Abstract
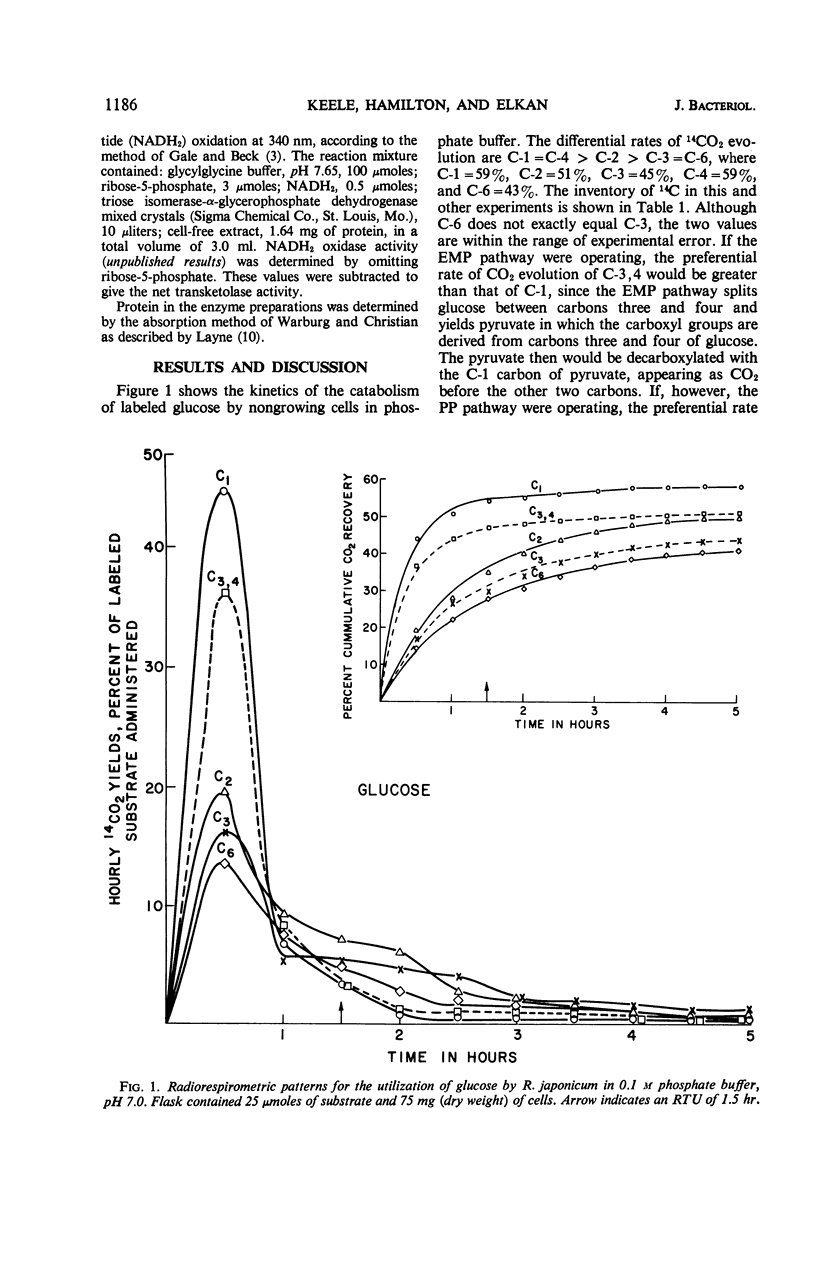
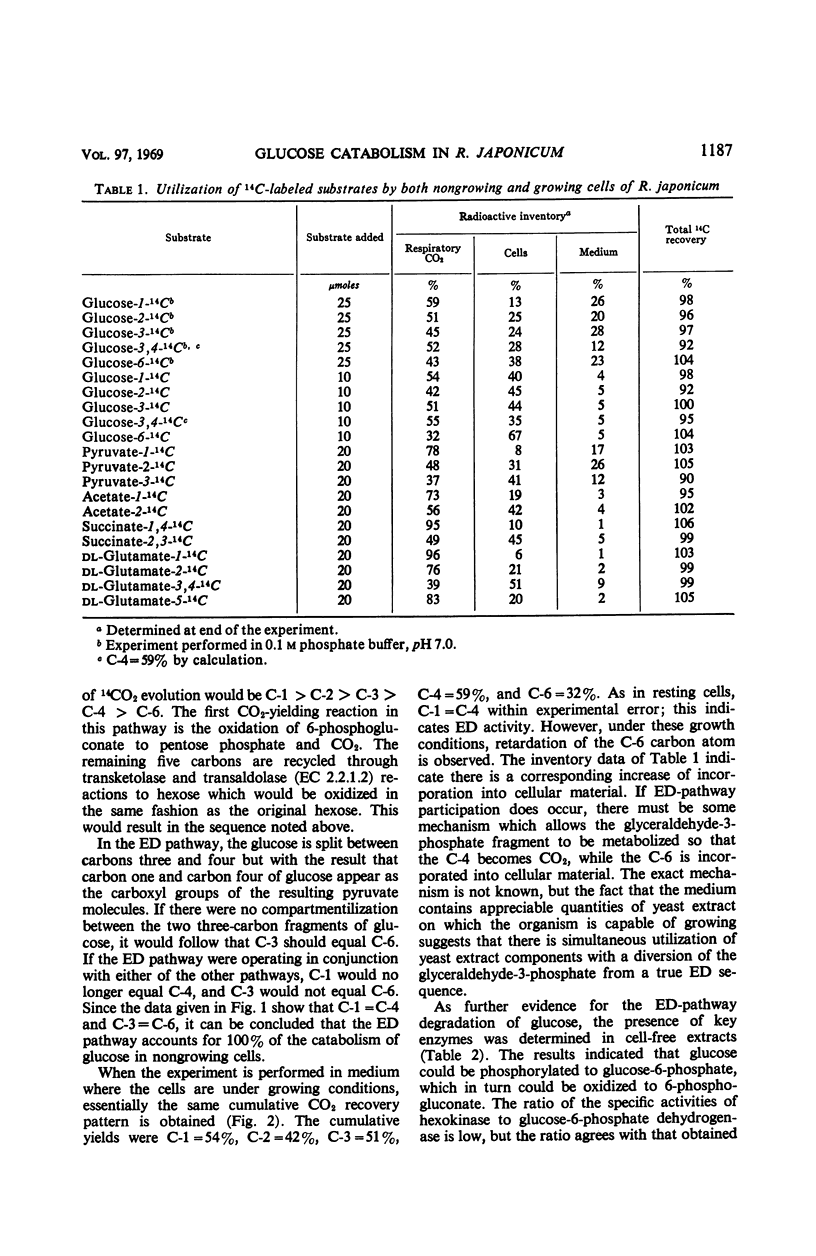
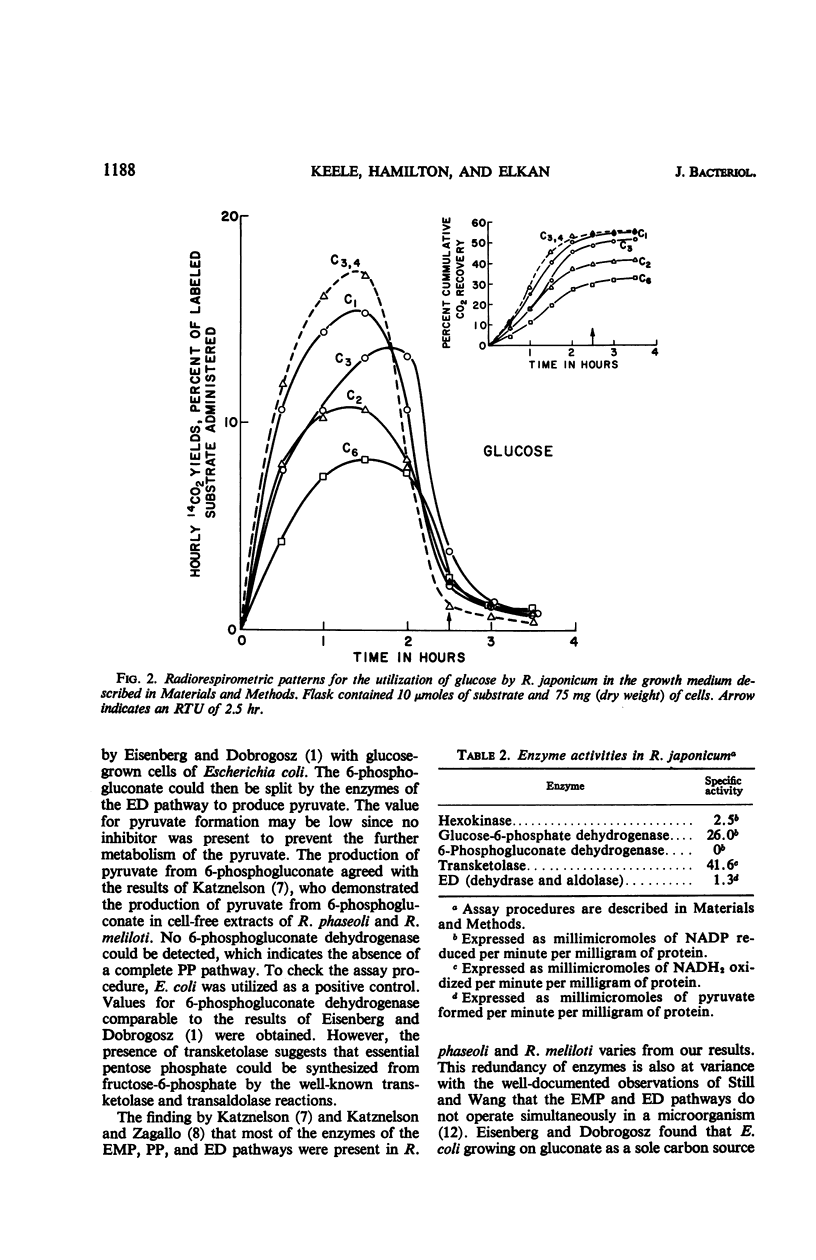
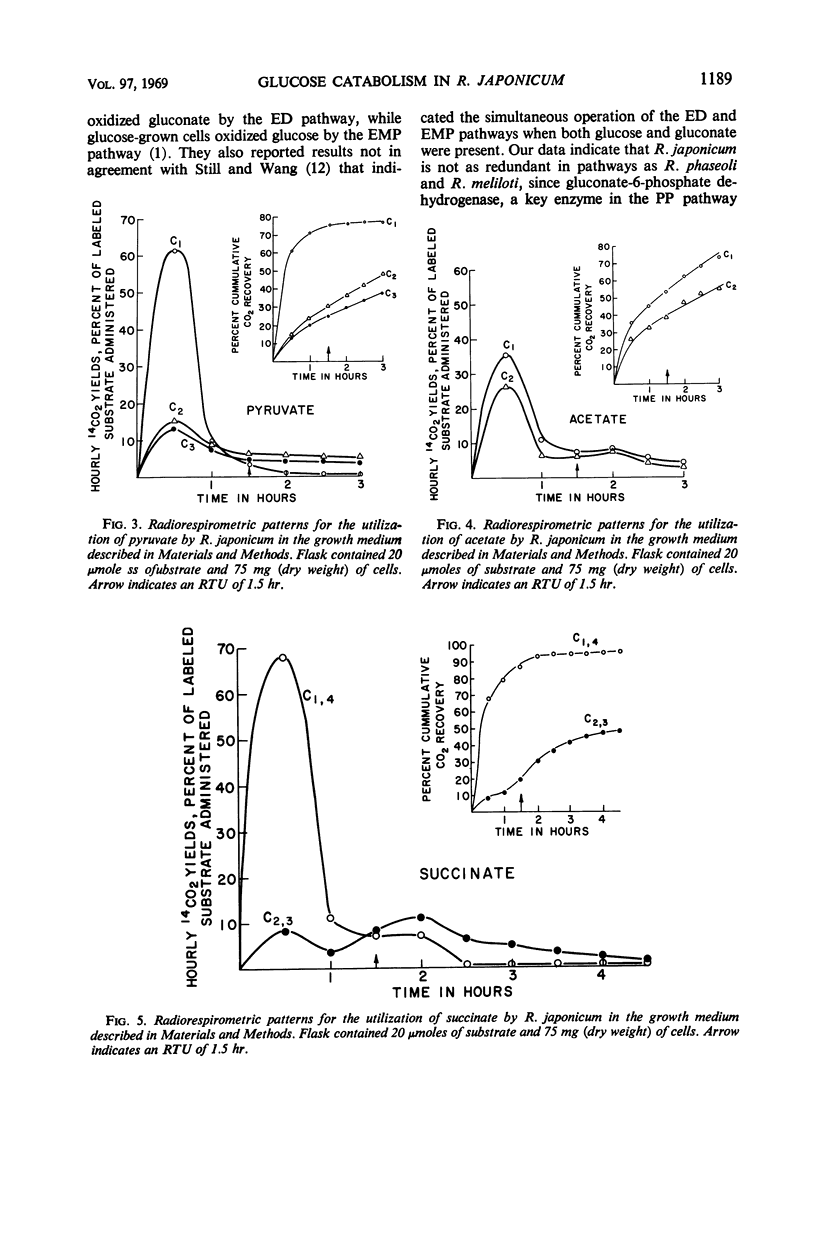
Glucose catabolism in Rhizobium japonicum ATCC 10324 was investigated by the radiorespirometric method and by assaying for key enzymes of the major energy-yielding pathways. Specifically labeled glucose gave the following results for resting cells, with values expressed as per cent 14CO2 evolution: C-1=59%, C-2=51%, C-3=45%, C-4=59%, and C-6=43%. These values indicate that glucose was degraded by the Entner-Doudoroff pathway alone. Cells which grew in glucose-yeast extract-salts medium gave essentially the same pattern except for retardation of the C-6 carbon. The rates were: C-1=54%, C-2=42%, C-3=51%, C-4=59%, and C-6=32%. Hexokinase, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, transketolase, and an enzyme system which produces pyruvate from 6-phosphogluconate were found to be present in these cells. No 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase was detected. Oxidation of specifically labeled pyruvate gave the following 14CO2 evolution pattern: C-1=78%, C-2=48%, and C-3=37%; the pattern from acetate was C-1=73%; and C-2=56%. Oxidation of glutamate showed the preferential rate of 14CO2 evolution to be C-1 > C-2=C-5 > C-3, 4, whereas a higher yield of 14CO2 was obtained from the C-1 and C-4 carbons of succinate than from the C-2 and C-3 carbons. These data are consistent with the operation of the Entner-Doudoroff pathway and tricarboxylic acid cycle as the catabolic pathways of glucose oxidation in R. japonicum.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Eisenberg R. C., Dobrogosz W. J. Gluconate metabolism in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):941–949. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.941-949.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAHAM P. H. STUDIES ON THE UTILISATION OF CARBOHYDRATES AND KREBS CYCLE INTERMEDIATES BY RHIZOBIA, USING AN AGAR PLATE METHOD. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1964;30:68–72. doi: 10.1007/BF02046703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale N. L., Beck J. V. Evidence for the Calvin cycle and hexose monophosphate pathway in Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1052–1059. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1052-1059.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JORDAN D. C. The bacteroids of the genus Rhizobium. Bacteriol Rev. 1962 Jun;26:119–141. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. V., Evans H. J., Ching T. Enzymes of the glyoxylate cycle in rhizobia and nodules of legumes. Plant Physiol. 1966 Oct;41(8):1330–1336. doi: 10.1104/pp.41.8.1330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZNELSON H. Production of pyruvate from 6-phosphogluconate by bacterial plant pathogens and legume bacteria. Nature. 1955 Mar 26;175(4456):551–552. doi: 10.1038/175551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZNELSON H., ZAGALLO A. C. Metabolism of rhizobia in relation to effectiveness. Can J Microbiol. 1957 Oct;3(6):879–884. doi: 10.1139/m57-097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raj H. D. Radiorespirometric studies of Leucothrix mucor. J Bacteriol. 1967 Sep;94(3):615–623. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.3.615-623.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERN I. J., WANG C. H., GILMOUR C. M. Comparative catabolism of carbohydrates in Pseudomonas species. J Bacteriol. 1960 Apr;79:601–611. doi: 10.1128/jb.79.4.601-611.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STILL G. G., WANG C. H. GLUCOSE CATABOLISM IN AZOTOBACTER VINELANDII. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Apr;105:126–132. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90243-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WANG C. H., STERN I., GILMOUR C. M., KLUNGSOYR S., REED D. J., BIALY J. J., CHRISTENSEN B. E., CHELDELIN V. H. Comparative study of glucose catabolism by the radiorespirometric method. J Bacteriol. 1958 Aug;76(2):207–216. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.2.207-216.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



