Abstract
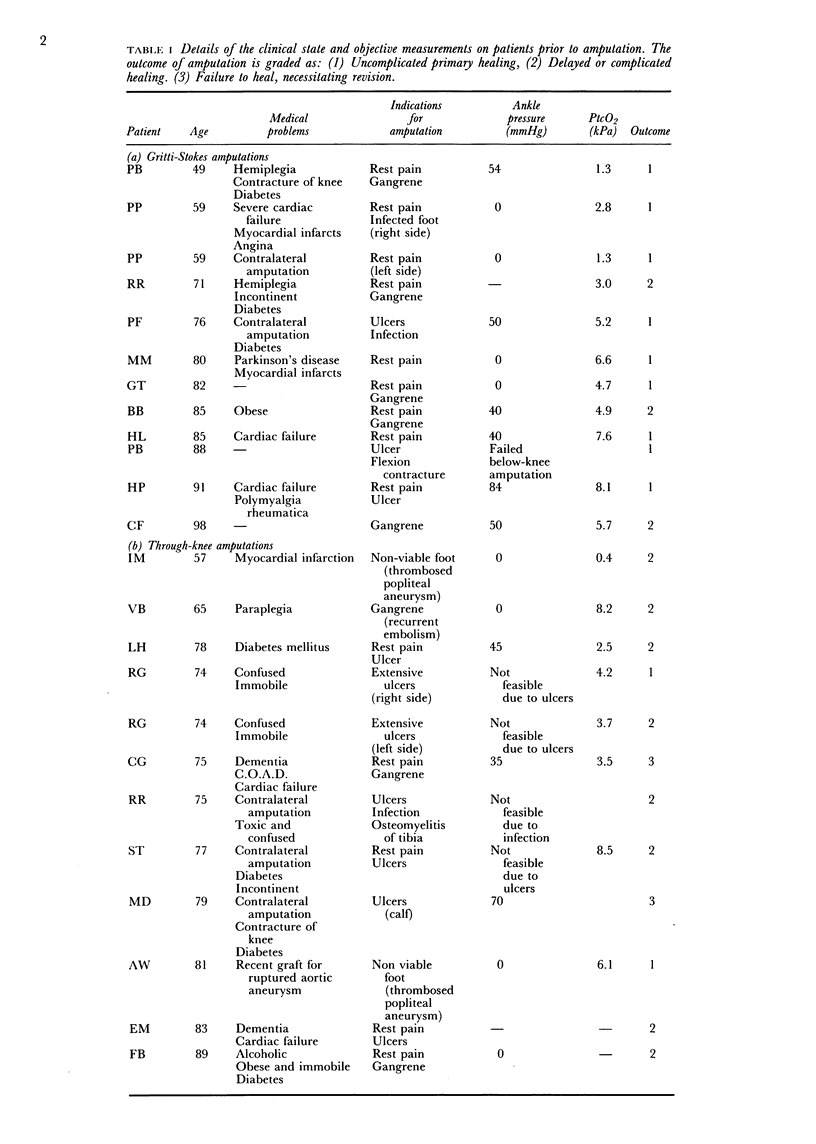
Twenty-two patients with a median age of 79 years had 24 amputations about knee joint level. The patients were randomised to undergo either Gritti-Stokes or through-knee amputations. In two-thirds of limbs transcutaneous oxygen was less than 4.65 KPa (35 mmHg) or there were no audible Doppler signals at the ankle, indicating that a below-knee amputation would have been at risk of failing to heal, and in the remainder an amputation at the knee joint was considered the preferable site for a variety of reasons. Nine of 12 (75%) Gritti-Stokes amputations underwent uncomplicated primary healing compared with only 2 of 12 (17%) through-knee procedures (P = 0.04). Two through-knee amputations required revision to above the knee (17%) while all Gritti-Stokes amputations healed. Three patients in each group became mobile on a prosthesis, the remainder being bilateral amputees or unable to manage an artificial limb.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes R. W., Shanik G. D., Slaymaker E. E. An index of healing in below-knee amputation: leg blood pressure by Doppler ultrasound. Surgery. 1976 Jan;79(1):13–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess E. M. Amputations. Surg Clin North Am. 1983 Jun;63(3):749–770. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)43040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilvers A. S., Briggs J., Browse N. L., Kinmonth J. B. Below- and through-knee amputations in ischaemic disease. Br J Surg. 1971 Nov;58(11):824–826. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800581105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doran J., Hopkinson B. R., Makin G. S. The Gritti-Stokes amputation in ischaemia: a review of 134 cases. Br J Surg. 1978 Feb;65(2):135–137. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800650219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. W., Hawkins B. S., Irvine W. T., Jamieson C. W. An assessment of above- and through-knee amputations. Br J Surg. 1972 Nov;59(11):873–875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard R. R., Chamberlain J., Macpherson A. I. Through-knee amputation in peripheral vascular disease. Lancet. 1969 Aug 2;2(7614):240–242. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen J. S., Poulsen T. M., Krasnik M. Through-knee amputations. Acta Orthop Scand. 1982 Jun;53(3):463–466. doi: 10.3109/17453678208992241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LISHMAN I. V. THE GRITTI-STOKES AMPUTATION IN PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 1965 Apr;10:212–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P., Renwick S., Thomas E. M. Gritti-Stokes amputation in atherosclerosis: a review of 237 cases. Br Med J. 1967 Sep 30;3(5569):837–838. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5569.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCollough N. G., 3rd, Shea J. D., Warren W. D., Sarmiento A. The dysvascular amputee: surgery and rehabilitation. Curr Probl Surg. 1971 Oct;:1–67. doi: 10.1016/s0011-3840(71)80015-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murdoch G. Levels of amputation and limiting factors. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1967 Apr;40(4):204–216. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustapha N. M., Redhead R. G., Jain S. K., Wielogorski J. W. Transcutaneous partial oxygen pressure assessment of the ischemic lower limb. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1983 May;156(5):582–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcombe J. F., Marcuson R. W. Through-knee amputation. Br J Surg. 1972 Apr;59(4):260–266. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800590404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholas G. G., Myers J. L., DeMuth W. E., Jr The role of vascular laboratory criteria in the selection of patients for lower extremity amputation. Ann Surg. 1982 Apr;195(4):469–473. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198204000-00014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratliff D. A., Clyne C. A., Chant A. D., Webster J. H. Prediction of amputation wound healing: the role of transcutaneous pO2 assessment. Br J Surg. 1984 Mar;71(3):219–222. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800710320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor G. W. Amputation of the lower limb for ischemic disease. Proc R Soc Med. 1967 Jan;60(1):69–70. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


