Abstract
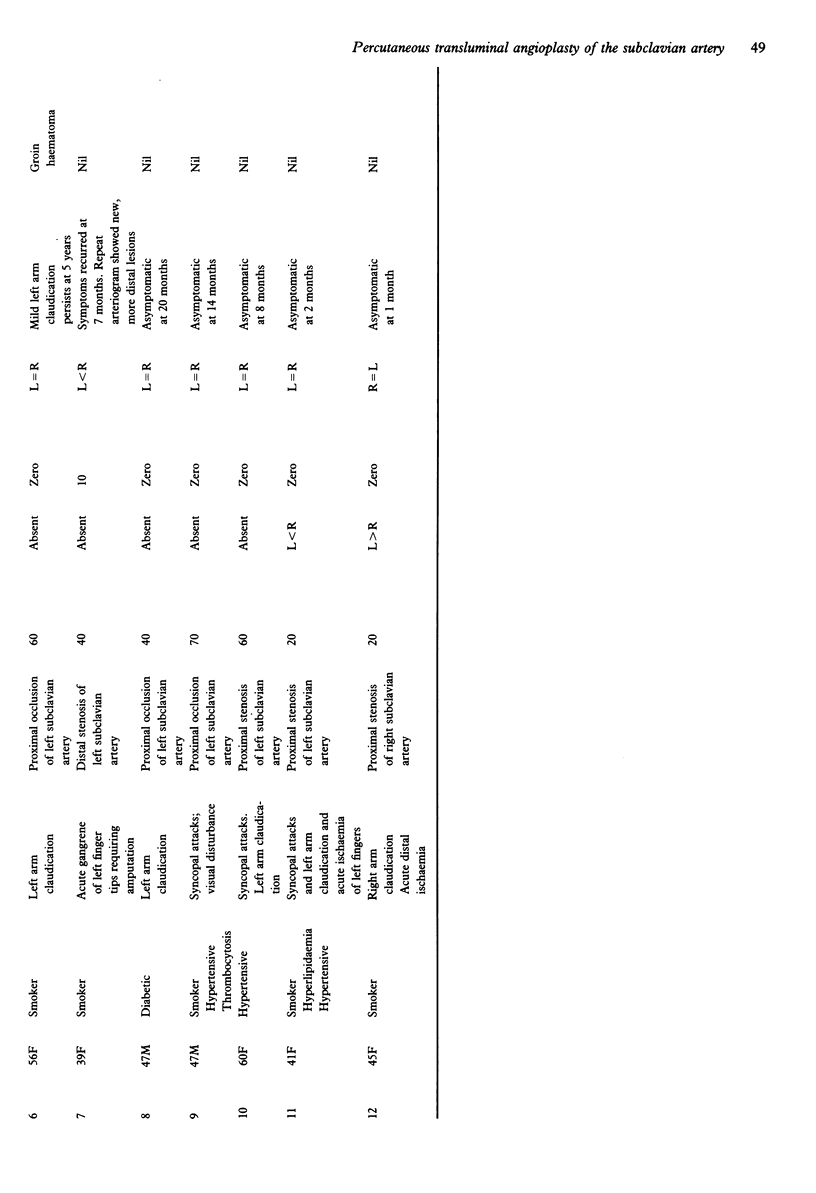
A series of 12 consecutive cases of symptomatic subclavian artery stenosis or occlusion treated by percutaneous transluminal angioplasty are described. In seven cases stenoses were successfully dilated, and in four out of five cases occlusions were recanalised using standard angioplasty technique. Complications were trivial and did not prolong hospital stay, all patients being discharged within 48 h of the procedure. Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty of the subclavian artery is a safe, effective procedure and recommended as the treatment of first choice in symptomatic subclavian stenosis or occlusion.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachman D. M., Kim R. M. Transluminal dilatation for subclavian steal syndrome. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1980 Nov;135(5):995–996. doi: 10.2214/ajr.135.5.995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beebe H. G., Stark R., Johnson M. L., Jolly P. C., Hill L. D. Choices of operation for subclavian-vertebral arterial disease. Am J Surg. 1980 May;139(5):616–623. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(80)90348-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block P. C., Elmer D., Fallon J. T. Release of atherosclerotic debris after transluminal angioplasty. Circulation. 1982 May;65(5):950–952. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.65.5.950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer M. L., Kinnison M. L., Perler B. A., White R. I., Jr Blue toe syndrome: treatment with anticoagulants and delayed percutaneous transluminal angioplasty. Radiology. 1988 Jan;166(1 Pt 1):31–36. doi: 10.1148/radiology.166.1.2962224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaneda-Zuniga W. R., Formanek A., Tadavarthy M., Vlodaver Z., Edwards J. E., Zollikofer C., Amplatz K. The mechanism of balloon angioplasty. Radiology. 1980 Jun;135(3):565–571. doi: 10.1148/radiology.135.3.7384437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook A. M., Dyet J. F. Six cases of subclavian stenosis treated by percutaneous angioplasty. Clin Radiol. 1989 Jul;40(4):352–354. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(89)80117-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOTTER C. T., JUDKINS M. P. TRANSLUMINAL TREATMENT OF ARTERIOSCLEROTIC OBSTRUCTION. DESCRIPTION OF A NEW TECHNIC AND A PRELIMINARY REPORT OF ITS APPLICATION. Circulation. 1964 Nov;30:654–670. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.30.5.654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erbstein R. A., Wholey M. H., Smoot S. Subclavian artery steal syndrome: treatment by percutaneous transluminal angioplasty. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1988 Aug;151(2):291–294. doi: 10.2214/ajr.151.2.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galichia J. P., Bajaj A. K., Vine D. L., Roberts R. W. Subclavian artery stenosis treated by transluminal angioplasty: six cases. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 1983;6(2):78–81. doi: 10.1007/BF02552776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon R. L., Haskell L., Hirsch M., Shifrin E., Weinman E., Romanoff H. Transluminal dilatation of the subclavian artery. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 1985;8(1):14–19. doi: 10.1007/BF02552634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grüntzig A., Hopff H. Perkutane Rekanalisation chronischer arterieller Verschlüsse mit einem neuen Dilatationskatheter. Modifikation der Dotter-Technik. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1974 Dec 6;99(49):2502-10, 2511. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1108161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motarjeme A., Keifer J. W., Zuska A. J., Nabawi P. Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty for treatment of subclavian steal. Radiology. 1985 Jun;155(3):611–613. doi: 10.1148/radiology.155.3.3159036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringelstein E. B., Zeumer H. Delayed reversal of vertebral artery blood flow following percutaneous transluminal angioplasty for subclavian steal syndrome. Neuroradiology. 1984;26(3):189–198. doi: 10.1007/BF00342413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson B. W., Read R. C., Campbell G. S. Operative correction of proximal blocks of the subclavian or innominate arteries. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino) 1980 Mar-Apr;21(2):125–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitek J. J. Subclavian artery angioplasty and the origin of the vertebral artery. Radiology. 1989 Feb;170(2):407–409. doi: 10.1148/radiology.170.2.2521398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Andel G. J., van Erp W. F., Krepel V. M., Breslau P. J. Percutaneous transluminal dilatation of the iliac artery: long-term results. Radiology. 1985 Aug;156(2):321–323. doi: 10.1148/radiology.156.2.3160060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





