Abstract
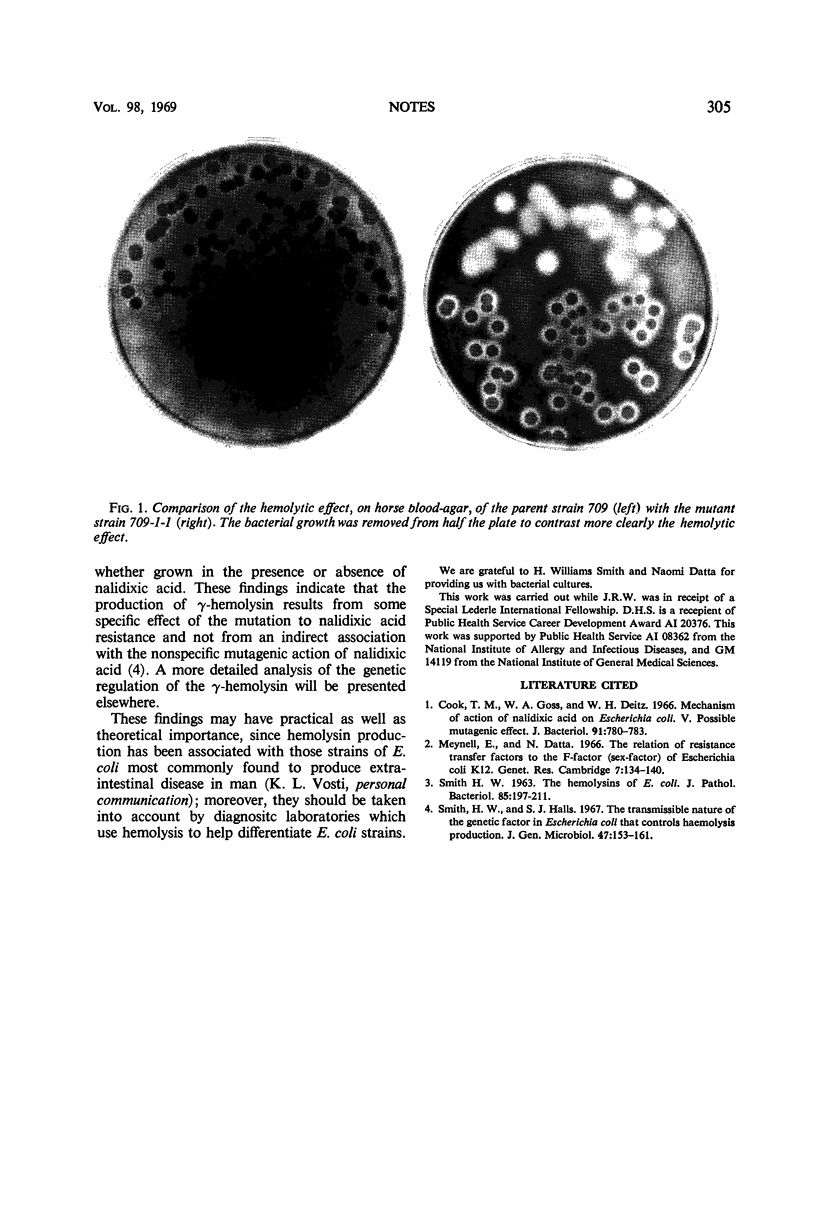
A new hemolysin (γ) of Escherichia coli, active in the absence of viable bacteria, has been recognized in mutants resistant to nalidixic acid. Nalidixic acid affects either the production or release of the hemolysin.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cook T. M., Goss W. A., Deitz W. H. Mechanism of Action of Nalidixic Acid on Escherichia coli V. Possible Mutagenic Effect. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):780–783. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.780-783.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meynell E., Datta N. The relation of resistance transfer factors to the F-factor (sex-factor) of Escherichia coli K12. Genet Res. 1966 Feb;7(1):134–140. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300009538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Halls S. The transmissible nature of the genetic factor in Escherichia coli that controls haemolysin production. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Apr;47(1):153–161. doi: 10.1099/00221287-47-1-153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]