Abstract
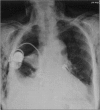
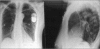
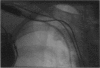
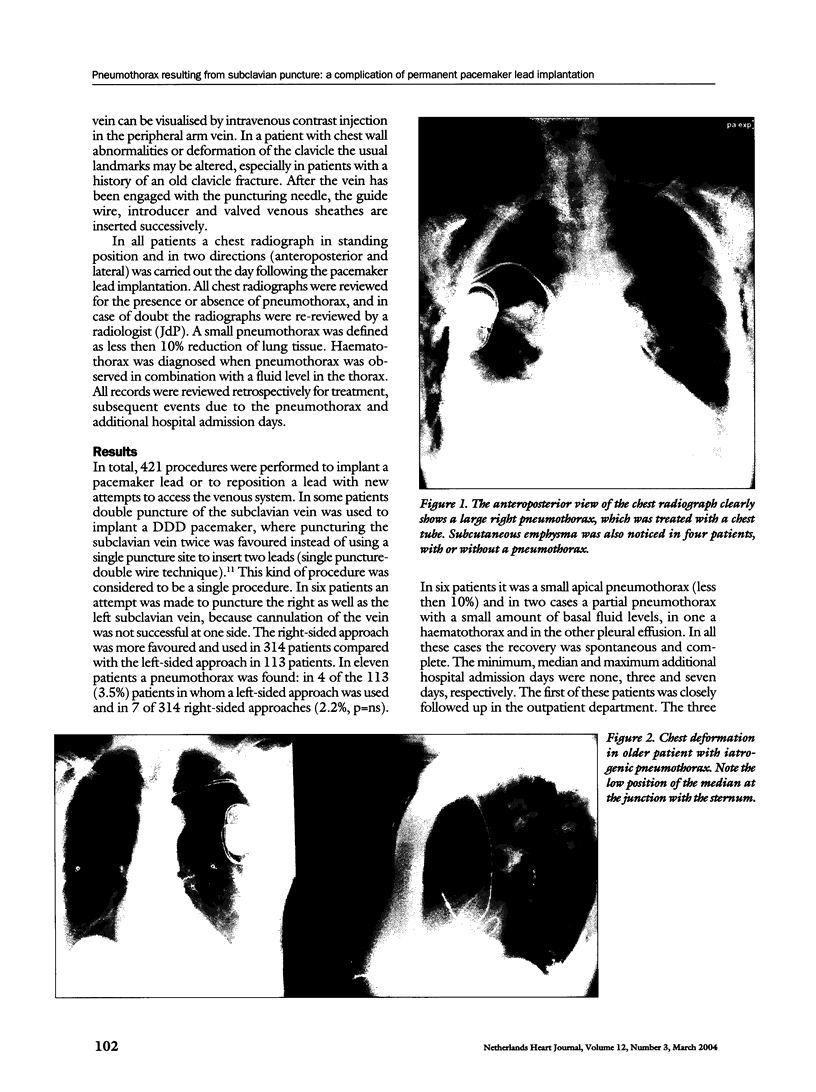
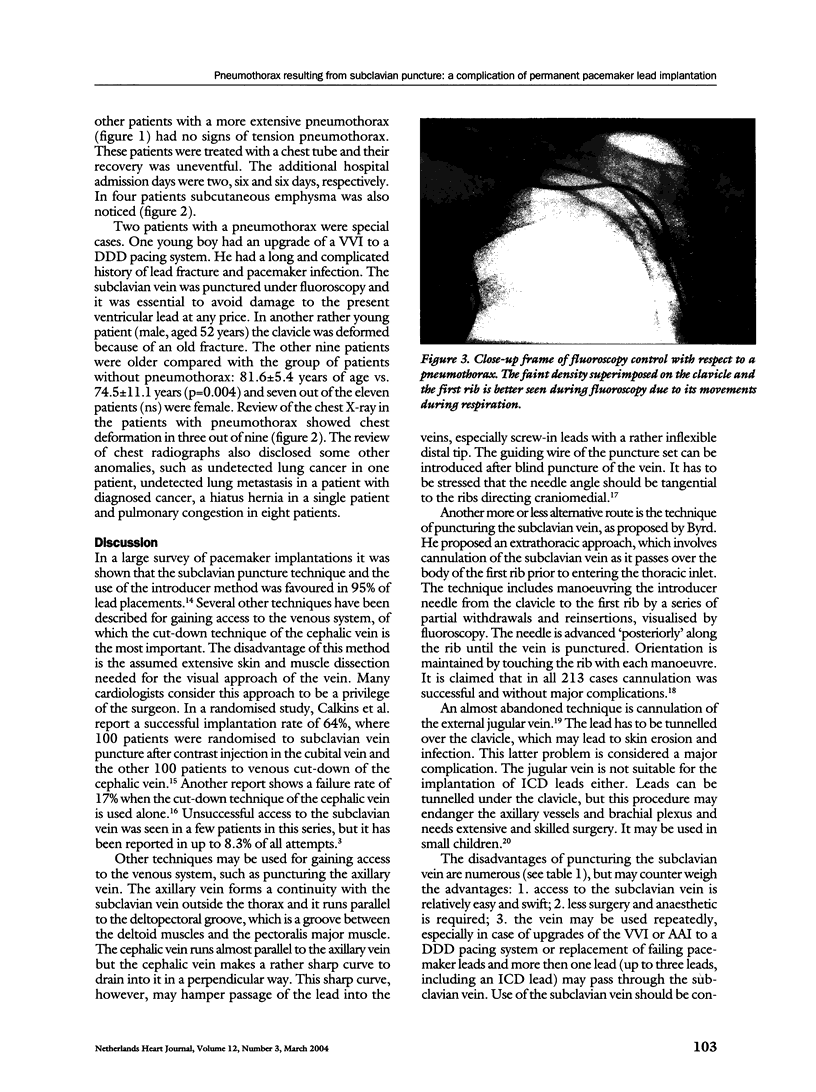
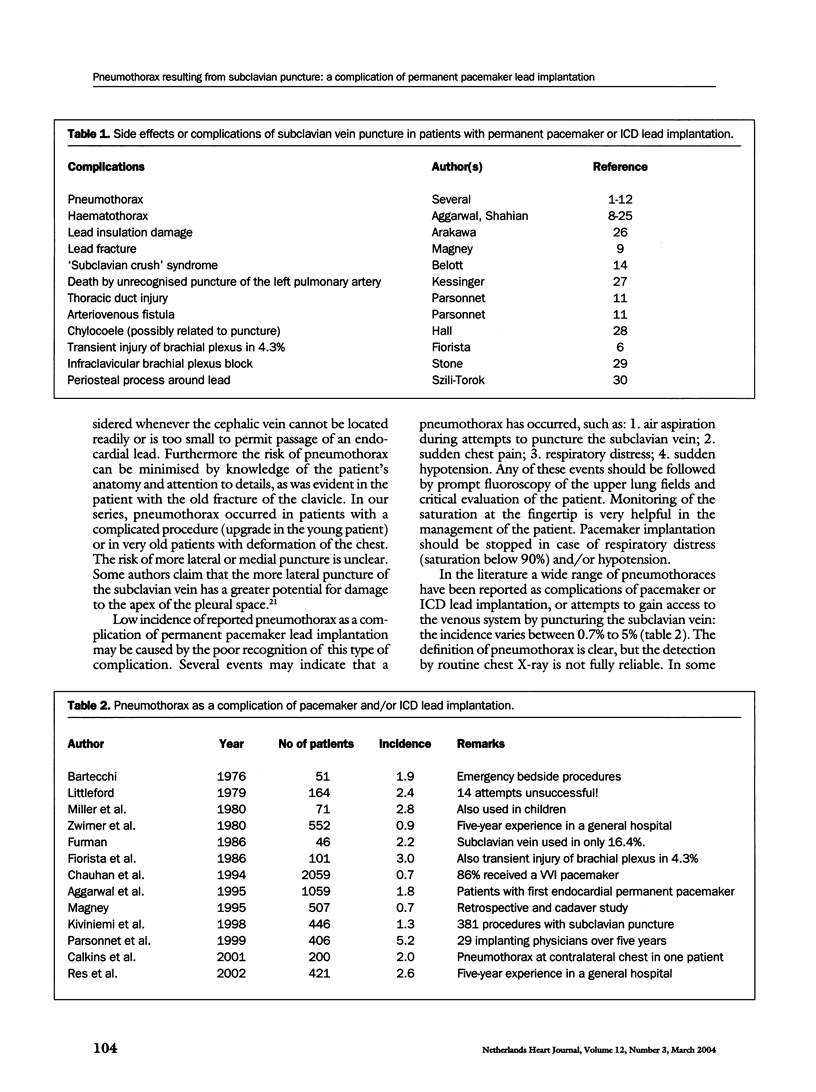
Pneumothorax is a mild complication during pacemaker lead implantation using the subclavian puncture technique. We report on five-year experience in 433 pacemaker lead implantation procedures in 379 patients. The cephalic vein route was solely used in twelve patients. Three procedures were performed over time in four patients and one patient needed four repetitive punctures for pacemaker lead implantation and replacement. Thus 421 punctures were carried out in 367 patients. Eleven case of pneumothorax were observed: in eight patients (1.9%) a partial pneumothorax occurred and in three patients (0.7%) the pneumothorax was nearly complete. In the latter patients a chest tube was inserted and hospital admission was prolonged for 3, 6 and 6 days, respectively. Old age with a corresponding abnormality in the form of chest deformation were predominantly found in the patients with this type of complication.
Keywords: lead implantation, morbidity, pneumothorax, subclavian puncture
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggarwal R. K., Connelly D. T., Ray S. G., Ball J., Charles R. G. Early complications of permanent pacemaker implantation: no difference between dual and single chamber systems. Br Heart J. 1995 Jun;73(6):571–575. doi: 10.1136/hrt.73.6.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arakawa M., Kambara K., Ito H., Hirakawa S., Umeda S., Hirose H. Intermittent oversensing due to internal insulation damage of temperature sensing rate responsive pacemaker lead in subclavian venipuncture method. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1989 Aug;12(8):1312–1316. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.1989.tb05044.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartecchi C. E. Bedside emergency transvenous cardiac pacing: experience in two community hospitals. JACEP. 1976 Mar;5(3):169–173. doi: 10.1016/s0361-1124(76)80338-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belott P. H. A variation on the introducer technique for unlimited access to the subclavian vein. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1981 Jan;4(1):43–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.1981.tb03673.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein A. D., Parsonnet V. Survey of cardiac pacing in the United States in 1989. Am J Cardiol. 1992 Feb 1;69(4):331–338. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(92)90229-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrd C. L. Clinical experience with the extrathoracic introducer insertion technique. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1993 Sep;16(9):1781–1784. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.1993.tb01810.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calkins H., Ramza B. M., Brinker J., Atiga W., Donahue K., Nsah E., Taylor E., Halperin H., Lawrence J. H., Tomaselli G. Prospective randomized comparison of the safety and effectiveness of placement of endocardial pacemaker and defibrillator leads using the extrathoracic subclavian vein guided by contrast venography versus the cephalic approach. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2001 Apr;24(4 Pt 1):456–464. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9592.2001.00456.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan A., Grace A. A., Newell S. A., Stone D. L., Shapiro L. M., Schofield P. M., Petch M. C. Early complications after dual chamber versus single chamber pacemaker implantation. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1994 Nov;17(11 Pt 2):2012–2015. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.1994.tb03791.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Despars J. A., Sassoon C. S., Light R. W. Significance of iatrogenic pneumothoraces. Chest. 1994 Apr;105(4):1147–1150. doi: 10.1378/chest.105.4.1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiorista F., Lazari M., Marzegalli M., Piane C., Cotti R., Casazza F., Molina L. Empleo de la vena subclavia para la estimulación cardíaca permanente. Arch Inst Cardiol Mex. 1986 Jul-Aug;56(4):309–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furman S. Venous cutdown for pacemaker implantation. Ann Thorac Surg. 1986 Apr;41(4):438–439. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(10)62705-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyke F. E., 3rd Doppler guided extrathoracic introducer insertion. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1995 May;18(5 Pt 1):1017–1021. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.1995.tb04742.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildick-Smith D. J., Lowe M. D., Newell S. A., Schofield P. M., Shapiro L. M., Stone D. L., Grace A. A., Petch M. C. Ventricular pacemaker upgrade: experience, complications and recommendations. Heart. 1998 Apr;79(4):383–387. doi: 10.1136/hrt.79.4.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessinger J. M., Holter A. R., Geha A. S. Implantation of permanent transvenous pacemaker via subclavian vein. Arch Surg. 1982 Aug;117(8):1105–1107. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1982.01380320087023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiviniemi M. S., Pirnes M. A., Eränen H. J., Kettunen R. V., Hartikainen J. E. Complications related to permanent pacemaker therapy. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1999 May;22(5):711–720. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.1999.tb00534.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littleford P. O., Parsonnet V., Spector S. D. Method for the rapid and atraumatic insertion of permanent endocardial pacemaker electrodes through the subclavian vein. Am J Cardiol. 1979 May;43(5):980–982. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(79)90363-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magney J. E., Parsons J. A., Flynn D. M., Hunter D. W. Pacemaker and defibrillator lead entrapment: case studies. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1995 Aug;18(8):1509–1517. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.1995.tb06737.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller F. A., Jr, Holmes D. R., Jr, Gersh B. J., Maloney J. D. Permanent transvenous pacemaker implantation via the subclavian vein. Mayo Clin Proc. 1980 May;55(5):309–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molina J. E., Dunnigan A. C., Crosson J. E. Implantation of transvenous pacemakers in infants and small children. Ann Thorac Surg. 1995 Mar;59(3):689–694. doi: 10.1016/0003-4975(94)01050-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsonnet V., Roelke M. The cephalic vein cutdown versus subclavian puncture for pacemaker/ICD lead implantation. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1999 May;22(5):695–697. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.1999.tb00531.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahian D. M., Venditti F. J., Jr Hemothorax associated with anticoagulation after placement of implantable cardioverter defibrillator: possible similarity to postinfarction Dressler's syndrome. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1992 Sep;15(9):1233–1235. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.1992.tb03131.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone C., Aquilina T. C., Mangar D., Fonte A. Left infraclavicular brachial plexus block during pacemaker placement through the left subclavian vein. Anesth Analg. 1994 Mar;78(3):602–602. doi: 10.1213/00000539-199403000-00034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tocino I. M., Miller M. H., Fairfax W. R. Distribution of pneumothorax in the supine and semirecumbent critically ill adult. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1985 May;144(5):901–905. doi: 10.2214/ajr.144.5.901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse H. F., Lau C. P., Leung S. K. A cephalic vein cutdown and venography technique to facilitate pacemaker and defibrillator lead implantation. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2001 Apr;24(4 Pt 1):469–473. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9592.2001.00469.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans C. R., Jr, Derrick J. R., Wallace J. M. Considerations of complications of permanent transvenous pacemakers. Am J Surg. 1967 Nov;114(5):704–710. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(67)90133-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwirner K. Fünfjährige Erfahrungen mit der Implantation permanenter Schrittmachersysteme unter primärer Verwendung der Vena subclavia. Z Kardiol. 1980 Dec;69(12):835–839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]