Abstract
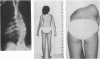
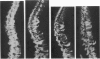
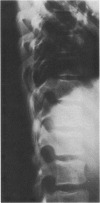
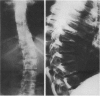
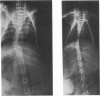
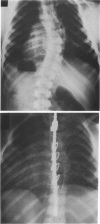
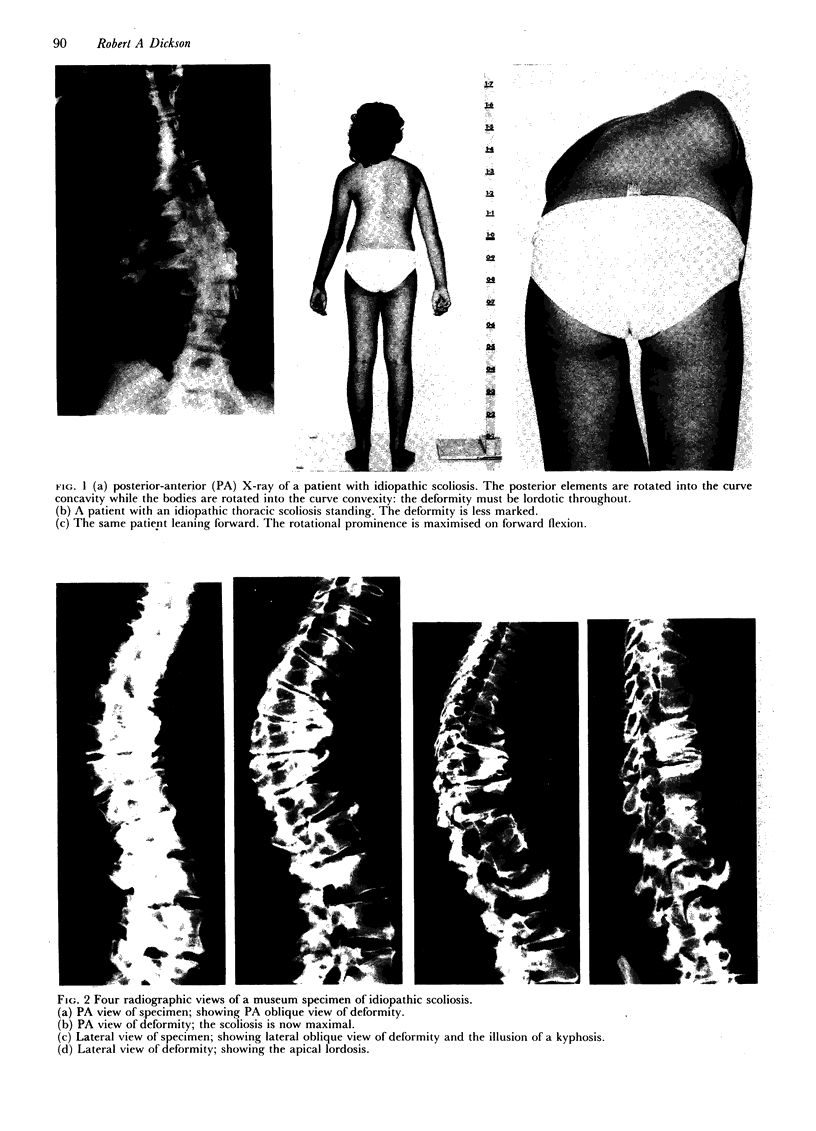
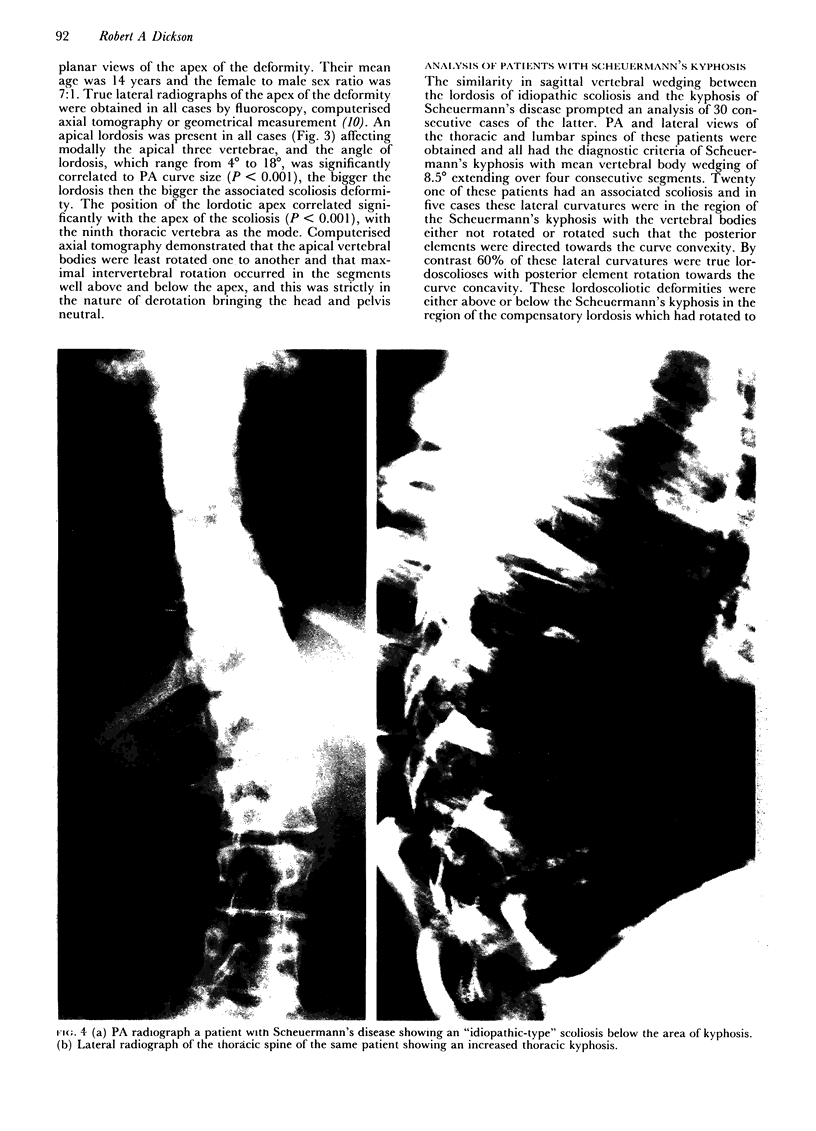
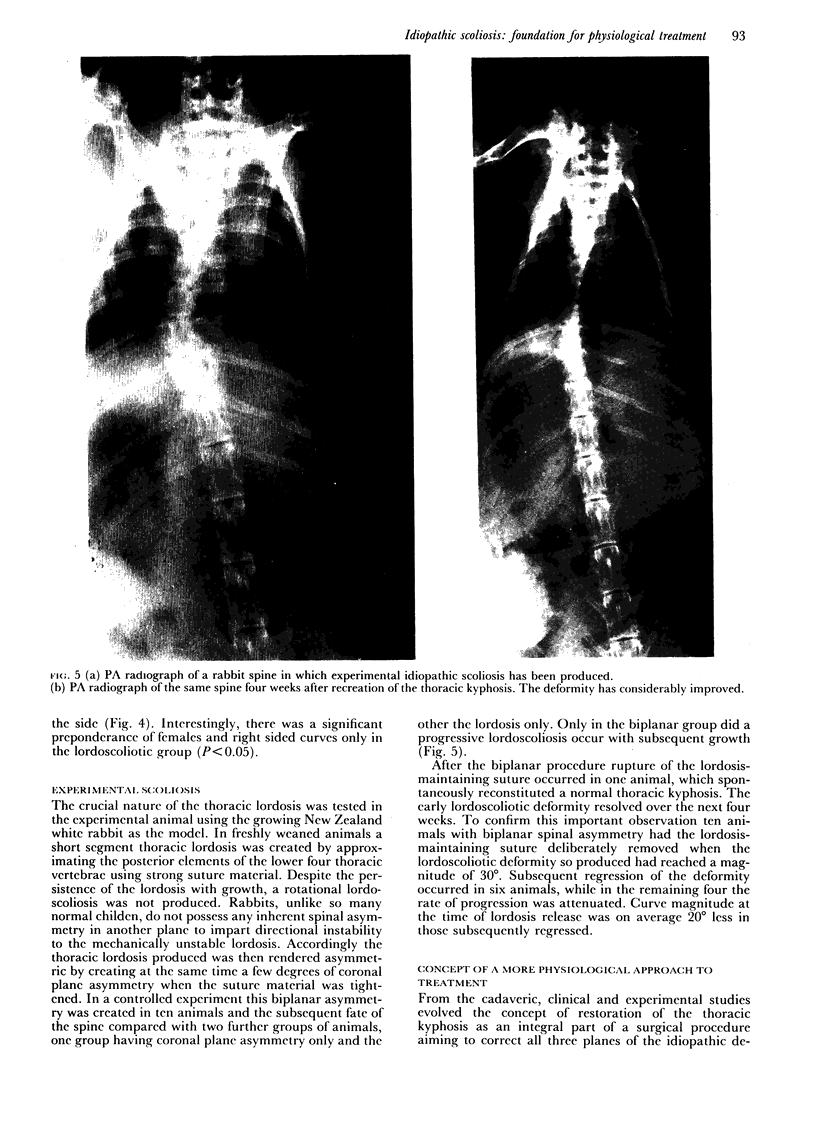
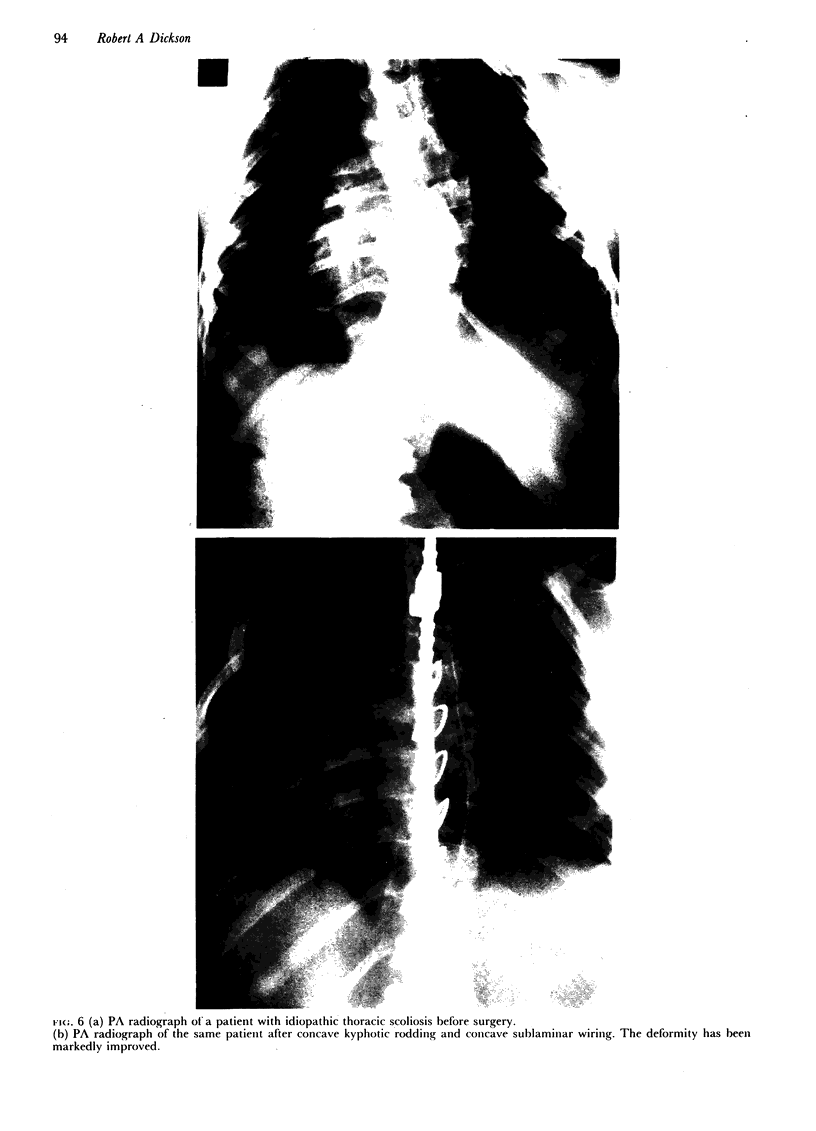
The three-dimensional nature of the idiopathic spinal deformity has been investigated in cadaveric specimens and patients with both idiopathic scoliosis and idiopathic kyphosis (Scheuermann's disease). In both scoliotic and kyphotic deformities the essential lesion lies in the sagittal plane with apical vertebral wedging. In idiopathic scoliosis there is an apical lordosis which being biomechanically unstable rotates to the side to produce a scoliotic deformity as a secondary component. In contradistinction the kyphotic wedging process of Scheuermann's disease is mechanically stable and any associated idiopathic type scoliosis occurs above and below the region of kyphosis. When an asymmetric lordosis is created in the growing New Zealand white rabbit, a progressive lordoscoliosis is readily produced and when the thoracic kyphosis is restored the scoliotic deformity shows evidence of regression and this forms the basis of physiological treatment. In 25 patients with idiopathic thoracic scoliosis the thoracic kyphosis has been restored and this leads to enhanced correction of the deformity in all three planes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander M. A., Season E. H. Idiopathic scoliosis: an electromyographic study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1978 Jul;59(7):314–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford D. S., Moe J. H., Montalvo F. J., Winter R. B. Scheuermann's kyphosis and roundback deformity. Results of Milwaukee brace treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1974 Jun;56(4):740–758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson R. A., Lawton J. O., Archer I. A., Butt W. P. The pathogenesis of idiopathic scoliosis. Biplanar spinal asymmetry. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1984 Jan;66(1):8–15. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.66B1.6693483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson R. A., Lawton J. O., Archer I. A., Butt W. P. The pathogenesis of idiopathic scoliosis. Biplanar spinal asymmetry. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1984 Jan;66(1):8–15. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.66B1.6693483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson R. A. Scoliosis in the community. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Feb 19;286(6365):615–618. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6365.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keiser R. P., Shufflebarger H. L. The Milwaukee brace in idiopathic scoliosis: evaluation of 123 completed cases. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976 Jul-Aug;(118):19–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LE FEBVRE J., TRIBOULET-CHASSEVANT A., MISSIRLIU M. F. Electromyographic data in idiopathic scoliosis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1961 Oct;42:710–711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luque E. R. Paralytic scoliosis in growing children. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1982 Mar;(163):202–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roaf R. The basic anatomy of scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1966 Nov;48(4):786–792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOMERVILLE E. W. Rotational lordosis; the development of single curve. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1952 Aug;34-B(3):421–427. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.34B3.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]