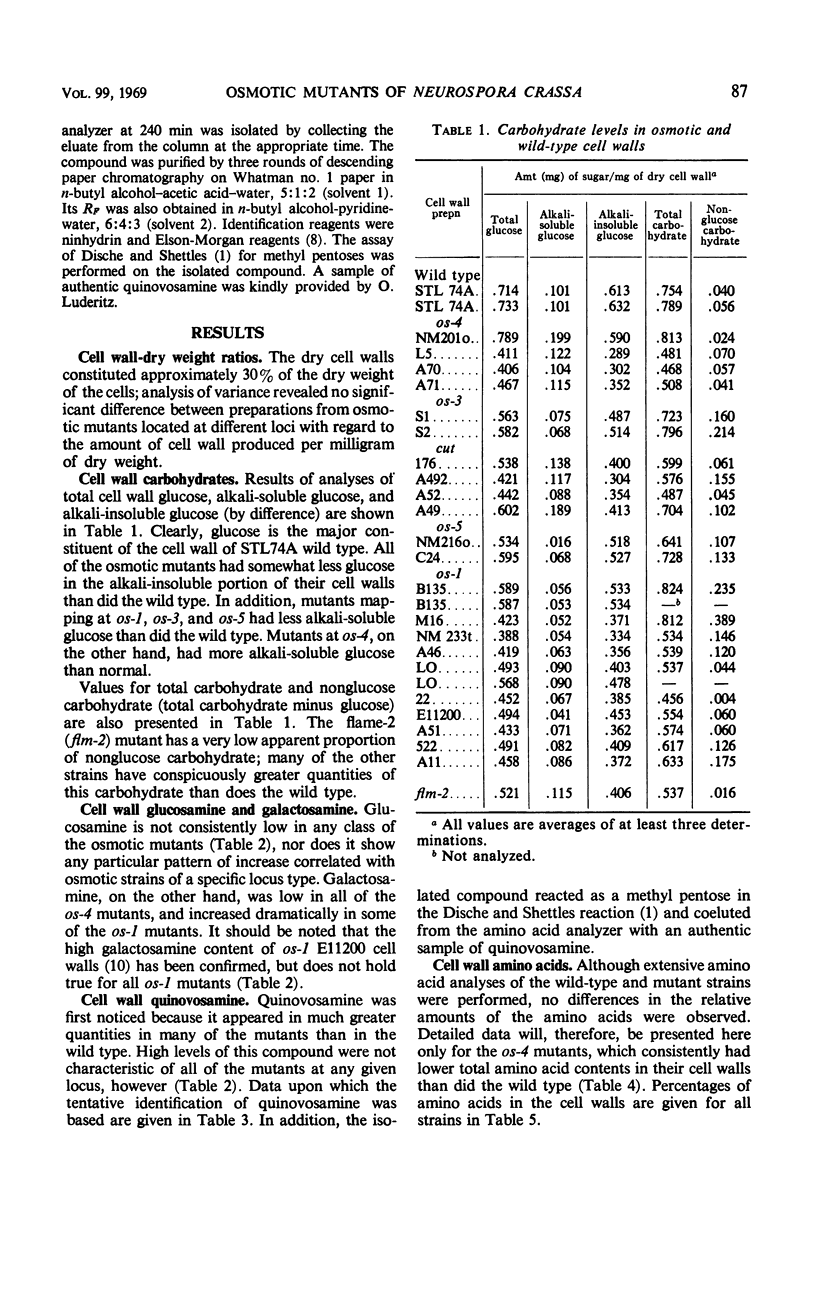
Abstract
The osmotic phenotype of Neurospora crassa is characterized by inhibition of growth at high osmolalities of growth medium. Mutations at six osmotic loci of linkage group I were examined to assess the biochemical and physiological effects of these mutants. Isolated cell walls from 23 osmotic strains were compared with the wild type with regard to quantitative levels of the following components: percentage of total dry weight, total glucose, alkali-soluble glucose, nonglucose carbohydrates, amino acids, glucosamine, galactosamine, and a compound tentatively identified as quinovosamine. The last component has not previously been observed in N. crassa cell walls. Although the cell wall dry weight content of osmotic mutants was not altered, walls isolated from all of the osmotic strains had less alkali-insoluble glucose than those from the wild type. In addition, all of the loci except cut exhibited other consistent differences from the wild type. The os-1, os-3, and os-5 mutants had low levels of alkali-soluble glucose. The os-3 and os-5 mutants had high levels of nonglucose carbohydrates, and flm-2 had a low level of nonglucose carbohydrates. The os-4 mutants had low levels of galactosamine and amino acids and high levels alkali-soluble glucose. An os-1 mutant, B135, produced less of the whole alkali-soluble fraction of the cell wall.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DISCHE Z., SHETTLES L. B. A new spectrophotometric test for the detection of methylpentose. J Biol Chem. 1951 Oct;192(2):579–582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson S., Emerson M. R. PRODUCTION, REPRODUCTION, AND REVERSION OF PROTOPLAST-LIKE STRUCTURES IN THE OSMOTIC STRAIN OF NEUROSPORA CRASSA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 Jul 15;44(7):668–671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.7.668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMILTON J. G., CALVET J. PRODUCTION OF PROTOPLASTS IN AN OSMOTIC MUTANT OF NEUROSPORA CRASSA WITHOUT ADDED ENZYME. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1084–1086. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1084-1086.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüderitz O., Gmeiner J., Kickhöfen B., Mayer H., Westphal O., Wheat R. W. Identification of D-mannosamine and quinovosamine in Salmonella and related bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):490–494. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.490-494.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevan P. R., Tatum E. L. Relationship of the major constituents of the Neurospora crassa cell wall to wild-type and colonial morphology. J Bacteriol. 1965 Oct;90(4):1073–1081. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.4.1073-1081.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins D D. New Markers and Multiple Point Linkage Data in Neurospora. Genetics. 1959 Nov;44(6):1185–1208. doi: 10.1093/genetics/44.6.1185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trevithick J. R., Metzenberg R. L. Genetic alteration of pore size and other properties of the Neurospora cell wall. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):1016–1020. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.1016-1020.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trevithick J. R., Metzenberg R. L. Molecular sieving by Neurospora cell walls during secretion of invertase isozymes. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):1010–1015. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.1010-1015.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


