Abstract
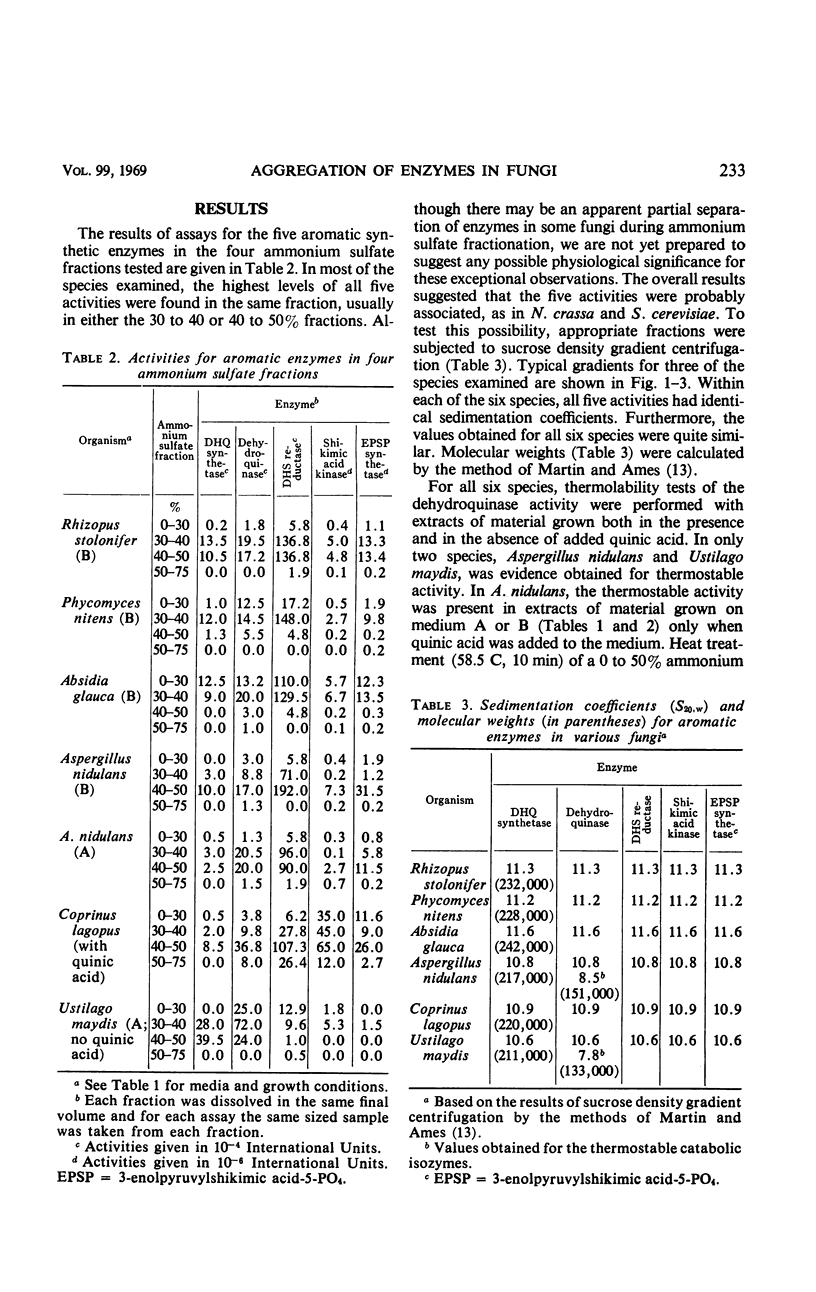
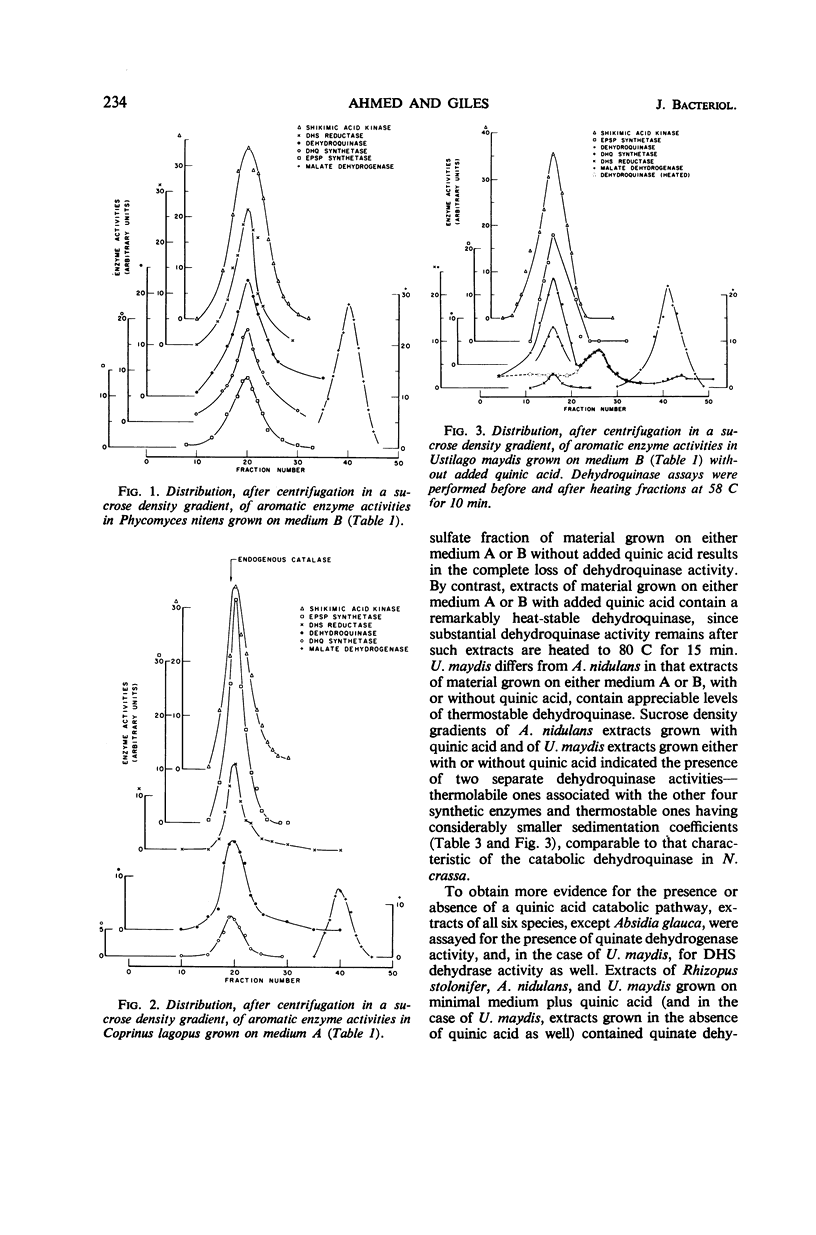
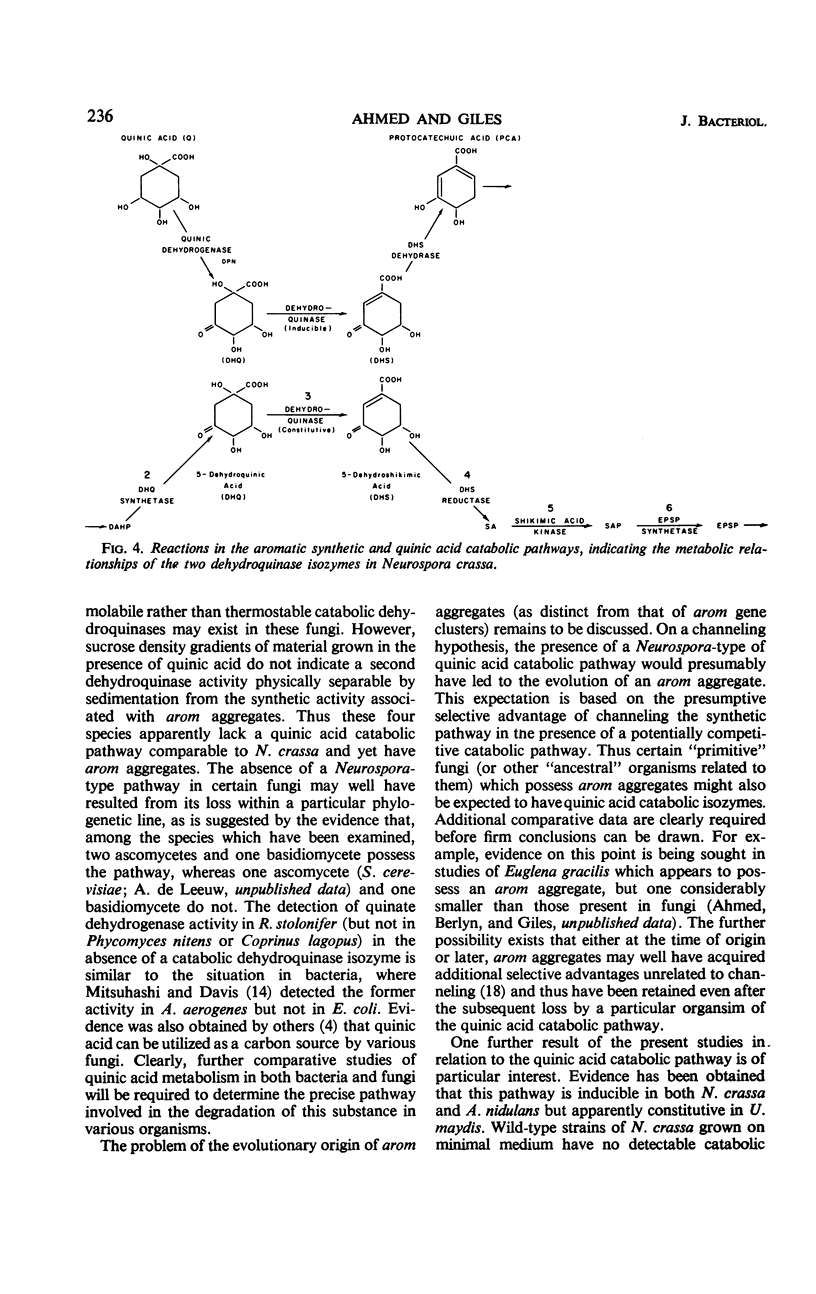
Centrifugation in sucrose density gradients of partially purified extracts from six species of fungi, i.e., Rhizopus stolonifer, Phycomyces nitens, Absidia glauca (Phycomycetes), Aspergillus nidulans (Ascomycetes), Coprinus lagopus, and Ustilago maydis (Basidiomycetes), indicate that the five enzymes catalyzing steps two to six in the prechorismic acid part of the polyaromatic synthetic pathway sediment together. The sedimentation coefficients for these enzymes are very similar in the six species and are comparable to those previously observed for the multienzyme complexes (arom aggregates) of Neurospora crassa and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. These results are interpreted as indicating the presence in each of these fungi of arom aggregates, presumably encoded by arom gene clusters similar to those in N. crassa and S. cerevisiae. Evidence has also been obtained for the presence in two species (A. nidulans and U. maydis) and the absence in the other four species of a second dehydroquinase isozyme which is distinguishable from the synthetic activity on the basis of both thermostability tests and S values. This second dehydroquinase, which is apparently involved in the catabolism of quinic acid via a pathway similar to that in N. crassa, is inducible in A. nidulans (as it is in N. crassa), but constitutive in U. maydis. These comparative findings are discussed in relation to the organization, evolution, and possible functional relationships of synthetic and catabolic aromatic pathways in fungi.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berlyn M. B., Giles N. H. Organization of enzymes in the polyaromatic synthetic pathway: separability in bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):222–230. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.222-230.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cain R. B., Bilton R. F., Darrah J. A. The metabolism of aromatic acids by micro-organisms. Metabolic pathways in the fungi. Biochem J. 1968 Aug;108(5):797–828. doi: 10.1042/bj1080797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS S. R. The enzymatic conversion of 5-dehydroshikimic acid to protocatechuic acid. J Biol Chem. 1958 Nov;233(5):1146–1151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles N. H., Case M. E., Partridge C. W., Ahmed S. I. A gene cluster in Nuerospora crassa coding for an aggregate of five aromatic synthetic enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1453–1460. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles N. H., Partridge C. W., Ahmed S. I., Case M. E. The occurrence of two dehydroquinases in Neurospora crassa, one constitutive and one inducible. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Nov;58(5):1930–1937. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.5.1930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hütter R., DeMoss J. A. Organization of the tryptophan pathway: a phylogenetic study of the fungi. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):1896–1907. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.1896-1907.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAFER E. An 8-chromosome map of Aspergillus nidulans. Adv Genet. 1958;9:105–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCGILVERY R. W., MOKRASCH L. C. Purification and properties of fructose-1, 6-diphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1956 Aug;221(2):909–917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITSUHASHI S., DAVIS B. D. Aromatic biosynthesis. XIII. Conversion of quinic acid to 5-dehydroquinic acid by quinic dehydrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1954 Oct;15(2):268–280. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(54)90069-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PONTECORVO G., ROPER J. A., HEMMONS L. M., MACDONALD K. D., BUFTON A. W. J. The genetics of Aspergillus nidulans. Adv Genet. 1953;5:141–238. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60408-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROMAN H. Studies of gene mutation in Saccharomyces. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1956;21:175–185. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1956.021.01.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



