Abstract
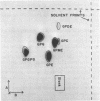
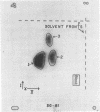
The lipid composition of the chemoautotroph Ferrobacillus ferrooxidans has been examined. Fatty acids represent 2% of the dry weight of the cells and 86% of the total are extractable with organic solvents. About 25% of the total fatty acids are associated with diacyl phospholipids. Polar carotenoids, the benzoquinone coenzyme Q-8, and most of the fatty acids are present in the neutral lipids. The phospholipids have been identified as phosphatidyl monomethylethanolamine (42%), phosphatidyl glycerol (23%), phosphatidyl ethanolamine (20%), cardiolipin (13%), phosphatidyl choline (1.5%), and phosphatidyl dimethylethanolamine (1%) by chromatography of the diacyl lipids, by chromatography in four systems of the glycerol phosphate esters derived from the lipids by mild alkaline methanolysis, and by chromatographic identification of the products of acid hydrolysis of the esters. No trace of phosphatidylserine (PS), glycerolphosphorylserine, or serine could be detected in the lipid extract or in derivatives of that extract. This casts some doubt on the postulated involvement of PS in iron metabolism. After growth in the presence of 14C and 32P, there was essentially no difference in the turnover of either isotope in the glycerolphosphate ester derived from each lipid in cells grown at pH 1.5 or 3.5.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLAYLOCK B. A., NASON A. ELECTRON TRANSPORT SYSTEMS OF THE CHEMOAUTOTROPH FERROBACILLUS FERROOXIDANS. I. CYTOCHROME C-CONTAINING IRON OXIDASE. J Biol Chem. 1963 Oct;238:3453–3462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barridge J. K., Shively J. M. Phospholipids of the thiobacilli. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2182–2185. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2182-2185.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DITTMER J. C., LESTER R. L. A SIMPLE, SPECIFIC SPRAY FOR THE DETECTION OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS ON THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAMS. J Lipid Res. 1964 Jan;5:126–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korczynski M. S., Agate A. D., Lundgren D. G. Phospholipids from the chemoautotroph Ferrobacillus ferrooxidans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Nov 30;29(4):457–462. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90505-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANE E. S. THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY OF LONG-CHAIN TERTIARY AMINES AND RELATED COMPOUNDS. J Chromatogr. 1965 May;18:426–430. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)80394-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LESTER R. L., RAMASARMA T. Chromatography of the coenzyme Q family of compounds on silicone-impregnated paper. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):672–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVAK M. COLORIMETRIC ULTRAMICRO METHOD FOR THE DETERMINATION OF FREE FATTY ACIDS. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:431–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remsen C., Lundgren D. G. Electron microscopy of the cell envelope of Ferrobacillus ferrooxidans prepared by freeze-etching and chemical fixation techniques. J Bacteriol. 1966 Dec;92(6):1765–1771. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.6.1765-1771.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT G., BESSMAN M. J., THANNHAUSER S. J. The hydrolysis of L- alpha-glycerylphosphorylethanolamine. J Biol Chem. 1953 Aug;203(2):849–853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILVERMAN M. P., LUNDGREN D. G. Studies on the chemoautotrophic iron bacterium Ferrobacillus ferrooxidans. I. An improved medium and a harvesting procedure for securing high cell yields. J Bacteriol. 1959 May;77(5):642–647. doi: 10.1128/jb.77.5.642-647.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salton M. R. Isolation and characterization of bacterial membranes. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Apr;29(6):764–781. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1967.tb02300.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shively J. M., Benson A. A. Phospholipids of Thiobacillus thiooxidans. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1679–1683. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1679-1683.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. C., Cox R. H. Indentification and localization of the fatty acids in Haemophilus parainfluenzae. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):1079–1088. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.1079-1088.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. C., Frerman F. E. Extraction, characterization, and cellular localization of the lipids of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):1854–1867. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.1854-1867.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. C. Lipid composition of the electron transport membrane of Haemophilus parainfluenzae. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1159–1170. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1159-1170.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. C., Tucker A. N. Phospholipid metabolism during bacterial growth. J Lipid Res. 1969 Mar;10(2):220–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuthier R. E. Two-dimensional chromatography on silica gel-loaded paper for the microanalysis of polar lipids. J Lipid Res. 1966 Jul;7(4):544–550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]