Abstract
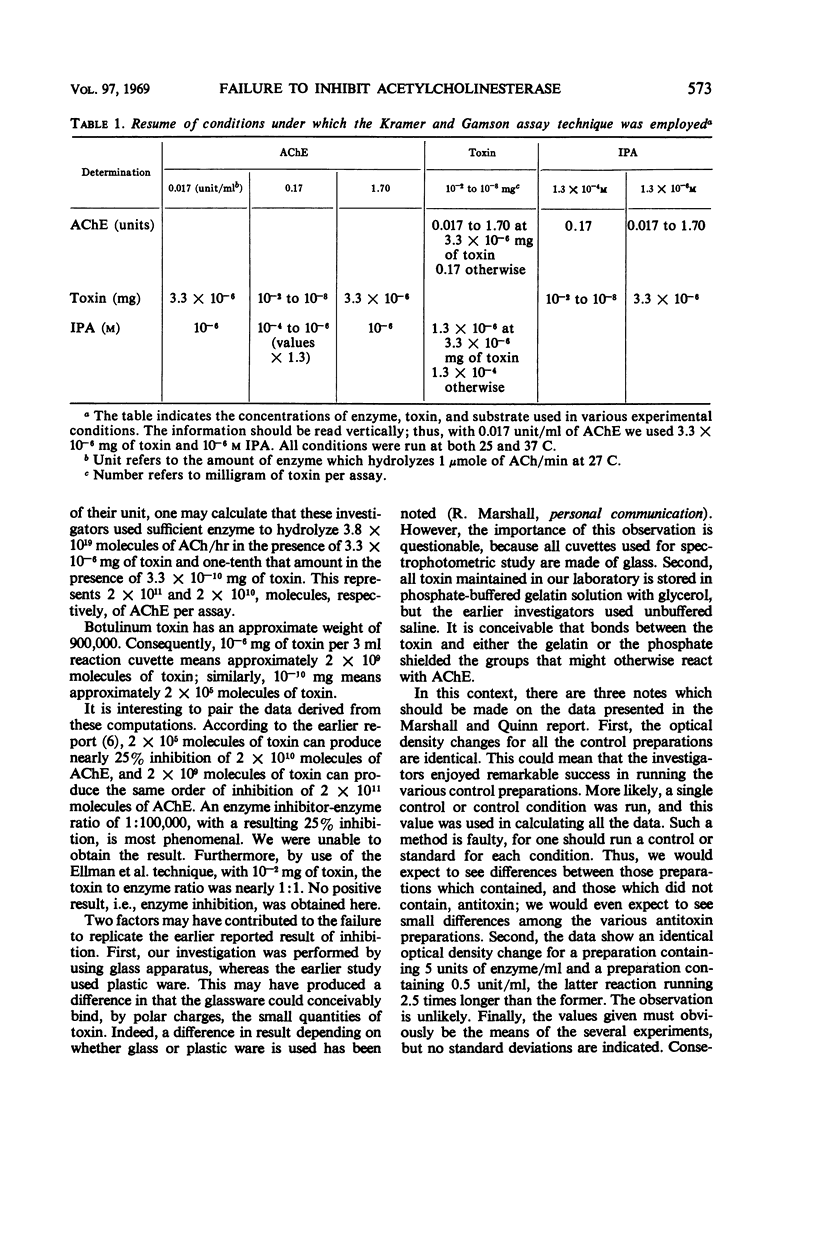
An attempt has been made to replicate an earlier finding that type A botulinum toxin can inhibit the in vitro activity of acetylcholinesterase. Two methods of enzyme assay were employed, but with neither technique were we able to reproduce the finding of in vitro enzyme inhibition. In fact, an examination of the data from the previous report leads us to question the possibility of the observations that were given. Furthermore, an investigation was carried out to determine if botulinum toxin can exert an inhibiting effect on acetylcholinesterase that is situated in the biological tissue. The answer again is negative. The experimental observations, coupled with several mathematical computations, do not support the notion that botulinum toxin is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ELLMAN G. L., COURTNEY K. D., ANDRES V., Jr, FEATHER-STONE R. M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1961 Jul;7:88–95. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(61)90145-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HART L. G., DIXON R. L., LONG J. P., MACKAY B. STUDIES USING CLOSTRIDIUM BOTULINUM TOXIN--TYPE A. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1965 Jan;7:84–89. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(65)90078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
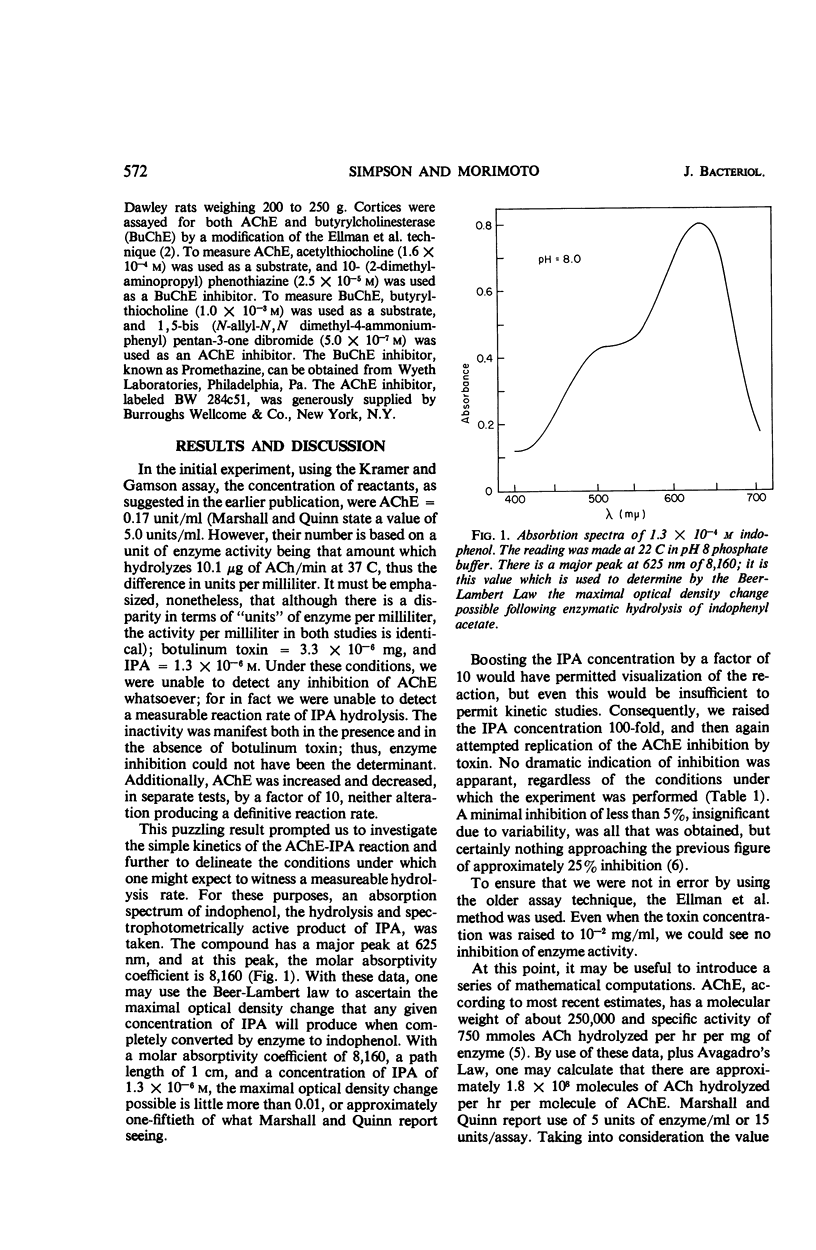
- Leuzinger W., Baker A. L. Acetylcholinesterase, I. Large-scale purification, homogeneity, and amino Acid analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):446–451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R., Quinn L. Y. In vitro acetylcholinesterase inhibition by type A botulinum toxin. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):812–814. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.812-814.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson L. L., De Balbian Verster F., Tapp J. T. Electrophysiological manifestations of experimental botulinal intoxication: depression of cortical EEG. Exp Neurol. 1967 Oct;19(2):199–211. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(67)90018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumyk G. B., Yocum C. F. Failure of type A botulinum toxin to inhibit acetylcholinesterase. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1970–1971. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1970-1971.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THESLEFF S. Supersensitivity of skeletal muscle produced by botulinum toxin. J Physiol. 1960 Jun;151:598–607. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZACKS S. I., METZGER J., SMITH C. W., BLUMBERG J. M. Localization of ferritin-labelled botulinus toxin in the neuromuscular junction of the mouse. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1962 Oct;21:610–633. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196210000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


