Abstract
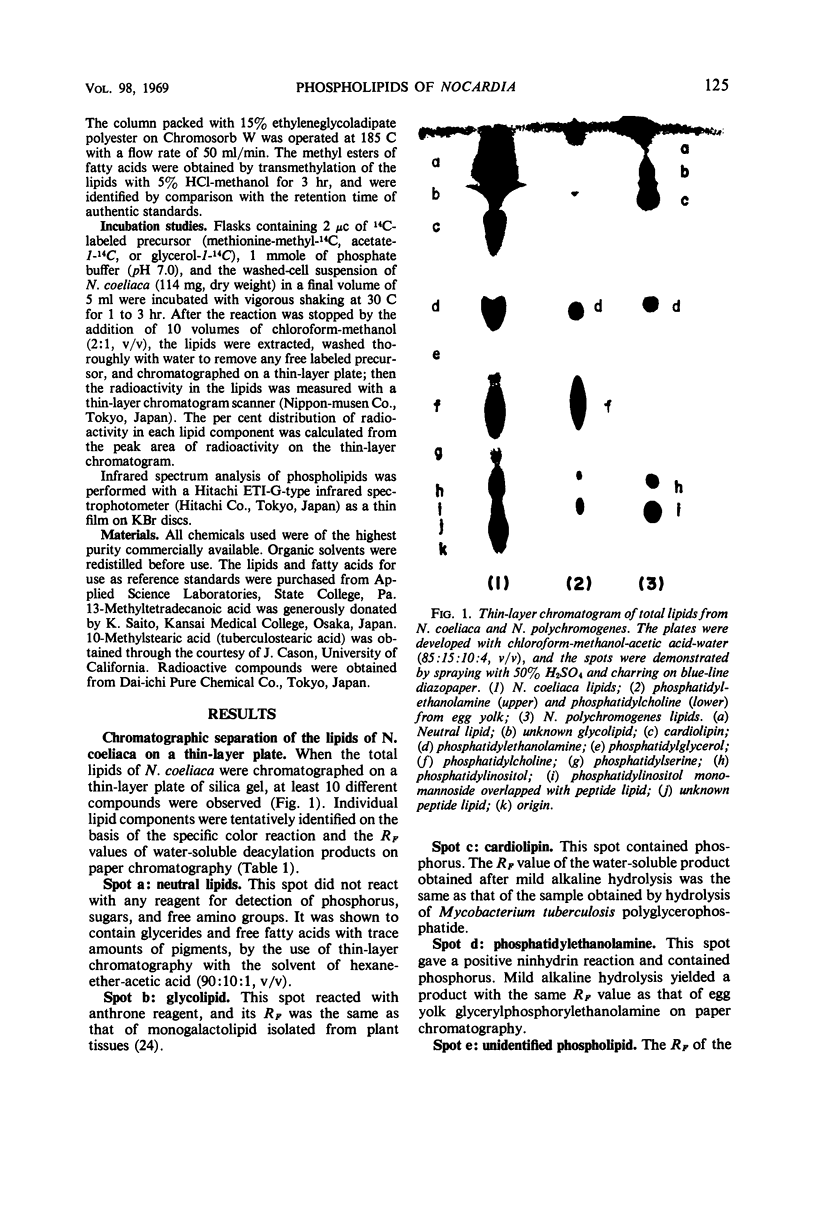
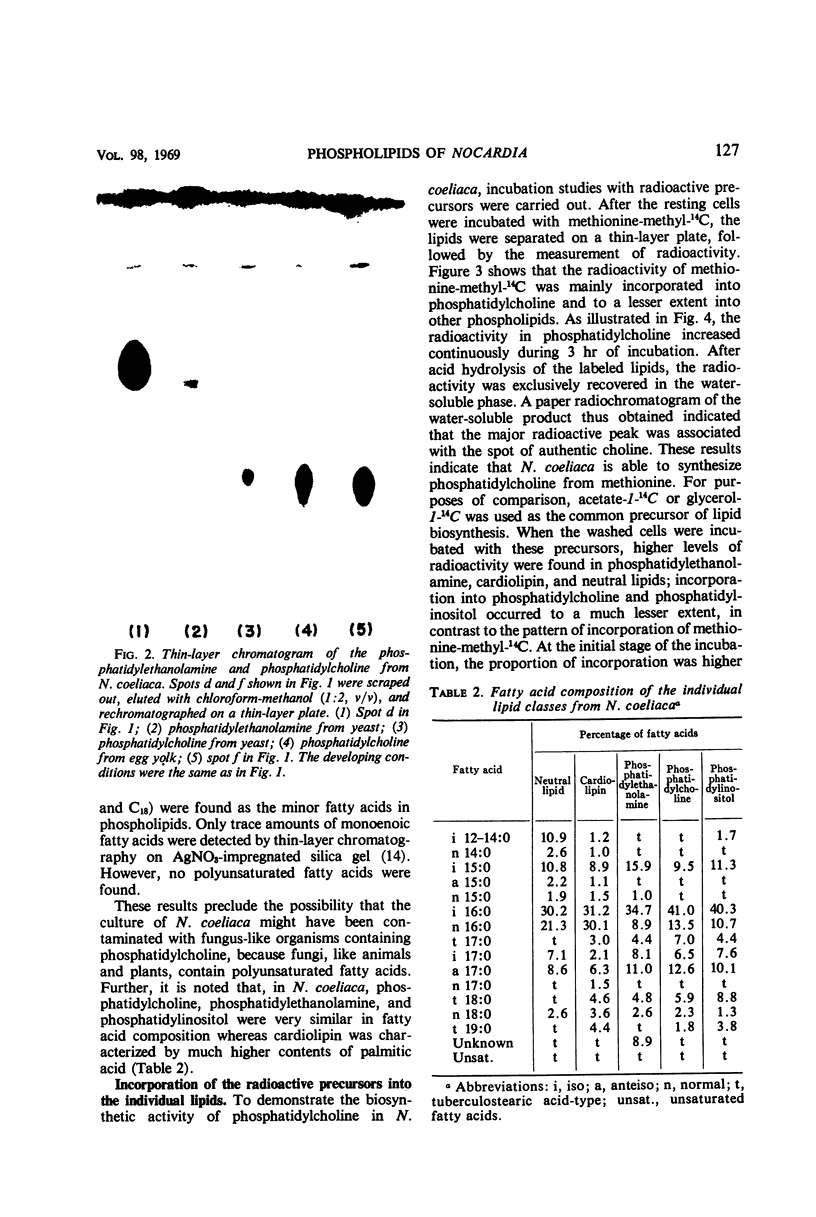
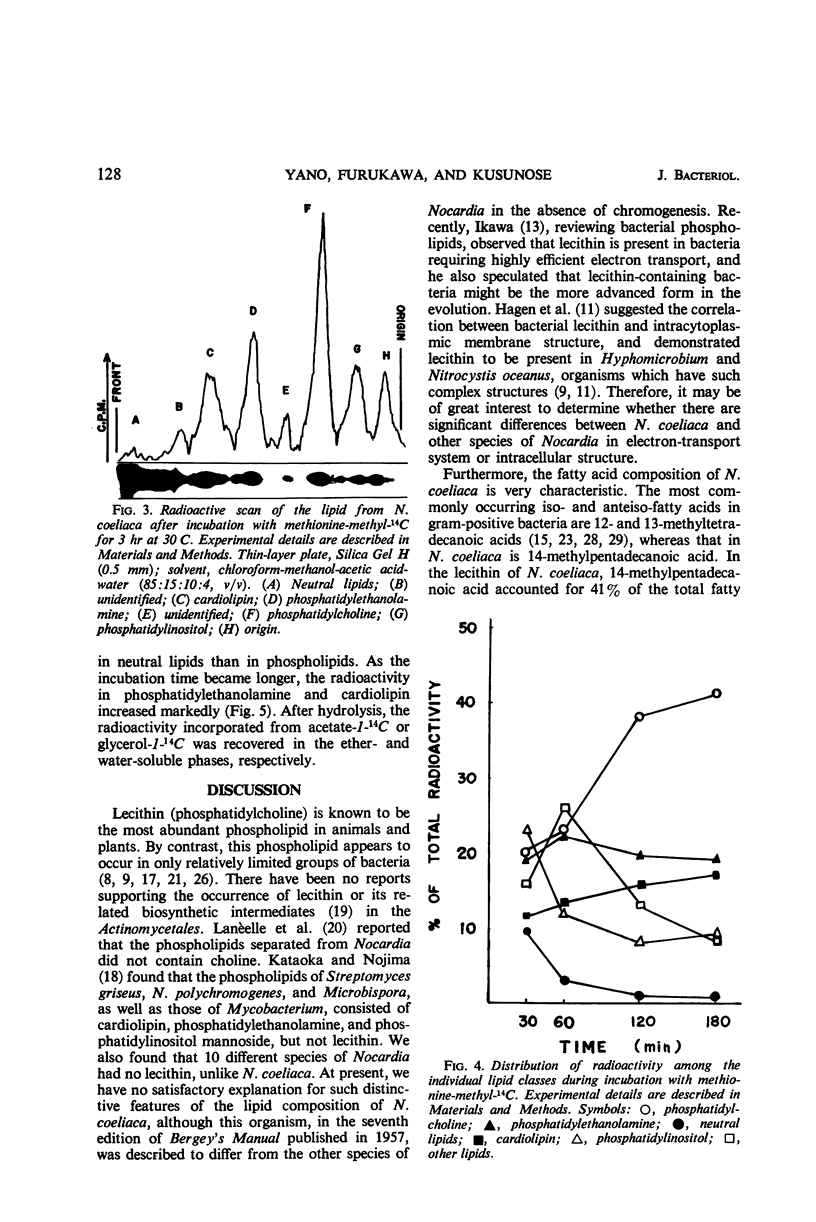
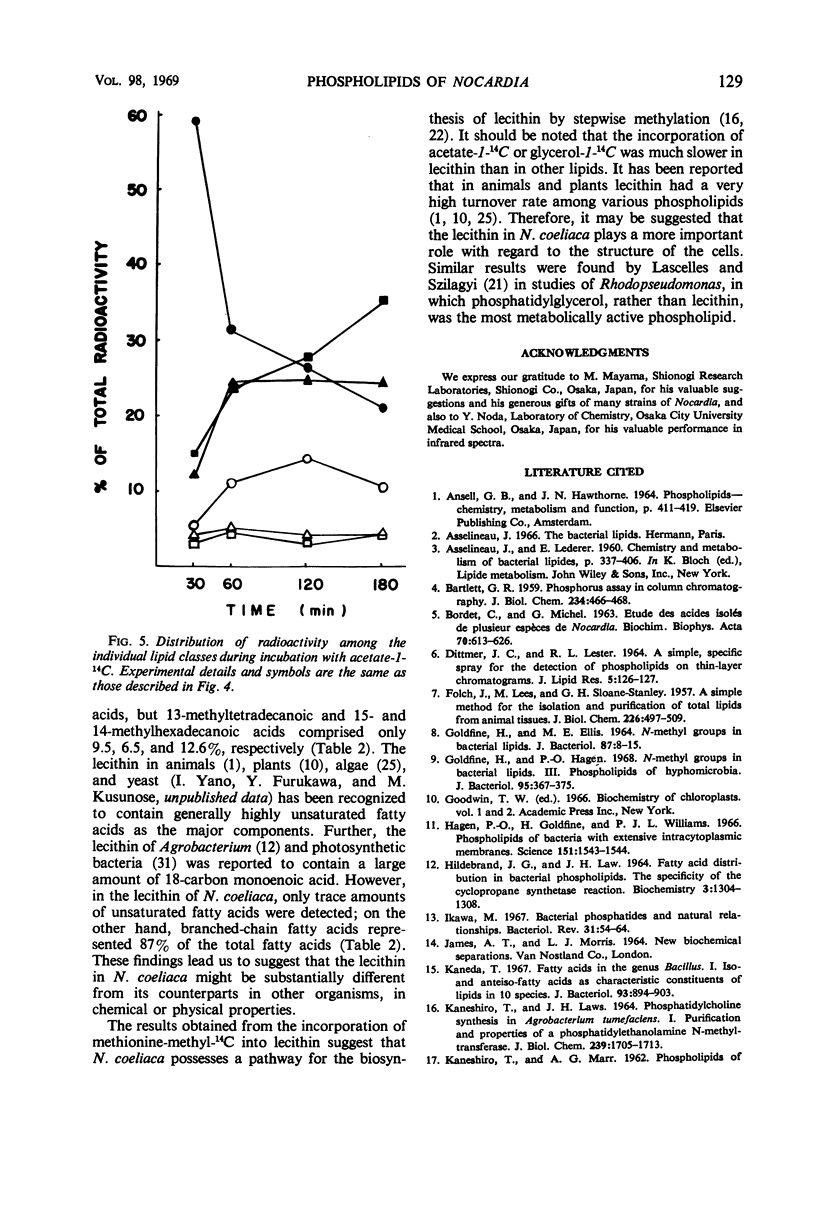
The lipids of Nocardia coeliaca were separated into at least 10 components by the use of thin-layer chromatography. Phosphatidylcholine was the most abundant phospholipid in this organism, accounting for 25 to 40% of the total phospholipids. The major fatty acid components of the phosphatidylcholine were 14-methyl-pentadecanoic acid (41%), the other C15 and C17 iso- and anteiso-fatty acids (29%), and palmitic acid (13.5%). The next most abundant phospholipid was phosphatidylethanolamine (25 to 30%), followed by phosphatidylinositol (11 to 14%) and cardiolipin (7 to 15%). Phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylinositol were very similar to the phosphatidylcholine in fatty acid composition, whereas cardiolipin was characterized by a higher content of palmitic acid (30%). In all of the phospholipids examined, only trace amounts of monounsaturated fatty acids were present. When washed cells of N. coeliaca were incubated with methionine-methyl-14C for 1 to 3 hr, the radioactivity was mainly incorporated into the choline moiety of the phosphatidylcholine. In contrast, acetate-1-14C or glycerol-1-14C was incorporated much more slowly into the phosphatidylcholine than into the other phospholipids and neutral lipids. No phosphatidylcholine was detected in 10 other species of Nocardia examined.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORDET C., MICHEL G. ETUDE DES ACIDES GRAS ISOL'ES DE PLUSIEURS ESP'ECES DE NOCARDIA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Dec 27;70:613–626. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90806-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DITTMER J. C., LESTER R. L. A SIMPLE, SPECIFIC SPRAY FOR THE DETECTION OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS ON THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAMS. J Lipid Res. 1964 Jan;5:126–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDFINE H., ELLIS M. E. N-METHYL GROUPS IN BACTERIAL LIPIDS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jan;87:8–15. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.1.8-15.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine H., Hagen P. N-methyl groups in bacterial lipids. 3. Phospholipids of hyphomicrobia. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):367–375. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.367-375.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILDEBRAND J. G., LAW J. H. FATTY ACID DISTRIBUTION IN BACTERIAL PHOSPHOLIPIDS. THE SPECIFICITY OF THE CYCLOPROPANE SYNTHETASE REACTION. Biochemistry. 1964 Sep;3:1304–1308. doi: 10.1021/bi00897a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen P. O., Goldfine H., Williams P. J. Phospholipids of bacteria with extensive intracytoplasmic membranes. Science. 1966 Mar 25;151(3717):1543–1544. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3717.1543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikawa M. Bacterial phosphatides and natural relationships. Bacteriol Rev. 1967 Mar;31(1):54–64. doi: 10.1128/br.31.1.54-64.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANESHIRO T., LAW J. H. PHOSPHATIDYLCHOLINE SYNTHESIS IN AGROBACTERIUM TUMEFACIENS. I. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF A PHOSPHATIDYLETHANOLAMINE N-METHYLTRANSFERASE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jun;239:1705–1713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneda T. Fatty acids in the genus Bacillus. I. Iso- and anteiso-fatty acids as characteristic constituents of lipids in 10 species. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):894–903. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.894-903.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka T., Nojima S. The phospholipid compositions of some Actinomycetes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Dec 5;144(3):681–683. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(67)90058-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kates M. Bacterial lipids. Adv Lipid Res. 1964;2:17–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANEELLE M. A., ASSELINEAU J., CASTELNUOVO G. ETUDES SUR LES MYCOBACT'ERIES ET LES NOCARDIAE. IV. COMPOSITION DES LIPIDES DE MYCOBACTERIUM RHODOCROUS, M. PELLEGRINO SP., ET DE QUELQUES SOUCHES DE NOCARDIAE. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1965 Jan;108:69–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASCELLES J., SZILAGYI J. F. PHOSPHOLIPID SYNTHESIS BY RHODOPSEUDOMONAS SPHEROIDES IN RELATION TO THE FORMATION OF PHOTOSYNTHETIC PIGMENTS. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Jan;38:55–64. doi: 10.1099/00221287-38-1-55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Dowell V. R., Jr, Lewis V. J., Schekter M. A. Cultural characteristics and fatty acid composition of Corynebacterium acnes. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1300–1305. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1300-1305.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols B. W., James A. T., Breuer J. Interrelationships between fatty acid biosynthesis and acyl-lipid synthesis in Chlorella vulgaris. Biochem J. 1967 Aug;104(2):486–496. doi: 10.1042/bj1040486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park C. E., Berger L. R. Complex lipids of Rhodomicrobium vannielii. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):221–229. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.221-229.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornabene T. G., Gelpi E., Oró J. Identification of fatty acids and aliphatic hydrocarbons in Sarcina lutea by gas chromatography and combined gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Bacteriol. 1967 Aug;94(2):333–343. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.2.333-343.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood B. J., Nichols B. W., James A. T. The lipids and fatty acid metabolism of photosynthetic bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Oct 4;106(2):261–273. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(65)90034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano I., Furukawa Y., Kusunose M. Incorporation of radioactivity from methionine-methyl-14C into phospholipids by Nocardia polychromogenes. J Biochem. 1968 Jan;63(1):133–135. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





