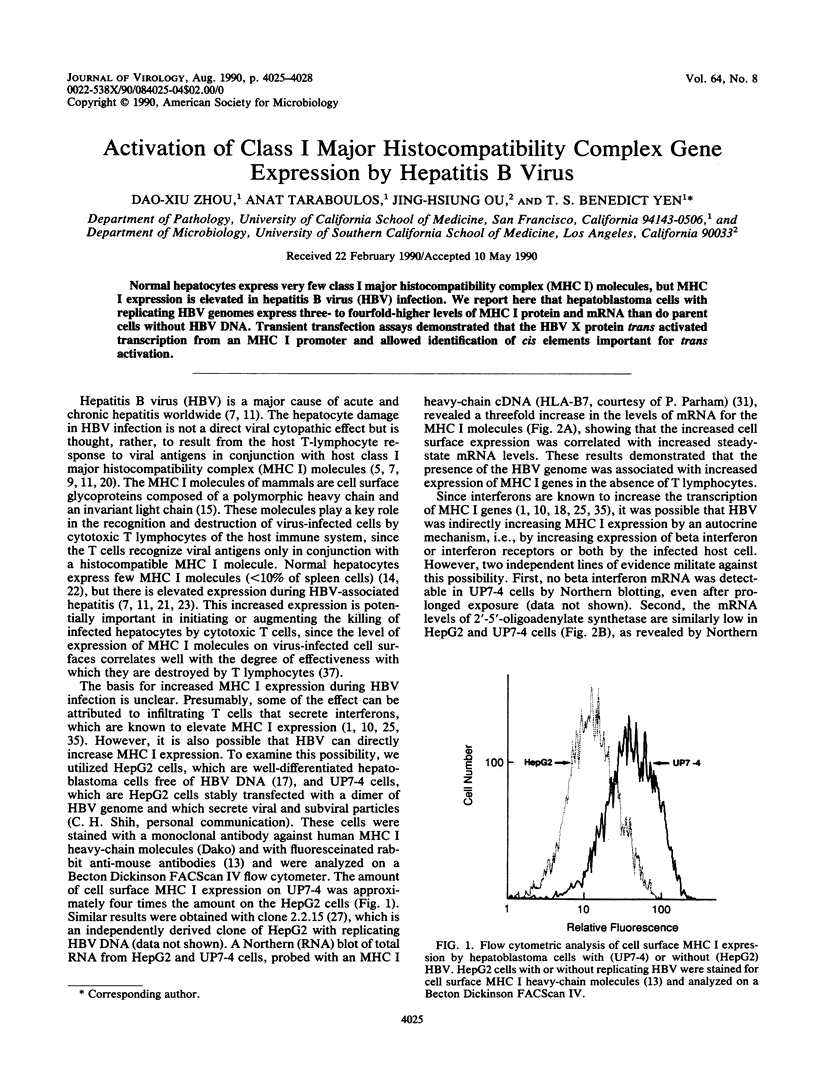


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Two transcription factors, NF-kappa B and H2TF1, interact with a single regulatory sequence in the class I major histocompatibility complex promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):723–727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benech P., Mory Y., Revel M., Chebath J. Structure of two forms of the interferon-induced (2'-5') oligo A synthetase of human cells based on cDNAs and gene sequences. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2249–2256. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03922.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell I. L., Harrison L. C., Ashcroft R. G., Jack I. Reovirus infection enhances expression of class I MHC proteins on human beta-cell and rat RINm5F cell. Diabetes. 1988 Mar;37(3):362–365. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.3.362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casini A., Alberti A., Banchetti E., Schiavon E., Patussi V., Pontisso P., Surrenti C., Realdi G. Cell-mediated immunity to HBcAg in chronic HBV infection. Am J Clin Pathol. 1987 Oct;88(4):494–498. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/88.4.494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisaka O., Araki K., Ochiya T., Tsurimoto T., Hiranyawasitte-Attatippaholkun W., Yanaihara N., Matsubara K. Purification of hepatitis B virus gene X product synthesized in Escherichia coli and its detection in a human hepatoblastoma cell line producing hepatitis B virus. Gene. 1987;60(2-3):183–189. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90226-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Ferrari C., Mondelli M. U. Hepatitis B virus structure and biology. Microb Pathog. 1989 May;6(5):311–325. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colgrove R., Simon G., Ganem D. Transcriptional activation of homologous and heterologous genes by the hepatitis B virus X gene product in cells permissive for viral replication. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):4019–4026. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.4019-4026.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari C., Penna A., Giuberti T., Tong M. J., Ribera E., Fiaccadori F., Chisari F. V. Intrahepatic, nucleocapsid antigen-specific T cells in chronic active hepatitis B. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):2050–2058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Manly S. P., McMahon M., Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of interferon-induced gene expression in human cells. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):745–755. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90270-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber M. A., Thung S. N. Molecular and cellular pathology of hepatitis B. Lab Invest. 1985 Jun;52(6):572–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakem R., Le Bouteiller P., Barad M., Trujillo M., Mercier P., Wietzerbin J., Lemonnier F. A. IFN-mediated differential regulation of the expression of HLA-B7 and HLA-A3 class I genes. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):297–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris H. W., Gill T. J., 3rd Expression of class I transplantation antigens. Transplantation. 1986 Aug;42(2):109–117. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198608000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood L., Steinmetz M., Malissen B. Genes of the major histocompatibility complex of the mouse. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:529–568. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.002525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel A., Kimura A., Fournier A., Fellous M., Kourilsky P. Interferon response sequence potentiates activity of an enhancer in the promoter region of a mouse H-2 gene. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):743–746. doi: 10.1038/322743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles B. B., Howe C. C., Aden D. P. Human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines secrete the major plasma proteins and hepatitis B surface antigen. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):497–499. doi: 10.1126/science.6248960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korber B., Mermod N., Hood L., Stroynowski I. Regulation of gene expression by interferons: control of H-2 promoter responses. Science. 1988 Mar 11;239(4845):1302–1306. doi: 10.1126/science.3125612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondelli M., Vergani G. M., Alberti A., Vergani D., Portmann B., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Specificity of T lymphocyte cytotoxicity to autologous hepatocytes in chronic hepatitis B virus infection: evidence that T cells are directed against HBV core antigen expressed on hepatocytes. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2773–2778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montano L., Miescher G. C., Goodall A. H., Wiedmann K. H., Janossy G., Thomas H. C. Hepatitis B virus and HLA antigen display in the liver during chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology. 1982 Sep-Oct;2(5):557–561. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840020508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natali P. G., Bigotti A., Nicotra M. R., Viora M., Manfredi D., Ferrone S. Distribution of human Class I (HLA-A,B,C) histocompatibility antigens in normal and malignant tissues of nonlymphoid origin. Cancer Res. 1984 Oct;44(10):4679–4687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paz M. O., Brenes F., Karayiannis P., Jowett T. P., Scheuer P. J., Thomas H. C. Chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Viral replication and patterns of inflammatory activity: serological, clinical and histological correlations. J Hepatol. 1986;3(3):371–377. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(86)80491-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., La Thangue N. B., Murphy D., Skene B. I. The regulation of cellular transcription by Simian virus 40 large T-antigen. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1985 Oct 22;226(1242):15–23. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1985.0076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal A., Wright S., Quade K., Gallimore P., Cedar H., Grosveld F. Increased MHC H-2K gene transcription in cultured mouse embryo cells after adenovirus infection. Nature. 1985 Jun 13;315(6020):579–581. doi: 10.1038/315579a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sells M. A., Chen M. L., Acs G. Production of hepatitis B virus particles in Hep G2 cells transfected with cloned hepatitis B virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1005–1009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto E., Yen T. S., Peterlin B. M., Ou J. H. Trans-activation of the human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat by the hepatitis B virus X protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8286–8290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirayoshi Y., Burke P. A., Appella E., Ozato K. Interferon-induced transcription of a major histocompatibility class I gene accompanies binding of inducible nuclear factors to the interferon consensus sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5884–5888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui A., Gaynor R., Srinivasan A., Mapoles J., Farr R. W. trans-activation of viral enhancers including long terminal repeat of the human immunodeficiency virus by the hepatitis B virus X protein. Virology. 1989 Apr;169(2):479–484. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sood A. K., Pan J., Biro P. A., Pereira D., Srivastava R., Reddy V. B., Duceman B. W., Weissman S. M. Structure and polymorphism of class I MHC antigen mRNA. Immunogenetics. 1985;22(2):101–121. doi: 10.1007/BF00563508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spandau D. F., Lee C. H. trans-activation of viral enhancers by the hepatitis B virus X protein. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):427–434. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.427-434.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twu J. S., Rosen C. A., Haseltine W. A., Robinson W. S. Identification of a region within the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat that is essential for transactivation by the hepatitis B virus gene X. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2857–2860. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2857-2860.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson L. D., Flyer D. C., Faller D. V. Murine retroviruses control class I major histocompatibility antigen gene expression via a trans effect at the transcriptional level. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2406–2415. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshie O., Schmidt H., Reddy E. S., Weissman S., Lengyel P. Mouse interferons enhance the accumulation of a human HLA RNA and protein in transfected mouse and hamster cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13169–13172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahm P., Hofschneider P. H., Koshy R. The HBV X-ORF encodes a transactivator: a potential factor in viral hepatocarcinogenesis. Oncogene. 1988 Aug;3(2):169–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. MHC-restricted cytotoxic T cells: studies on the biological role of polymorphic major transplantation antigens determining T-cell restriction-specificity, function, and responsiveness. Adv Immunol. 1979;27:51–177. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]