Abstract
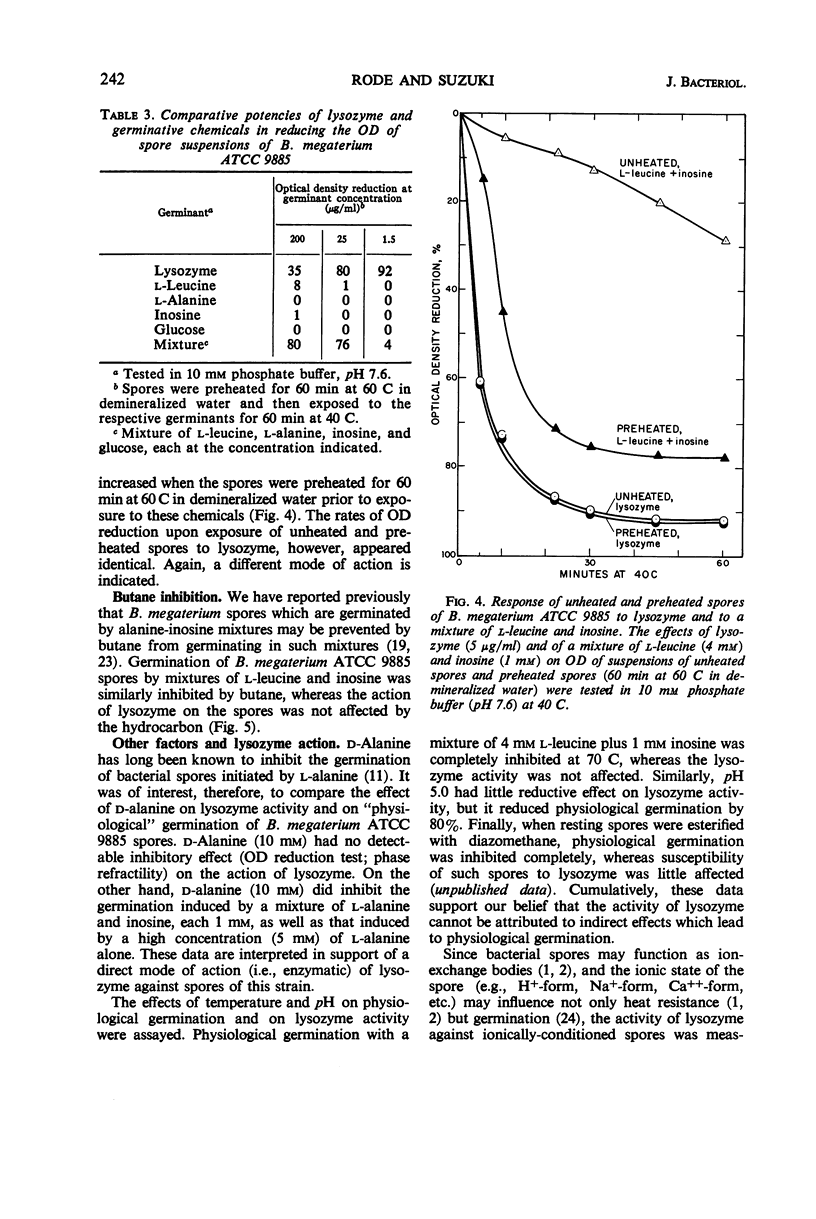
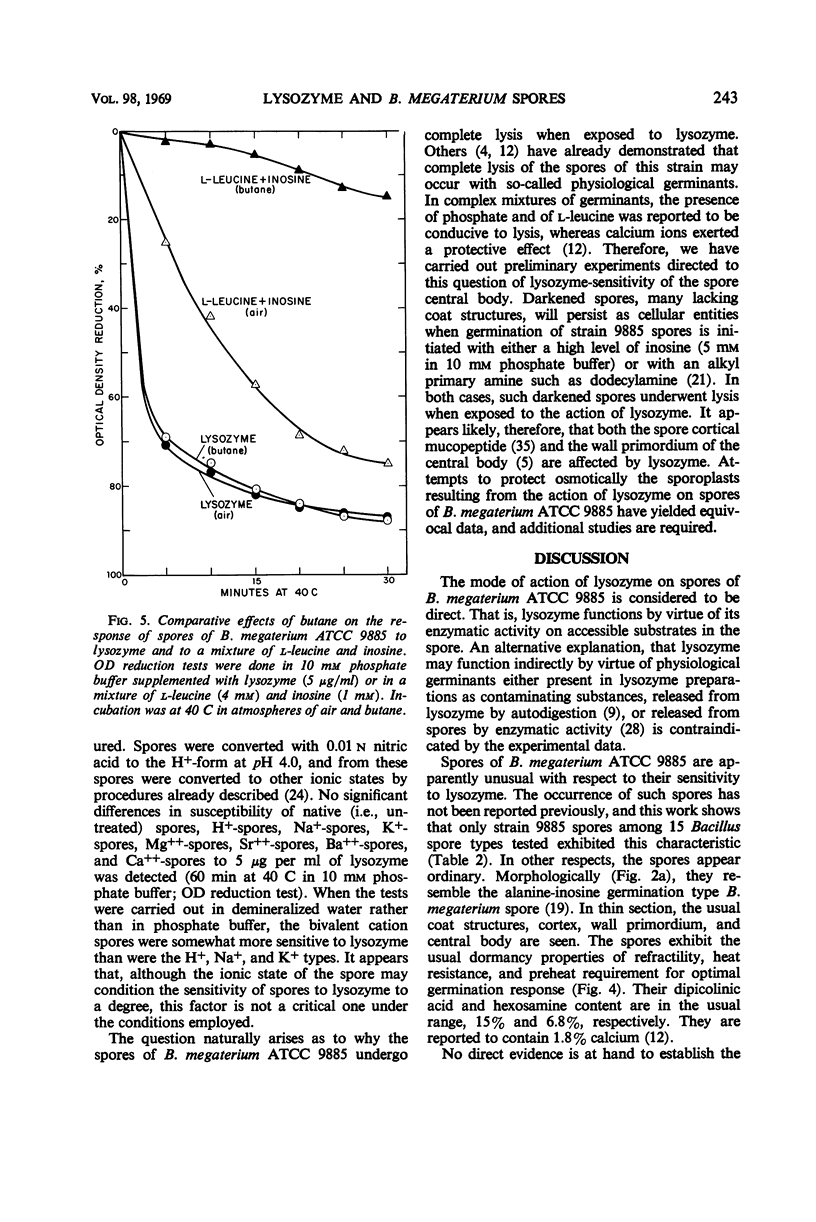
Resting spores of Bacillus megaterium ATCC 9885 were found to be markedly affected by lysozyme. Exposure to as little as 1.5 μg of lysozyme per ml caused the spores to lose refractility, the darkened spores to shed their coat structures, and the spore central bodies to lyse. The spores of seven other strains of B. megaterium and seven other Bacillus species were not similarly affected by lysozyme. Proteolytic enzymes such as pronase, trypsin, pepsin, and subtilisin did not induce the change. The action of lysozyme differed in certain important respects from that of common “physiological” germinants. Its action was considered to be direct via its enzymatic attack on exposed sites directly accessible in the resting spores of B. megaterium ATCC 9885.
Full text
PDF
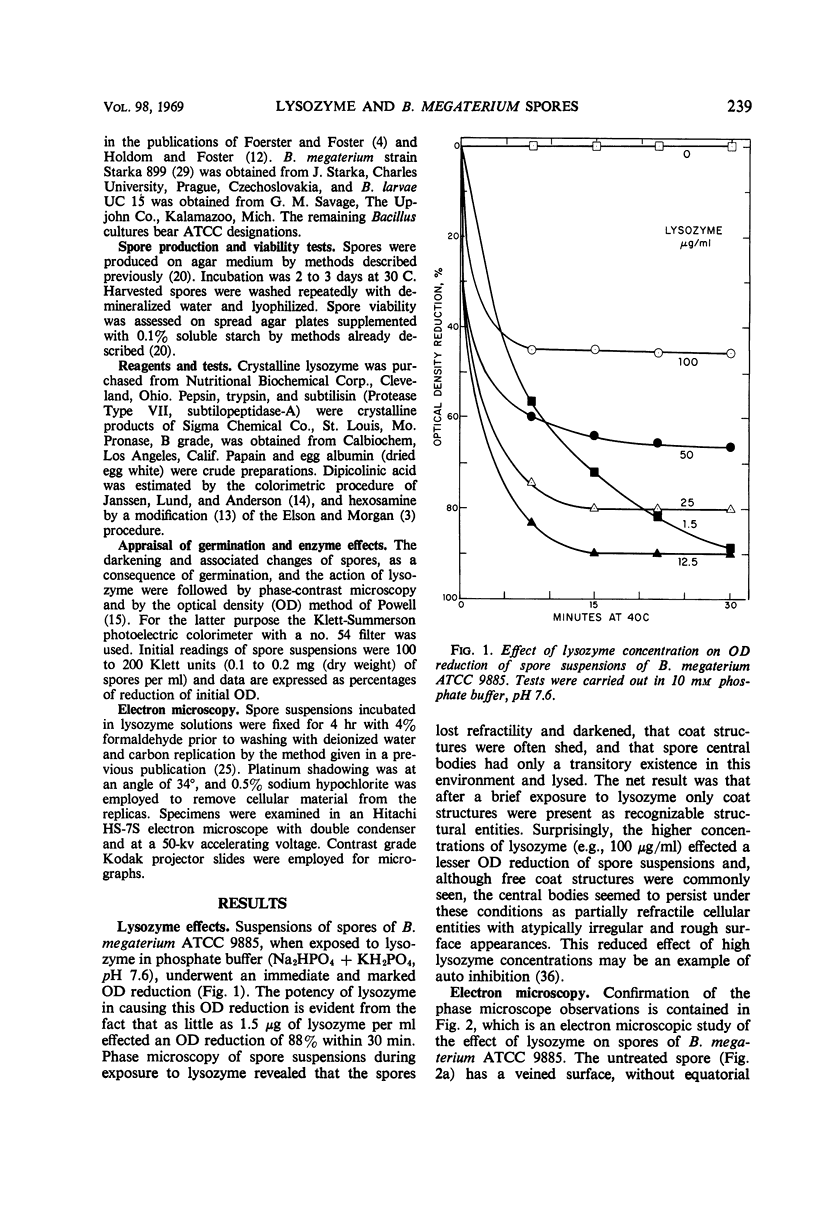
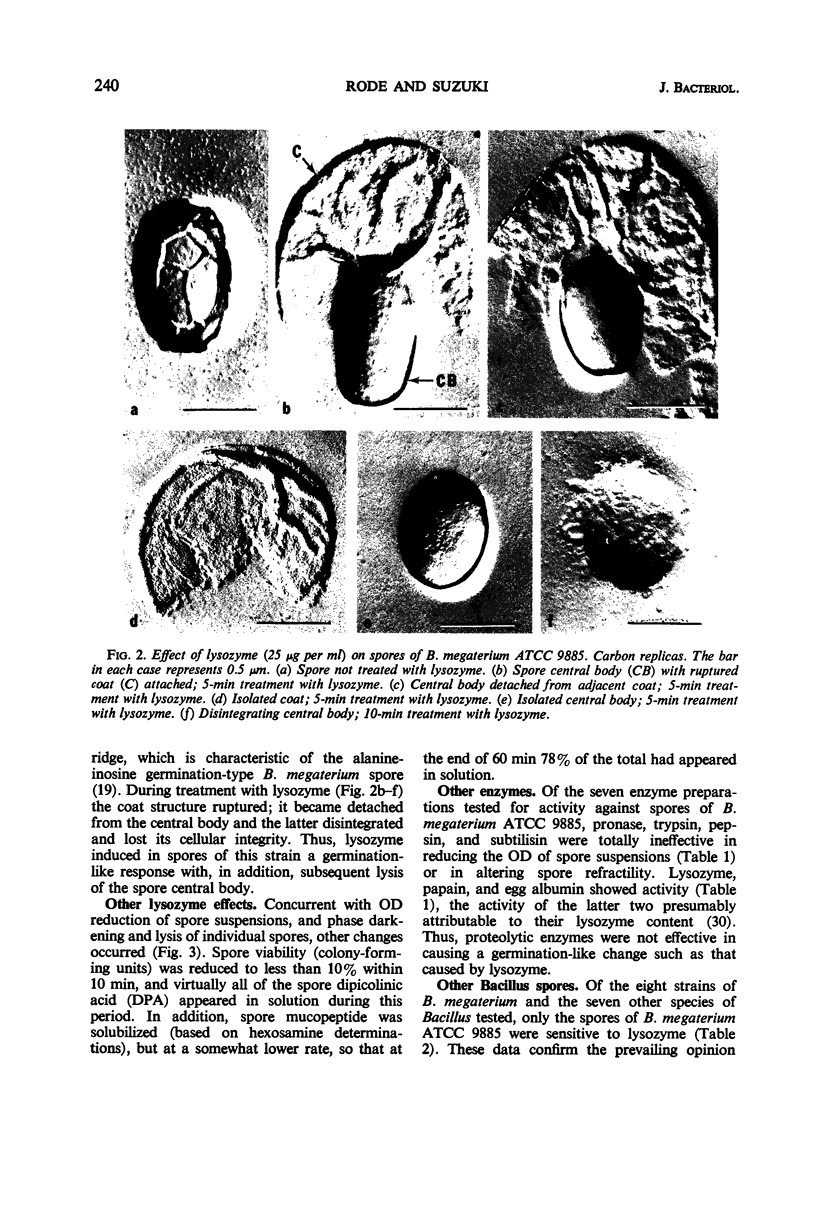
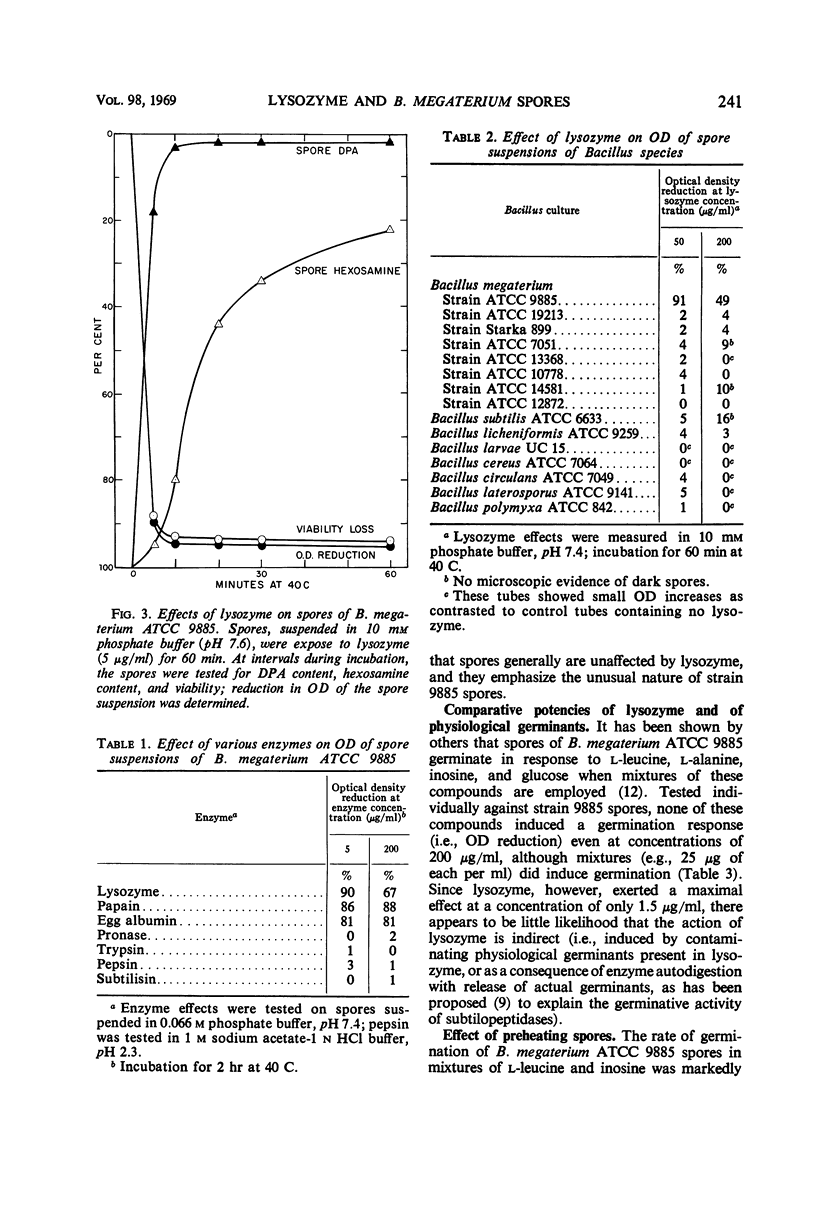


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALDERTON G., SNELL N. Base exchange and heat resistance in bacterial spores. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Jan 31;10:139–143. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90039-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALDERTON G., THOMPSON P. A., SNELL N. HEAT ADAPTATION AND ION EXCHANGE IN BACILLUS MEGATERIUM SPORES. Science. 1964 Jan 10;143(3602):141–143. doi: 10.1126/science.143.3602.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson L. A., Morgan W. T. A colorimetric method for the determination of glucosamine and chondrosamine. Biochem J. 1933;27(6):1824–1828. doi: 10.1042/bj0271824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foerster H. F., Foster J. W. Response of Bacillus spores to combinations of germinative compounds. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1168–1177. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1168-1177.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freer J. H., Levinson H. S. Fine structure of Bacillus megaterium during microcycle sporogenesis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Aug;94(2):441–457. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.2.441-457.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOULD G. W., GEORGALA D. L., HITCHINS A. D. FLUOROCHROME-LABELLED LYSOZYME: REAGENT FOR THE DETECTION OF LYSOZYME SUBSTRATE IN CELLS. Nature. 1963 Oct 26;200:385–386. doi: 10.1038/200385b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOULD G. W., HITCHINS A. D. SENSITIZATION OF BACTERIAL SPORES TO LYSOZYME AND TO HYDROGEN PEROXIDE WITH AGENTS WHICH RUPTURE DISULPHIDE BONDS. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Dec;33:413–423. doi: 10.1099/00221287-33-3-413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould G. W., King W. L. Role of amino-acids in the germination of bacterial spores by subtilisn. Nature. 1966 Sep 24;211(5056):1431–1432. doi: 10.1038/2111431a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILLS G. M. Chemical factors in the germination of spore-bearing aerobes; the effect of yeast extract on the germination of Bacillus anthracis and its replacement by adenosine. Biochem J. 1949;45(3):353–362. doi: 10.1042/bj0450353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILLS G. M. Chemical factors in the germination of spore-bearing aerobes; the effects of amino acids on the germination of Bacillus anthracis, with some observations on the relation of optical form to biological activity. Biochem J. 1949;45(3):363–370. doi: 10.1042/bj0450363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IMMERS J., VASSEUR E. Influence of sugars and amines on the colorimetric hexosamine method of elson and morgan and its possible elimination. Nature. 1950 Jun 3;165(4205):898–898. doi: 10.1038/165898a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANSSEN F. W., LUND A. J., ANDERSON L. E. Colorimetric assay for dipicolinic acid in bacterial spores. Science. 1958 Jan 3;127(3288):26–27. doi: 10.1126/science.127.3288.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POWELL J. F. Factors affecting the germination of thick suspensions of bacillus subtilis spores in L-alanine solution. J Gen Microbiol. 1950 Sep;4(3):330–338. doi: 10.1099/00221287-4-3-330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POWELL J. F., STRANGE R. E. Biochemical changes occurring during the germination of bacterial spores. Biochem J. 1953 May;54(2):205–209. doi: 10.1042/bj0540205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIEMANN H., ORDAL Z. J. Germination of bacterial endospores with calcium and dipicolinic acid. Science. 1961 May 26;133(3465):1703–1704. doi: 10.1126/science.133.3465.1703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODE L. J., FOSTER J. W. GASEOUS HYDROCARBONS AND THE GERMINATION OF BACTERIAL SPORES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jan;53:31–38. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODE L. J., FOSTER J. W. Germination of bacterial spores with alkyl primary amines. J Bacteriol. 1961 May;81:768–779. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.5.768-779.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODE L. J., FOSTER J. W. Ionic germination of spores of Bacillus megaterium QM B 1551. Arch Mikrobiol. 1962;43:183–200. doi: 10.1007/BF00406435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rode L. J. Correlation between spore structure and spore properties in Bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):1979–1986. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.1979-1986.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rode L. J., Foster J. W. Influence of exchangeable ions on germinability of bacterial spores. J Bacteriol. 1966 Apr;91(4):1582–1588. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.4.1582-1588.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rode L. J., Foster J. W. MECHANICAL GERMINATION OF BACTERIAL SPORES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Jan;46(1):118–128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.1.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rode L. J., Williams M. G. Utility of sodium hypochlorite for ultrastructure study of bacterial spore integuments. J Bacteriol. 1966 Dec;92(6):1772–1778. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.6.1772-1778.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley D. B., Levinson H. S. Changes in spores of Bacillus megaterium treated with thioglycolate at a low pH and restoration of germinability and heat resistance by cations. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):1017–1022. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.1017-1022.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIERRA G. GERMINATION OF BACTERIAL SPORES BY SUBTILISIN. Can J Microbiol. 1964 Dec;10:929–931. doi: 10.1139/m64-123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STARKA J., CASLAVSKA J. SPORULATION OF PROTOPLASTS. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1964 Jan;23:21–23. doi: 10.1007/BF02875896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRANGE R. E., DARK F. A. A cell-wall lytic enzyme associated with spores of Bacillus species. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Feb;16(1):236–249. doi: 10.1099/00221287-16-1-236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRANGE R. E., DARK F. A. The composition of the spore coats of Bacillus megatherium, B. subtilis and B. cereus. Biochem J. 1956 Mar;62(3):459–465. doi: 10.1042/bj0620459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRANGE R. E., POWELL J. F. Hexosamine-containing peptides in spores of Bacillus subtilis, B. megatherium and B. cereus. Biochem J. 1954 Sep;58(1):80–85. doi: 10.1042/bj0580080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sierra G. Germination of bacterial endospores with subtilopeptidases. Can J Microbiol. 1967 May;13(5):489–501. doi: 10.1139/m67-064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vary J. C., Halvorson H. O. Initiation of bacterial spore germination. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1327–1334. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1327-1334.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARTH A. D., OHYE D. F., MURRELL W. G. Location and composition of spore mucopeptide in Bacillus species. J Cell Biol. 1963 Mar;16:593–609. doi: 10.1083/jcb.16.3.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILCOX F. H., Jr, DANIEL L. J. Reduced lysis at high concentrations of lysozyme. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1954 Oct;52(2):305–312. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(54)90128-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]