Abstract
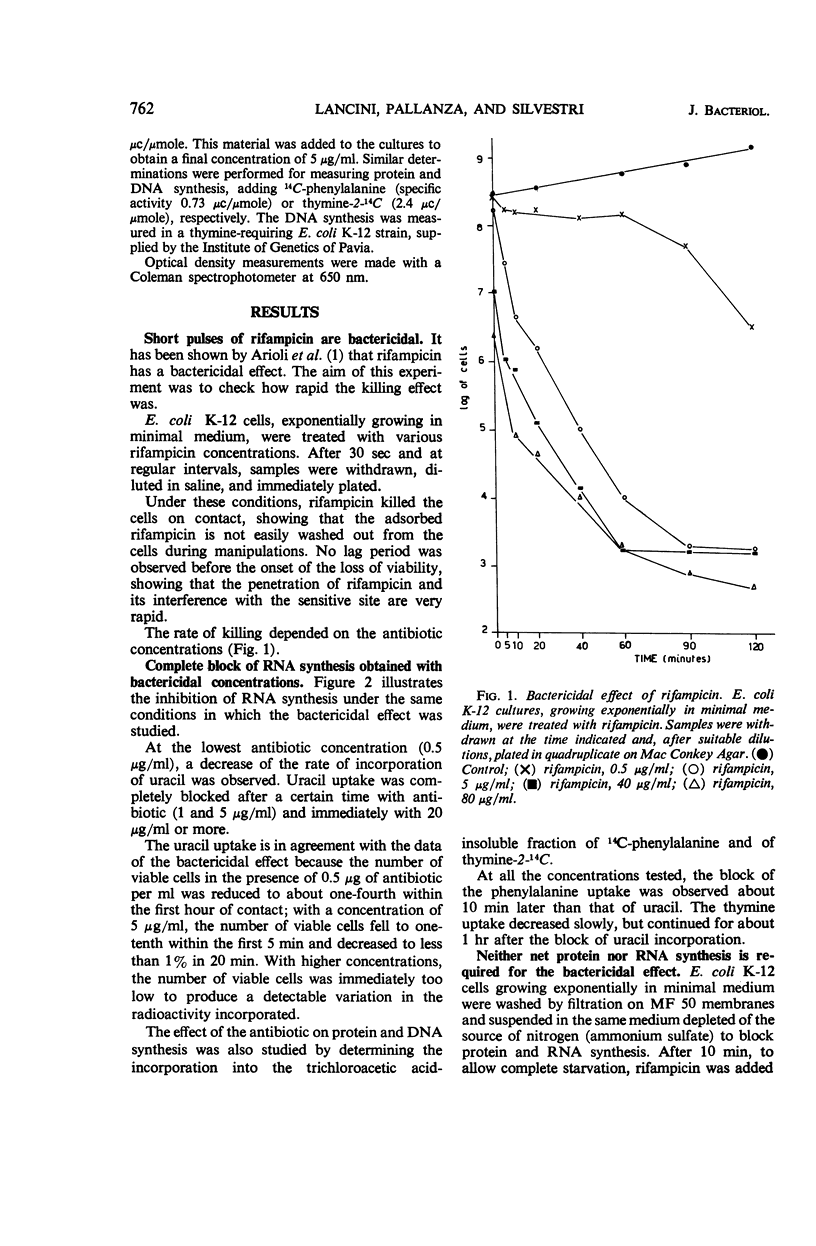
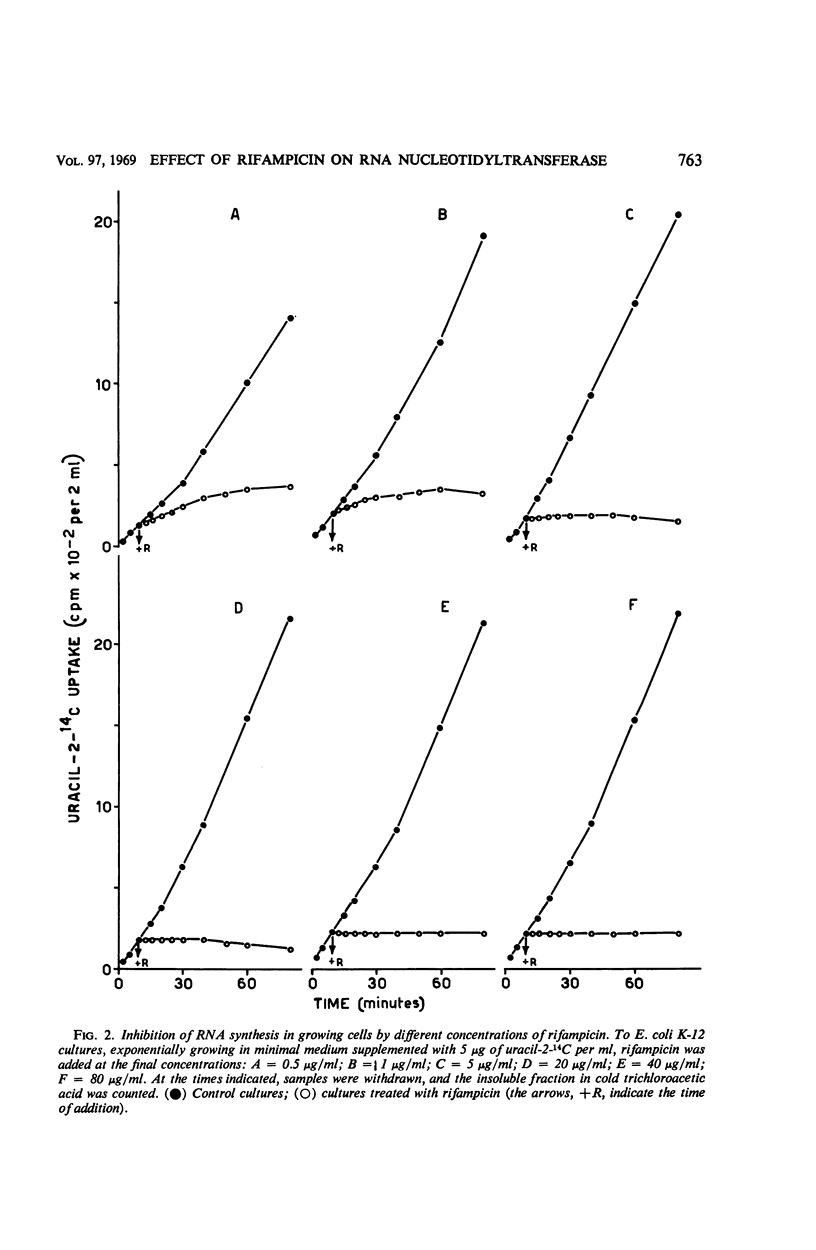
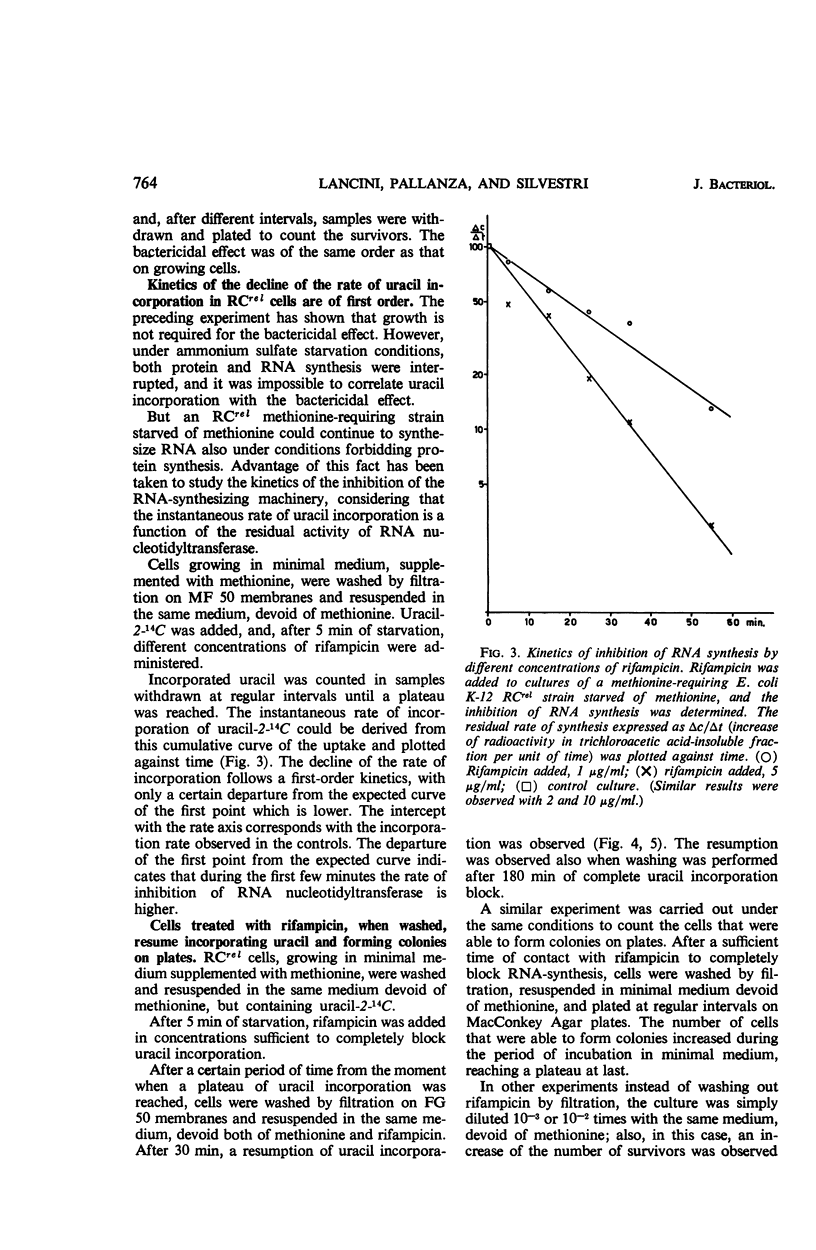
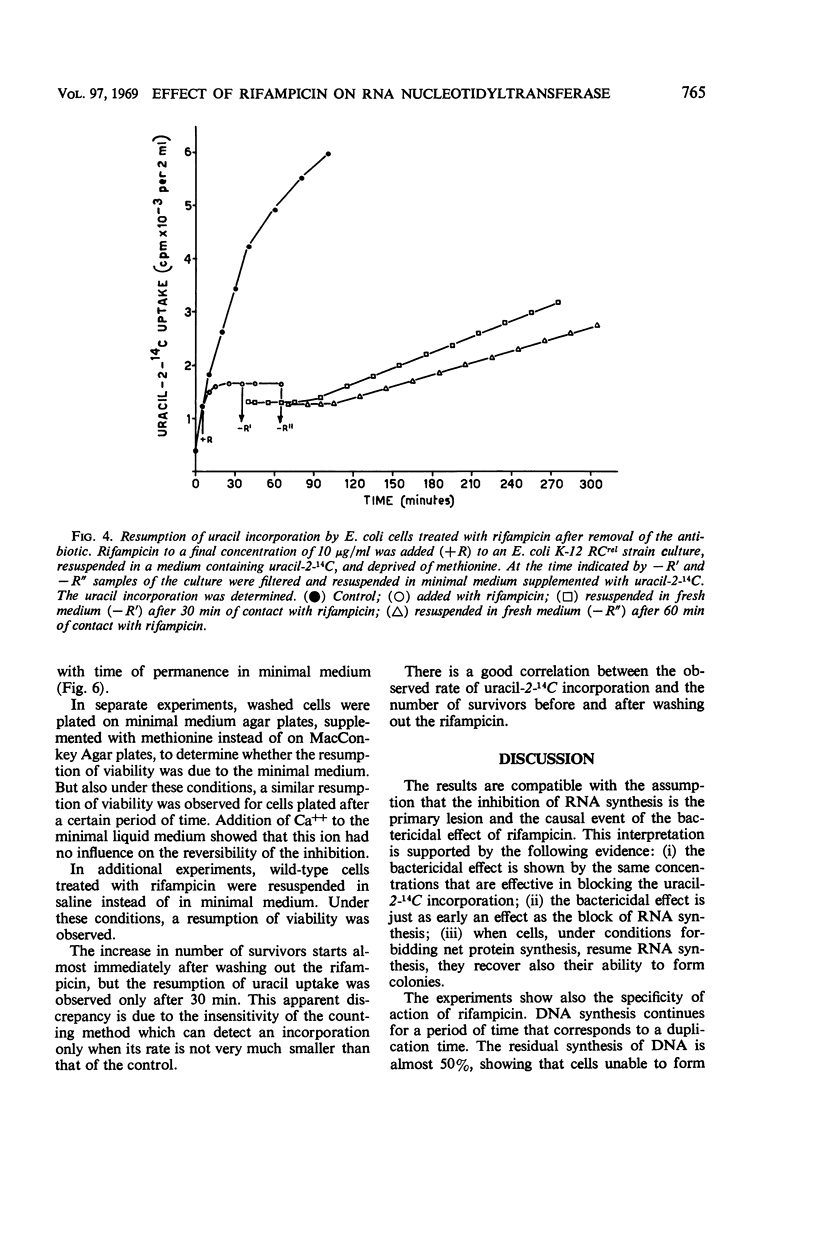
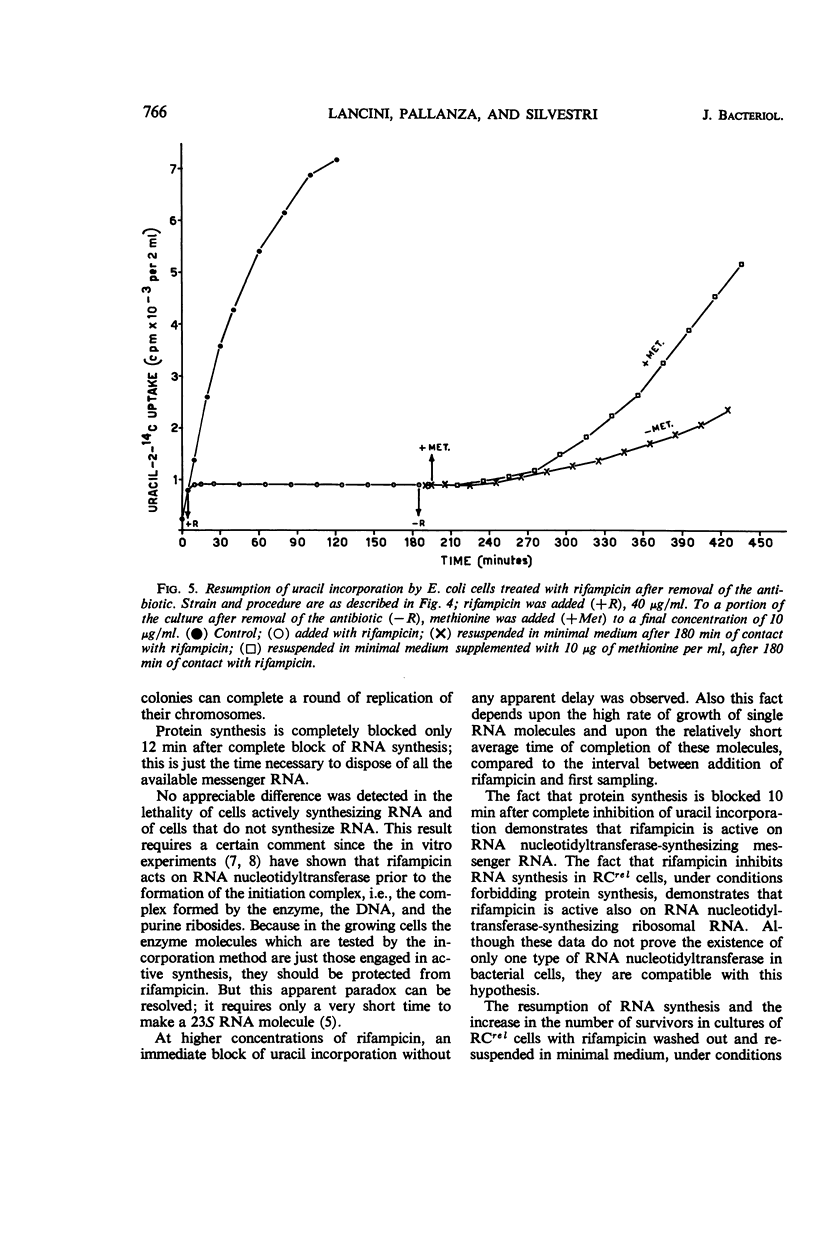
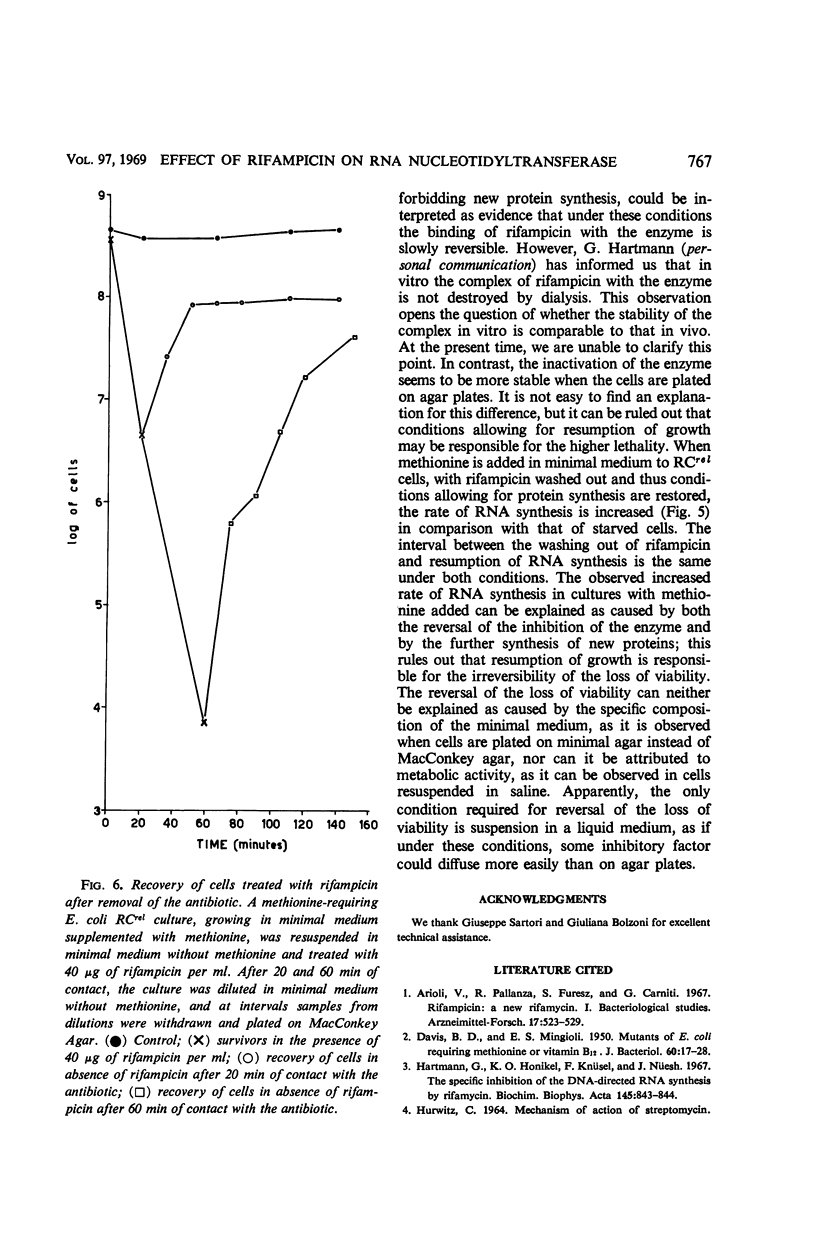
The mechanism of action of rifampicin, an antibiotic which inhibits in vitro the polycondensation of ribonucleotides by ribonucleic acid (RNA) nucleotidyltransferase, was studied in vivo in Escherichia coli. It is argued that the inhibition of RNA nucleotidyltransferase represents the primary lesion and is responsible for the bactericidal effect. This conclusion is based on (i) the correlation between concentrations of the antibiotic which block in vivo incorporation of labeled uracil and the bactericidal concentrations, (ii) the evidence that the loss of viability of the cells immediately follows the block of RNA synthesis, and (iii) the observation that the reversal of the inhibition of RNA synthesis goes together with a reversal of the loss of viability.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arioli V., Pallanza R., Furesz S., Carniti G. Rifampicin: a new rifamycin. I. Bacteriological studies. Arzneimittelforschung. 1967 May;17(5):523–529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D., MINGIOLI E. S. Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;60(1):17–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.1.17-28.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann G., Honikel K. O., Knüsel F., Nüesch J. The specific inhibition of the DNA-directed RNA synthesis by rifamycin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967;145(3):843–844. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90147-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi N., Pasqualucci C. R., Ballotta R., Sensi P. Rifampicin: a new orally active rifamycin. Chemotherapy. 1966;11(5):285–292. doi: 10.1159/000220462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sippel A., Hartmann G. Mode of action of rafamycin on the RNA polymerase reaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 18;157(1):218–219. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90286-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H., Mizuno S., Yamazaki H., Nitta K. Inhibition of DNA-dependent RNA synthesis by rifamycins. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1968 Mar;21(3):234–236. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.21.234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehrli W., Nüesch J., Knüsel F., Staehelin M. Action of rifamycins on RNA polymerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 18;157(1):215–217. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90285-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



