Abstract
Background
Persistent atrial fibrillation (AF) does not terminate spontaneously and may cause left ventricular dysfunction and thromboembolic complications. For restoration of sinus rhythm electrical cardioversion (ECV) is most effective. However, AF frequently relapses, necessitating re-ECV and institution of potentially harmful antiarrhythmic drugs. If AF is accepted, rate control and prevention of thromboembolic complications using negative chronotropic drugs and warfarin is pursued. It is our hypothesis that rate control therapy is not inferior to ECV therapy in preventing morbidity and mortality.
Methods
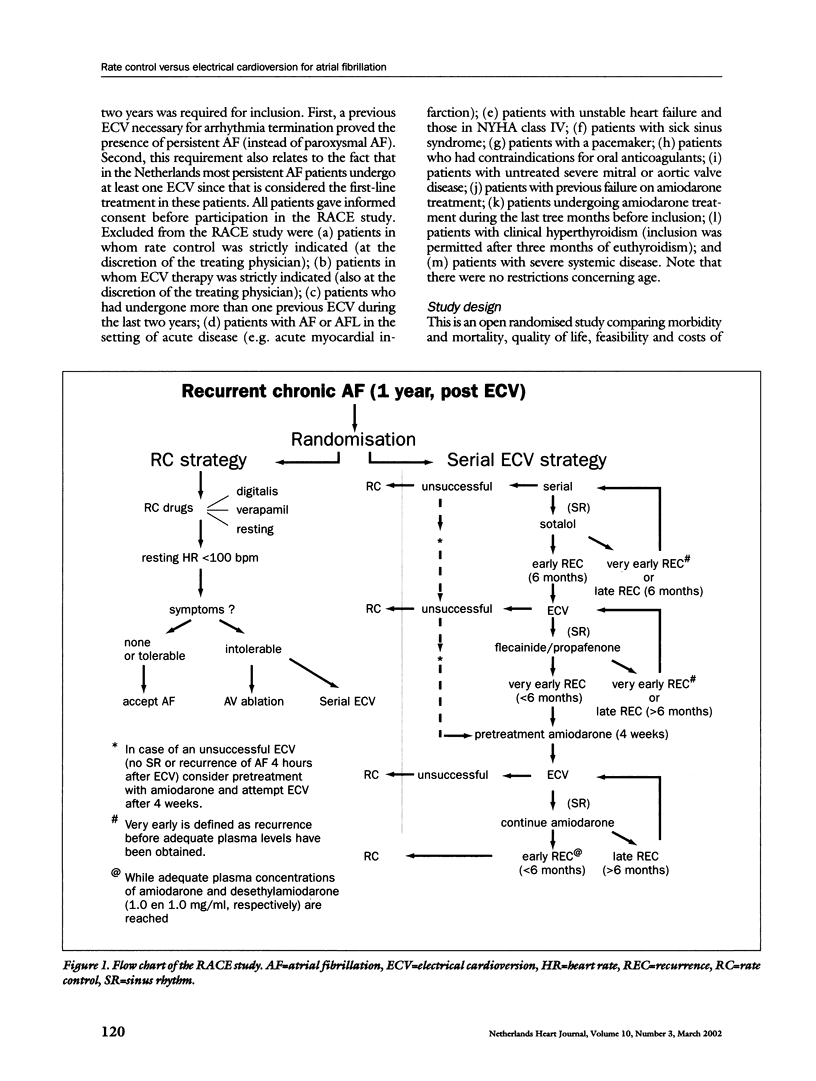
RACE (RAte Control versus Electrical cardioversion for atrial fibrillation) is a randomised comparison of serial ECV therapy (repeat ECV as soon as possible after a relapse and institution of an antiarrhythmic drug: sotalol, class IC drug and amiodarone) and rate control therapy (resting heart rate <100 bpm using digitalis, calcium channel blockers and/or β-blockers) in patients with persistent AF. Morbidity (heart failure, side effects of drugs, thromboembolic complications, bleeding and pacemaker implantation), mortality, quality of life and cost-effectiveness are primary and secondary endpoints. Included are patients with a recurrence of persistent AF, present episode <1 year and a maximum of two previous successful ECVs during the last two years. This study is a multicentre study in 31 centres throughout the Netherlands. All 520 patients have now been included. Follow-up is two years. The results are expected this year.
Keywords: atrial fibrillation, electrical cardioversion, rhythm control
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blair S. N., Capuzzi D. M., Gottlieb S. O., Nguyen T., Morgan J. M., Cater N. B. Incremental reduction of serum total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol with the addition of plant stanol ester-containing spread to statin therapy. Am J Cardiol. 2000 Jul 1;86(1):46–52. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(00)00976-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coplen S. E., Antman E. M., Berlin J. A., Hewitt P., Chalmers T. C. Efficacy and safety of quinidine therapy for maintenance of sinus rhythm after cardioversion. A meta-analysis of randomized control trials. Circulation. 1990 Oct;82(4):1106–1116. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.82.4.1106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crijns H. J., van Gelder I. C., Lie K. I. Supraventricular tachycardia mimicking ventricular tachycardia during flecainide treatment. Am J Cardiol. 1988 Dec 1;62(17):1303–1306. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(88)90282-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaker G. C., Blackshear J. L., McBride R., Kronmal R. A., Halperin J. L., Hart R. G. Antiarrhythmic drug therapy and cardiac mortality in atrial fibrillation. The Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Investigators. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1992 Sep;20(3):527–532. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(92)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuster V., Rydén L. E., Asinger R. W., Cannom D. S., Crijns H. J., Frye R. L., Halperin J. L., Kay G. N., Klein W. W., Lévy S. ACC/AHA/ESC Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: Executive Summary A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the European Society of Cardiology Committee for Practice Guidelines and Policy Conferences (Committee to Develop Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation) Developed in Collaboration With the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Circulation. 2001 Oct 23;104(17):2118–2150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher M. M., Camm A. J. Classification of atrial fibrillation. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1997 Jun;20(6):1603–1605. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.1997.tb03527.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosselink A. T., Crijns H. J., Van Gelder I. C., Hillige H., Wiesfeld A. C., Lie K. I. Low-dose amiodarone for maintenance of sinus rhythm after cardioversion of atrial fibrillation or flutter. JAMA. 1992 Jun 24;267(24):3289–3293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohnloser S. H., Kuck K. H., Lilienthal J. Rhythm or rate control in atrial fibrillation--Pharmacological Intervention in Atrial Fibrillation (PIAF): a randomised trial. Lancet. 2000 Nov 25;356(9244):1789–1794. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(00)03230-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouven X., Desnos M., Guerot C., Ducimetiere P. Idiopathic atrial fibrillation as a risk factor for mortality. The Paris Prospective Study I. Eur Heart J. 1999 Jun;20(12):896–899. doi: 10.1053/euhj.1998.1397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juul-Möller S., Edvardsson N., Rehnqvist-Ahlberg N. Sotalol versus quinidine for the maintenance of sinus rhythm after direct current conversion of atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 1990 Dec;82(6):1932–1939. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.82.6.1932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlson B. W., Torstensson I., Abjörn C., Jansson S. O., Peterson L. E. Disopyramide in the maintenance of sinus rhythm after electroconversion of atrial fibrillation. A placebo-controlled one-year follow-up study. Eur Heart J. 1988 Mar;9(3):284–290. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a062498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krahn A. D., Manfreda J., Tate R. B., Mathewson F. A., Cuddy T. E. The natural history of atrial fibrillation: incidence, risk factors, and prognosis in the Manitoba Follow-Up Study. Am J Med. 1995 May;98(5):476–484. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9343(99)80348-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisel W. H., Kuntz K. M., Reimold S. C., Lee T. H., Antman E. M., Friedman P. L., Stevenson W. G. Risk of initiating antiarrhythmic drug therapy for atrial fibrillation in patients admitted to a university hospital. Ann Intern Med. 1997 Aug 15;127(4):281–284. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-127-4-199708150-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus F. I. The hazards of using type 1C antiarrhythmic drugs for the treatment of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 1990 Aug 1;66(3):366–367. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(90)90851-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murgatroyd F. D., Camm A. J. Atrial arrhythmias. Lancet. 1993 May 22;341(8856):1317–1322. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90824-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimold S. C., Cantillon C. O., Friedman P. L., Antman E. M. Propafenone versus sotalol for suppression of recurrent symptomatic atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 1993 Mar 1;71(7):558–563. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(93)90511-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuinenburg A. E., Van Gelder I. C., Van Den Berg M. P., Brügemann J., De Kam P. J., Crijns H. J. Lack of prevention of heart failure by serial electrical cardioversion in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation. Heart. 1999 Oct;82(4):486–493. doi: 10.1136/hrt.82.4.486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Gelder I. C., Crijns H. J., Tieleman R. G., Brügemann J., De Kam P. J., Gosselink A. T., Verheugt F. W., Lie K. I. Chronic atrial fibrillation. Success of serial cardioversion therapy and safety of oral anticoagulation. Arch Intern Med. 1996 Dec 9;156(22):2585–2592. doi: 10.1001/archinte.156.22.2585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Gelder I. C., Crijns H. J., Van Gilst W. H., Van Wijk L. M., Hamer H. P., Lie K. I. Efficacy and safety of flecainide acetate in the maintenance of sinus rhythm after electrical cardioversion of chronic atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter. Am J Cardiol. 1989 Dec 1;64(19):1317–1321. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(89)90574-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware J. E., Jr, Sherbourne C. D. The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Med Care. 1992 Jun;30(6):473–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellens H. J. Atrial fibrillation--the last big hurdle in treating supraventricular tachycardia. N Engl J Med. 1994 Oct 6;331(14):944–945. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199410063311413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf P. A., Abbott R. D., Kannel W. B. Atrial fibrillation: a major contributor to stroke in the elderly. The Framingham Study. Arch Intern Med. 1987 Sep;147(9):1561–1564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



