Abstract
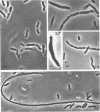
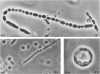
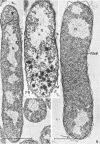
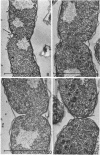
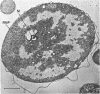
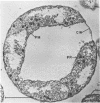
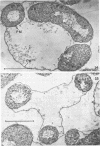
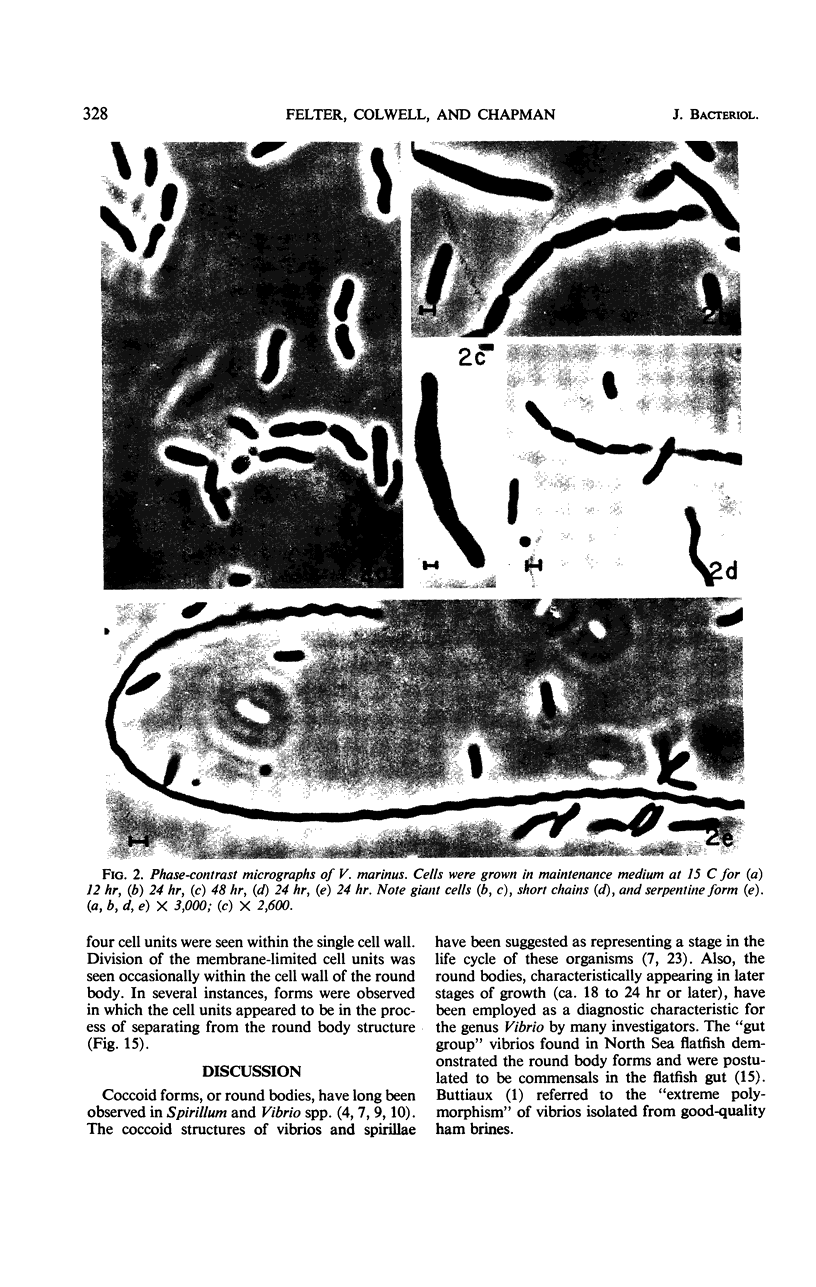
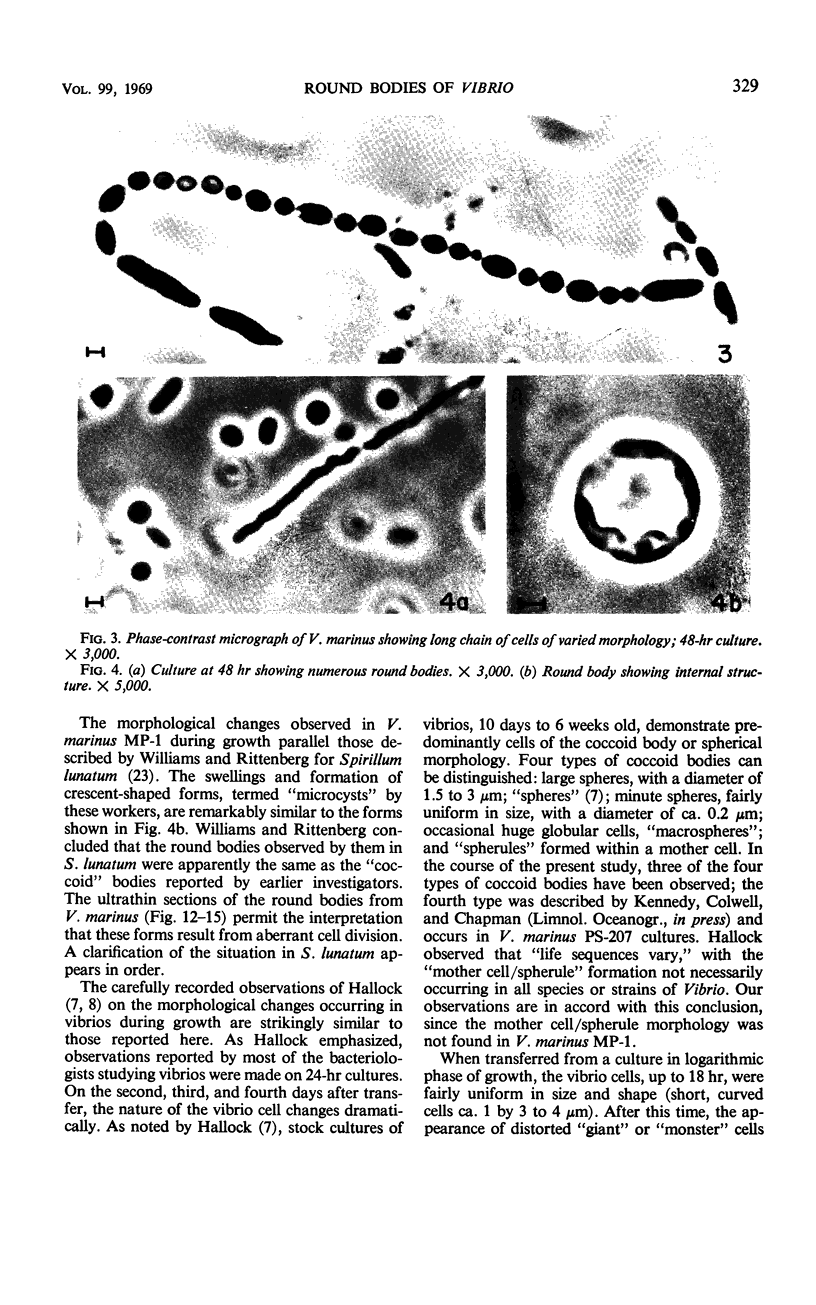
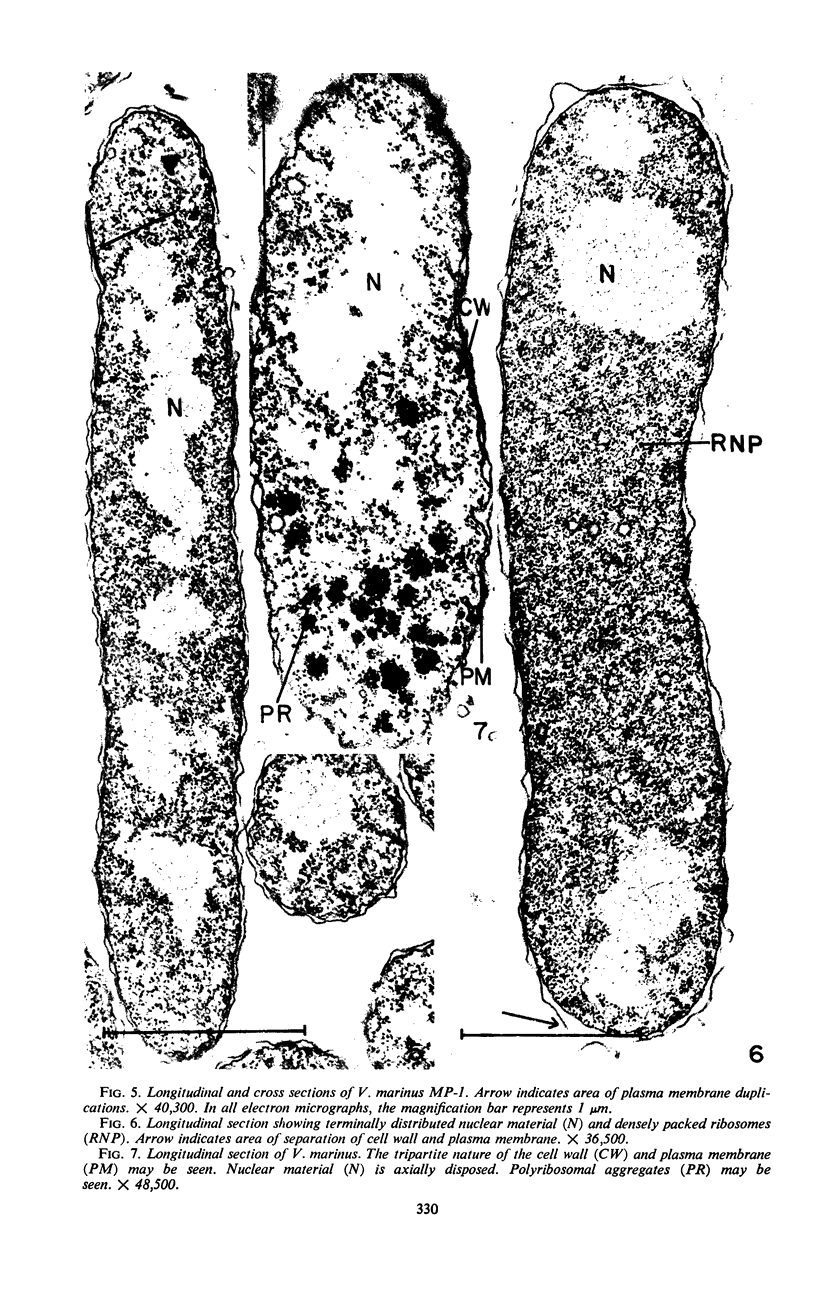
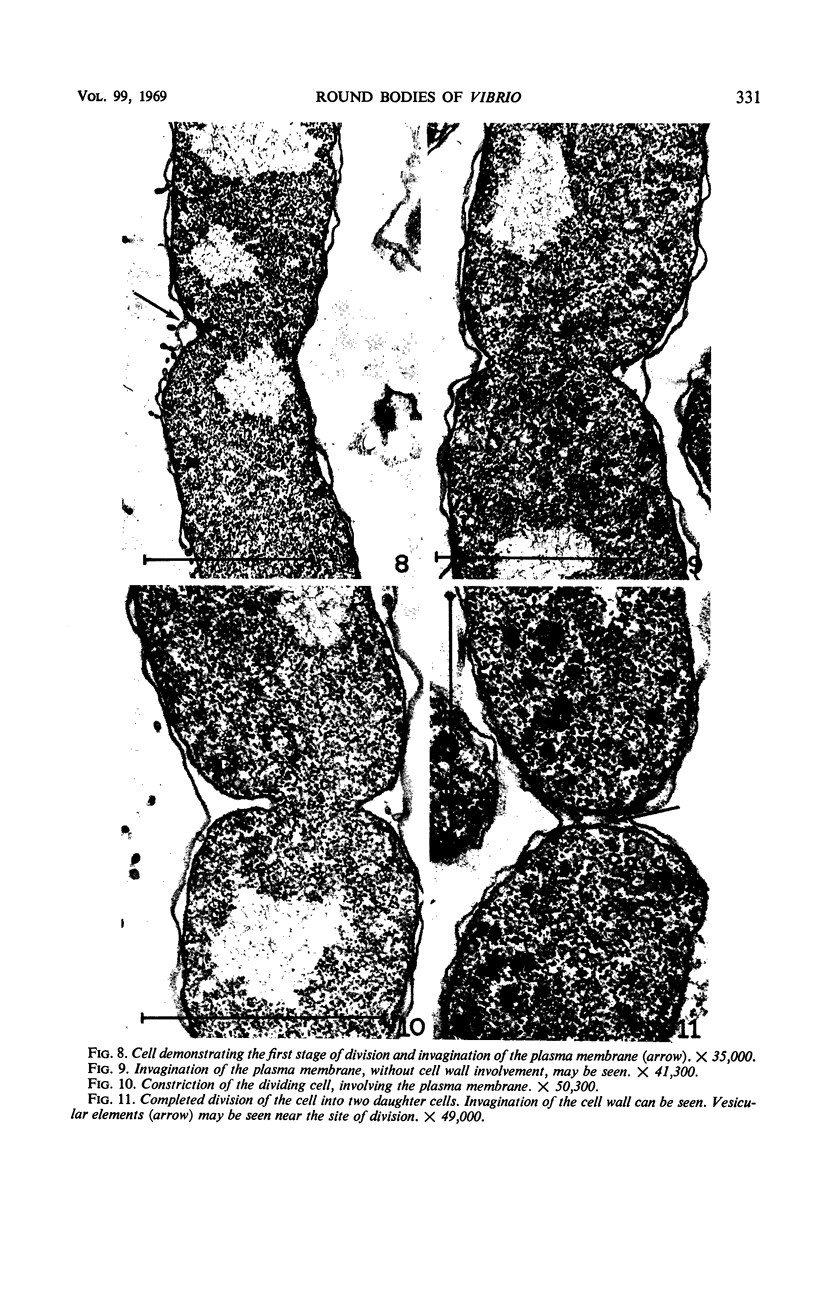
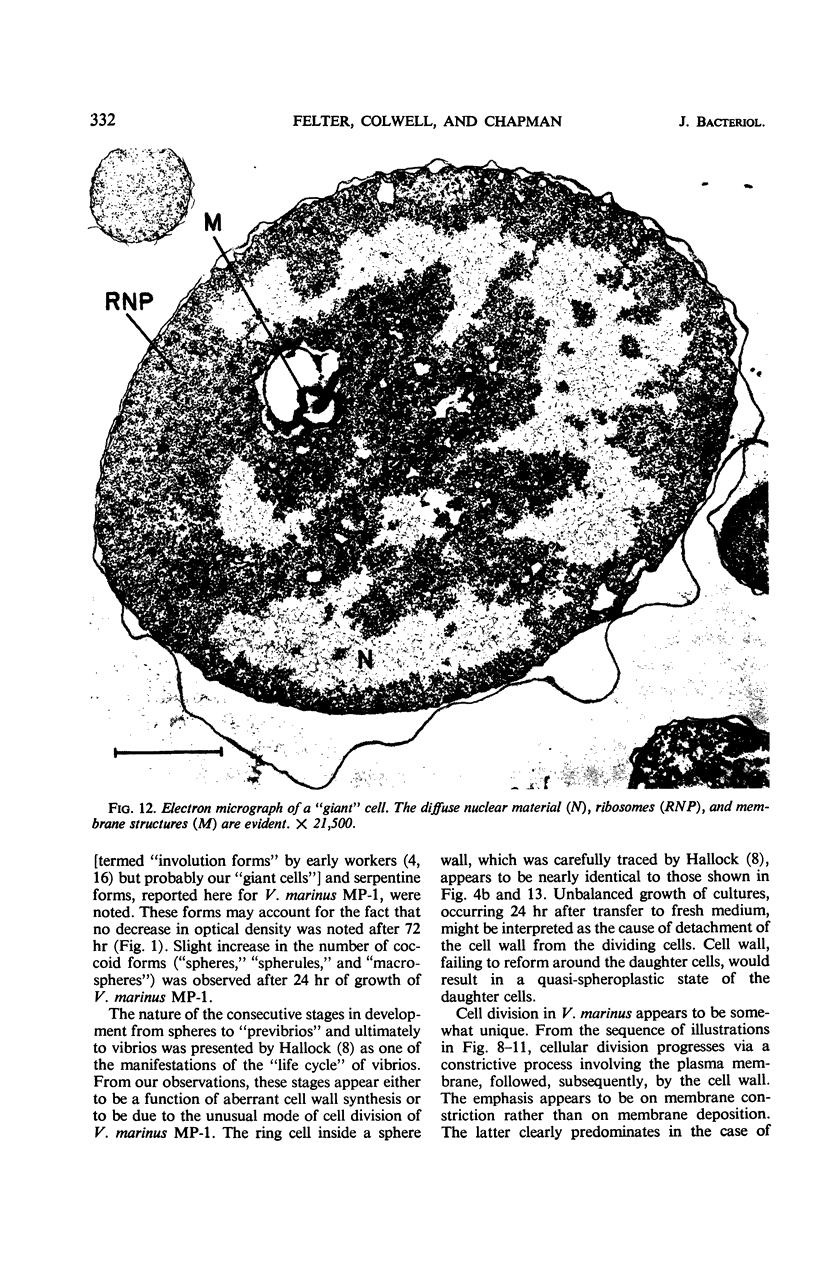
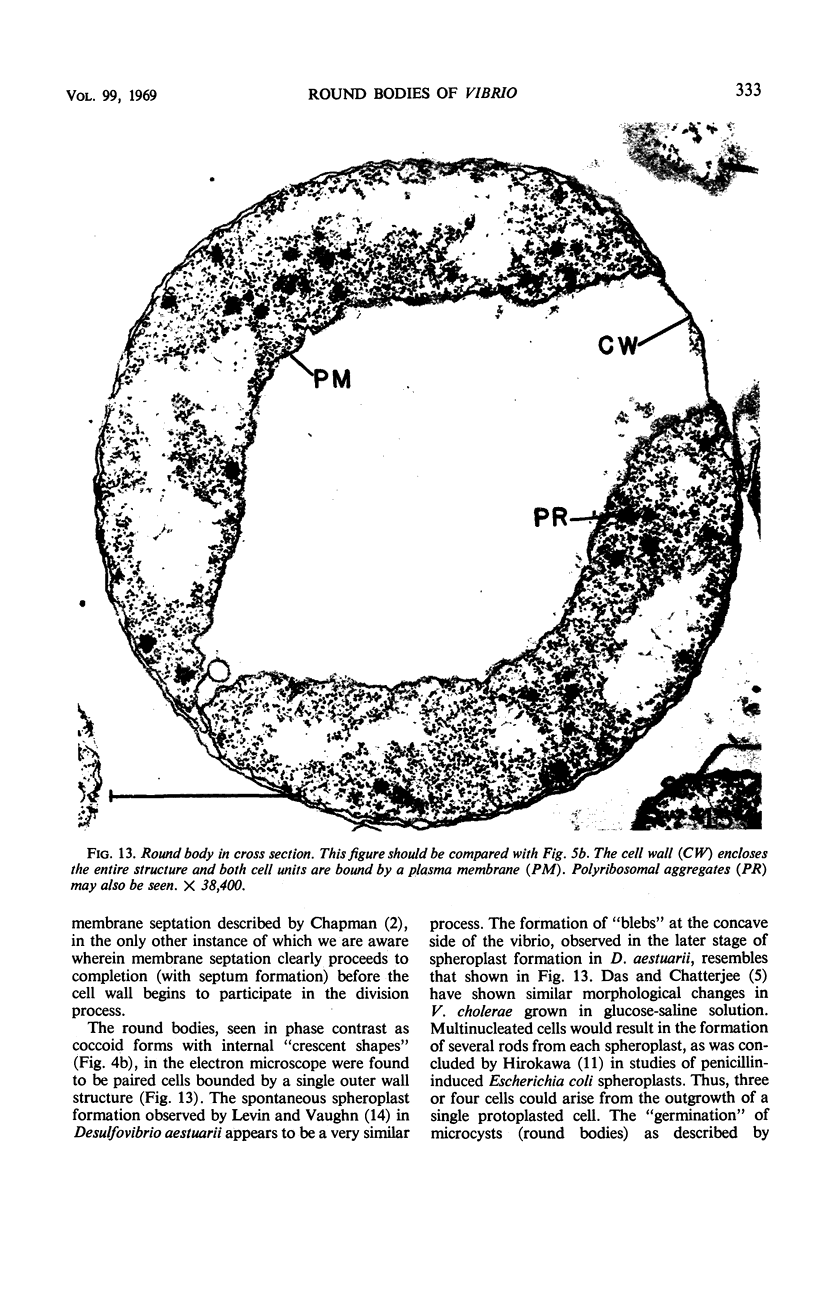
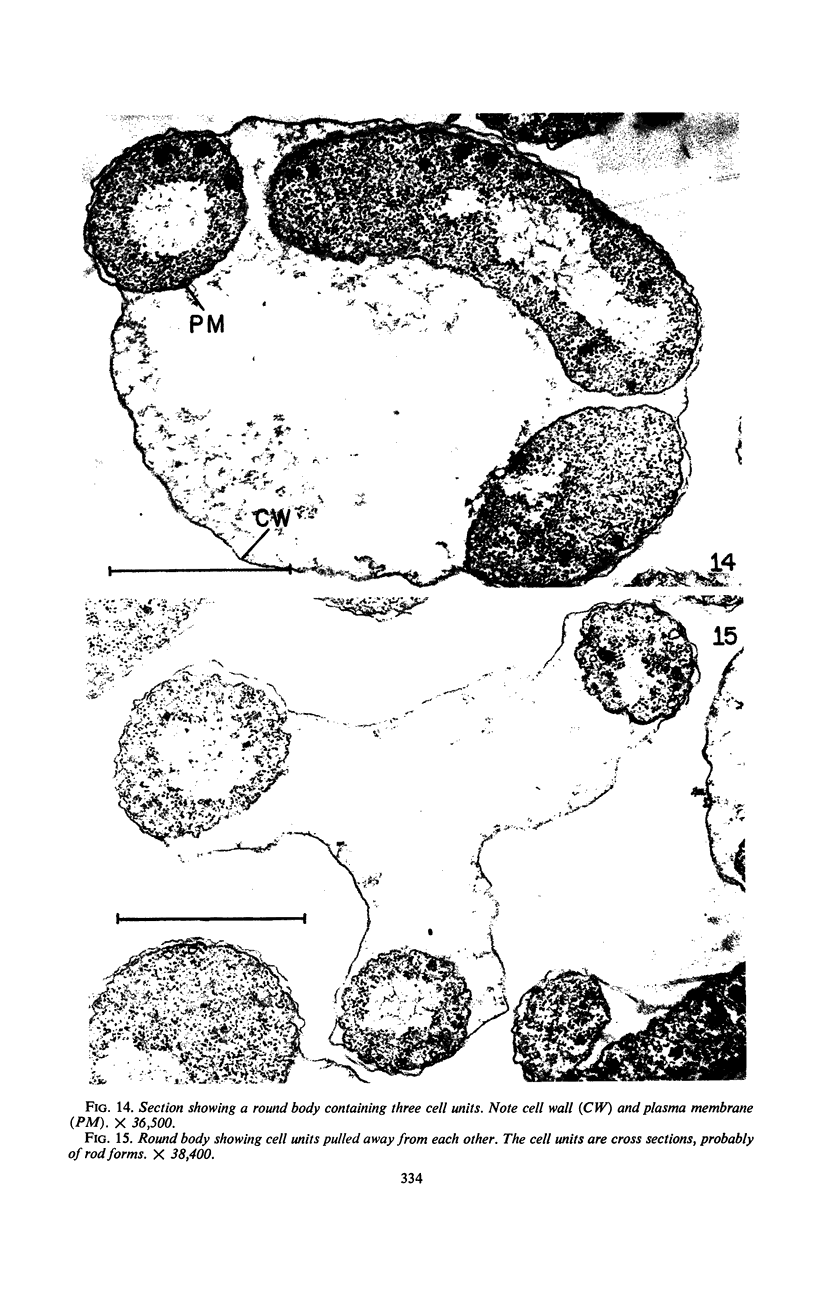
The morphology of Vibrio marinus MP-1 was studied by phase and electron microscopy. The ultrastructure of the vibrio form of V. marinus was found to be typically gram-negative with a trilaminar plasma membrane and cell wall. The coccoid or round bodies noted in otherwise pure cultures of V. marinus were frequently found in early and late stationary phase of growth. The round bodies in ultrathin section were found to contain at least one, and often three or four, cell units. Three types of round bodies were observed in ultrathin section, each differing in size and behavior: “spherules,” “spheres” or the “round body,” and “giant cells” or “macrospheres.” The round bodies appeared to be associated with, or to result from, the constrictive cell division of V. marinus.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHAPMAN G. B. Electron microscope observations on the behavior of the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane during cellular division. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1959 Oct;6:221–224. doi: 10.1083/jcb.6.2.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLWELL R. R., MORITA R. Y. REISOLATION AND EMENDATION OF DESCRIPTION OF VIBRIO MARINUS (RUSSELL) FORD. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:831–837. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.831-837.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das J., Chatterjee S. N. Morphological changes of Vibrio cholerae organisms in glucose saline. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Dec;54(3):445–450. doi: 10.1099/00221287-54-3-445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitroff V. T. SPIROCHAETES IN BALTIMORE MARKET OYSTERS. J Bacteriol. 1926 Aug;12(2):135–177. doi: 10.1128/jb.12.2.135-177.1926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIROKAWA H. Biochemical and cytological observations during the reversing process from spheroplasts to rod-form cells in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1962 Dec;84:1161–1168. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.6.1161-1168.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E., RYTER A. Cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 May 25;4(3):323–326. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.3.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LISTON J. The occurrence and distribution of bacterial types on flatfish. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Feb;16(1):205–216. doi: 10.1099/00221287-16-1-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin R. E., Vaughn R. H. Spontaneous spheroplast formation by Desulfovibrio aestuarii. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Dec;14(12):1271–1276. doi: 10.1139/m68-213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE R. T., CHAPMAN G. B. Observations of the fine structure and modes of growth of a streptomycete. J Bacteriol. 1959 Dec;78:878–885. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.6.878-885.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RITTENBERG S. C., WILLIAMS M. A. Microcyst formation and germination in Spirillum lunatum. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Aug;15(1):205–209. doi: 10.1099/00221287-15-1-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAKAZAKI R., IWANAMI S., FUKUMI H. STUDIES ON THE ENTEROPATHOGENIC, FACULTATIVELY HALOPHILIC BACTERIA, VIBRIO PARAHAEMOLYTICUS. I. MORPHOLOGICAL, CULTURAL AND BIOCHEMICAL PROPERTIES AND ITS TAXONOMICAL POSITION. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1963 Aug;16:161–188. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.16.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VENABLE J. H., COGGESHALL R. A SIMPLIFIED LEAD CITRATE STAIN FOR USE IN ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Cell Biol. 1965 May;25:407–408. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.2.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]